Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Asano, Masaharu*; Terai, Takayuki*
Journal of Membrane Science, 587, p.117171_1 - 117171_9, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.64(Engineering, Chemical)Electro-electrodialysis (EED) has been applied to thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production in order to enhance the HI component in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity (
O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity ( ) and transport number (
) and transport number ( ) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H
) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H and I
and I content and the diffusion coefficients of H
content and the diffusion coefficients of H and I
and I in the evaluated membranes on
in the evaluated membranes on  and
and  were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of
were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of  and t
and t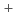 , which indicates that the dominant factors for
, which indicates that the dominant factors for  and
and  would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For
would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For  of Nafion 212, H
of Nafion 212, H diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I
diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I
was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I diffusion should be considered. I
diffusion should be considered. I diffusion could more strongly affect
diffusion could more strongly affect  for the evaluated membranes rather than H
for the evaluated membranes rather than H diffusion, which indicates that H
diffusion, which indicates that H selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I
selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I behavior in the membranes.
behavior in the membranes.
 -tetrafluoroethylene) films using different media
-tetrafluoroethylene) films using different mediaNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(4), p.359 - 362, 2015/12
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion-conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
 -H
-H O mixture
O mixtureTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Terai, Takayuki*; Onuki, Kaoru
Journal of Membrane Science, 456, p.31 - 41, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.89(Engineering, Chemical)Electro-electrodialysis (EED) has been applied to thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production in order to enhance the HI uptake from a HI-I -H
-H O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, the constitution of the HIx solution absorbed in grafted membranes and in Nafion 212 is evaluated. The affinity of the membranes for the HIx solution is discussed based on the measurement results. The behavior of each component in the membrane was as follows: The strong affinity of the ETFE-St membrane for I
O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, the constitution of the HIx solution absorbed in grafted membranes and in Nafion 212 is evaluated. The affinity of the membranes for the HIx solution is discussed based on the measurement results. The behavior of each component in the membrane was as follows: The strong affinity of the ETFE-St membrane for I was shown because of the formation of a charge-transfer complex with electron-donating aromatic groups, whereas I
was shown because of the formation of a charge-transfer complex with electron-donating aromatic groups, whereas I absorption by Nafion 212 was minimal. The difference of affinity for the ions can be attributed to the formation of the I
absorption by Nafion 212 was minimal. The difference of affinity for the ions can be attributed to the formation of the I - complex from I- and I
- complex from I- and I absorbed in the grafted membranes, which was precluded in Nafion 212.
absorbed in the grafted membranes, which was precluded in Nafion 212.
Chen, J.; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari
Advanced Materials Research, 881-883, p.1157 - 1160, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.76(Engineering, Chemical)Cation and anion exchange membranes were prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization of ethyl styrenesulfonate and chloromethyl styrene, respectively, onto poly(ethylene- -tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films, followed by hydrolysis in the former case and quaternization in the latter case. The degree of grafting as well as the ion exchange capacity (IEC) and the conductivity of the prepared membranes were investigated. Furthermore, the cation and anion exchange membranes were tested in an electrodialysis cell using caesium ion aqueous solution in the dilute compartment. It was found that the high-IEC membranes enhanced the electrodialysis speed, while the low-IEC membranes showed the high percent removal.
-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films, followed by hydrolysis in the former case and quaternization in the latter case. The degree of grafting as well as the ion exchange capacity (IEC) and the conductivity of the prepared membranes were investigated. Furthermore, the cation and anion exchange membranes were tested in an electrodialysis cell using caesium ion aqueous solution in the dilute compartment. It was found that the high-IEC membranes enhanced the electrodialysis speed, while the low-IEC membranes showed the high percent removal.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.77 - 81, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ion-track membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF), a type of fluoropolymer, could find wide applications due to its superior chemical and mechanical properties. In order to produce track-etched pores in PVDF films, we have independently employed much milder etching conditions without any oxidant additives in the alkaline etching solution. The goal of this work is to pursue the possibility of varying beam parameters and applying the effect of the etching pretreatment to control the pore size and shape. Ongoing in-situ/on-line analyses at the M-branch of the UNILAC would shed light on the detailed chemistry of not only ion-induced degradation but also the post-irradiation reactivity.
