Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Oketani, Kazuki*; Fujii, Hirokazu*; Zhao, Y.*; Kato, Masaji*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Matsui, Hiroya; Kono, Masanori*
Zairyo, 73(3), p.220 - 225, 2024/03
The fractures in the rock are the main pass of groundwater flow and solute transport. The filling of fine-grained particle, such as clay minerals, was confirmed to decrease the permeability of rock by laboratory experiment. This research aimed to verify the occurance of the phoenomena in the fild. The water containing the clay minerals was injected into the rock at the 200m stage of the Mizunami undearground research laboratory. The hydraulic conductivity decreased two order before and after the injection. This result suggested that the decrease of hydraulic conductivity by the filling of fine-grained particle in the fractures occured in the real field.
Kijima, Jun; Koyama, Hayato; Owada, Mitsuhiro; Hagiwara, Masayoshi; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka
JAEA-Technology 2022-012, 14 Pages, 2022/07
Steam reforming system has been developed for the treatment of organic wastes which are not suitable materials (halogenated oil) for the incineration due to generation of corrosive compounds and plugging materials. The refractory material is cast inside the main reactor, which is a part of the steam reforming system. Since the surface of this refractory material has deteriorated over time, the main reactor was replaced. If the refractory material surface of the used main reactor can be repaired, the used main reactor can be reused as a spare. The refractory material surface was repaired using two types of repair materials ("S" and "P"). Combustion tests were conducted on samples simulating organic wastes to evaluate each repair material. As a result of the combustion test, it was concluded that the repair of the main reactor was possible to use the repair material "P" because no cracks or flakes were observed.
Sakashita, Koichi; Ishii, Naoyuki; Kijima, Jun; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hagiwara, Masayoshi; Fukushima, Mineo
JAEA-Testing 2020-003, 20 Pages, 2020/07
Steam reforming method has been developed for the treatment of organic wastes which are not suitable materials (halogenated oil) for the incineration. This method consists of the gasification process in which organics are vaporized and decomposed with superheated steam and the oxidation process in which vaporized organics are decomposed by oxidizing reaction with heated air. In the gasification process, nonvolatile radionuclides are separated from vaporized waste. Therefore it can be expected that treatment of liquid waste generated from an off-gas treatment system and maintenance operation of the off-gas treatment system become easy to perform. 1,500L of waste oil contaminated with halogen, solvent and uranium was treated using the demonstration scale steam reforming system to examine the performance of the system in 2018. Results obtained this study were as follows; (1) The temperature in the steam reforming system was controlled under the self-regulation temperature. (2) The concentration of CO and NO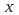 in the off-gas were controlled less than 100 ppm and 250 ppm respectively. (3) The gasification ratio of waste oil was more than 99%. (4) Concentration of fluorine oil in waste oil is needed to be less than 20wt% to perform stable continuance treatment.
in the off-gas were controlled less than 100 ppm and 250 ppm respectively. (3) The gasification ratio of waste oil was more than 99%. (4) Concentration of fluorine oil in waste oil is needed to be less than 20wt% to perform stable continuance treatment.
Terunuma, Akihiro; Mimura, Ryuji; Nagashima, Hisao; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hirokawa, Katsunori*; Uta, Masato; Ishimori, Yuu; Kuwabara, Jun; Okamoto, Hisato; Kimura, Yasuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-008, 98 Pages, 2016/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency formulated the plan to achieve the medium-term target in the period of April 2010 to March 2015(hereinafter referred to as "the second medium-term plan"). JAEA determined the plan for the business operations of each year (hereinafter referred to as "the year plan"). This report is that the Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Waste Management has summarized the results of the decommissioning technology development and decommissioning of nuclear facilities which were carried out in the second medium-term plan.
Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Kimura, Haruyuki; Saigusa, Mikio; Akiba, Masato; Ando, Toshiro; ; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; ; Azumi, Masafumi; Fukuda, Takeshi; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research 1988, Vol.1, p.605 - 610, 1989/00
no abstracts in English