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.95 - 98, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)Our efforts have been focused on ion-track etched membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). This study deals with the effect of the transmembrane potential applied during the conductometry in order to offer a higher degree of freedom to control the pore size. We can say that higher voltage application during the conductometry would accelerate the etching in the tracks. The electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurring out of each pore might be one of the reasons for this enhanced pore evolution and growth.
Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sinnananchi, W.; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Yamamoto, Kazuya*; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 214(15), p.1756 - 1762, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:43.24(Polymer Science)Graft-type anion-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization of chloromethylstyrene into poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films and subsequent quaternization with trimethylamine to evaluate the counter anion effects on fuel cell properties. The hydroxide form was maintained in -saturated water to prevent the bicarbonate formation. The hydroxide form showed conductivity and water uptake four and two times higher than the chloride and bicarbonate forms. The hydroxide form is thermally and chemically less stable, resulting in the tendency to absorb water and to convert to the bicarbonate form.
Park, J.*; Takayama, Toshio*; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Kudo, Kazuaki*; Takayama, Toshio*
Polymer, 54(17), p.4570 - 4577, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:19.37(Polymer Science)Graft-type sulfonated polybenzimidazole was prepared through radiation-induced graft polymerization of styrenes into an alicyclic polybenzimidazole film and subsequent sulfonation. The alicyclic polybenzimidazole, ChPBI, was prepared from  -1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid and 3,3'-diaminobenzidine using typical polycondensation. Anisotropic domains with a size of several tens of micrometers were found in the ChPBI films casted from LiCl-containing
-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid and 3,3'-diaminobenzidine using typical polycondensation. Anisotropic domains with a size of several tens of micrometers were found in the ChPBI films casted from LiCl-containing  ,
, -dimethylacetamide. Irradiation of the ChPBI membranes with a 220 kGy dose of
-dimethylacetamide. Irradiation of the ChPBI membranes with a 220 kGy dose of  -rays created radical species with mean lifetimes of two days. The treatment of this membrane with a 50/50 (v/v) mixture of 1-propanol and styrene produced polystyrene graft chains. Sulfonation of the resulting grafted membrane with ClSOH
-rays created radical species with mean lifetimes of two days. The treatment of this membrane with a 50/50 (v/v) mixture of 1-propanol and styrene produced polystyrene graft chains. Sulfonation of the resulting grafted membrane with ClSOH OH occurred selectively on the polystyrene grafts. The sulfonated films showed proton conductivity on the order of 10
OH occurred selectively on the polystyrene grafts. The sulfonated films showed proton conductivity on the order of 10 to 10
to 10 S/cm with an ion exchange capacity between 2.1 and 2.9 mmol/g. SEM-EDX analysis of the membrane indicated the presence of macrophase separated domains up to 1
S/cm with an ion exchange capacity between 2.1 and 2.9 mmol/g. SEM-EDX analysis of the membrane indicated the presence of macrophase separated domains up to 1  m in diameter. The proton conductivity of the membrane did not decrease for 600 h at 120
m in diameter. The proton conductivity of the membrane did not decrease for 600 h at 120 C in liquid water.
C in liquid water.
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.105 - 108, 2013/03
We report here how conditions of the conductometric analysis affected the etching characteristics of 25  m-thick poly(vinylidene fluoride) film irradiated with 450 MeV
m-thick poly(vinylidene fluoride) film irradiated with 450 MeV  Xe ions. The etching was performed in a 9 mol dm
Xe ions. The etching was performed in a 9 mol dm aqueous potassium hydroxide solution at 80
aqueous potassium hydroxide solution at 80 C in a conductometric cell. According to the scanning electron microscope observations, the ion-track membrane obtained with an applied AC voltage of 1.0 V had the surface pores of 168
C in a conductometric cell. According to the scanning electron microscope observations, the ion-track membrane obtained with an applied AC voltage of 1.0 V had the surface pores of 168 20 nm in diameter. On the other hand, the etching without an applied voltage gave the approximately two-thirds smaller pores. The conductomeric etching would provide a higher degree of freedom for controlling the pore diameter.
20 nm in diameter. On the other hand, the etching without an applied voltage gave the approximately two-thirds smaller pores. The conductomeric etching would provide a higher degree of freedom for controlling the pore diameter.
 -H
-H O mixture for IS process
O mixture for IS processTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Terai, Takayuki*; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
Research and development of a water-splitting hydrogen-production method, called iodine-sulfur (IS) process, has been conducting as one of the heat applications of high temperature gas-cooled reactor. Among the unit operations in this IS process, we have investigated electro-electrodialysis (EED) using an ion-exchange membrane to concentrate HI in an HI-I -H
-H O mixture. Aiming at maximizing EED performance, new membrane materials were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization and were examined in terms of their proton permeability through the membrane, i.e., transport number and conductivity at different iodine (I
O mixture. Aiming at maximizing EED performance, new membrane materials were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization and were examined in terms of their proton permeability through the membrane, i.e., transport number and conductivity at different iodine (I ) concentrations in the HI-I
) concentrations in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture. The transport number increased and the conductivity decreased with an increase in the feed I
O mixture. The transport number increased and the conductivity decreased with an increase in the feed I molality. The EED model derived by the Nernst-Planck theory suggested that this trend could be explained exclusively by the variation of diffusion coefficient of I
molality. The EED model derived by the Nernst-Planck theory suggested that this trend could be explained exclusively by the variation of diffusion coefficient of I .
.
 -H
-H O mixture using ion exchange membranes
O mixture using ion exchange membranesTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Terai, Takayuki*; Onuki, Kaoru
Journal of Membrane Science, 411-412, p.99 - 108, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.73(Engineering, Chemical)In the thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production, an electro-electrodialysis was applied to increase the HI molality of a HI-I -H
-H O mixture. In order to investigate the temperature dependence of the membrane performance for increasing the HI concentration, a theoretical formula for the performance indexes (proton transport number, initial cell voltage, and ratio of water permeation to proton permeation in the membrane) was derived on the basis of the Nernst-Planck equation and electrophoresis theory. The obtained formula could reproduce the experimental values of the grafted membranes and Nafion 212 in the temperature range 313-373 K and was validated.
O mixture. In order to investigate the temperature dependence of the membrane performance for increasing the HI concentration, a theoretical formula for the performance indexes (proton transport number, initial cell voltage, and ratio of water permeation to proton permeation in the membrane) was derived on the basis of the Nernst-Planck equation and electrophoresis theory. The obtained formula could reproduce the experimental values of the grafted membranes and Nafion 212 in the temperature range 313-373 K and was validated.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 37(2), p.223 - 226, 2012/06
The aim of this study is to investigate the formation of the poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) track membranes in detail by electrolytic conductometry. A PVDF film was irradiated with a 450 MeV  Xe or 2.2 GeV
Xe or 2.2 GeV  Au ion beam, and then the latent tracks were etched in a 9 mol dm
Au ion beam, and then the latent tracks were etched in a 9 mol dm aqueous KOH solution at 80
aqueous KOH solution at 80 C that had been poured into a conductometric cell. At the same time, the evolution of cylindrical nanopores was monitored by measuring the conductance through the membrane. The etching kinetics significantly depended on the deposited energy within each track, which is represented by the LET. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the cell promoted track etching up to the breakthrough probably because the electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
C that had been poured into a conductometric cell. At the same time, the evolution of cylindrical nanopores was monitored by measuring the conductance through the membrane. The etching kinetics significantly depended on the deposited energy within each track, which is represented by the LET. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the cell promoted track etching up to the breakthrough probably because the electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Proceedings in Radiochemistry, 1(1), p.409 - 413, 2011/09
In polymer electrolyte fuel cells, the water transport properties of the polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs) would affect the cell performance. In this study, we investigated the self-diffusion coefficient of water molecules in the PEMs by using radioactivated-tracer permeation technique. The PEMs were synthesized from crosslinked-polytetrafluoroethylene (cPTFE) by the radiation-induced grafting method. The Dw of the PEMs increased with their ion exchange capacities (IECs), and reached the maximum value of 3.7 10
10 m
m /s at the IEC of 2.4 meq/g. interestingly, commercially-available Nafion membrane exhibited the highest Dw of 4.9
/s at the IEC of 2.4 meq/g. interestingly, commercially-available Nafion membrane exhibited the highest Dw of 4.9 10
10 m
m /s despite of its low IEC. The lower Dw in the cPTFE PEMs is probably attributed to the geometry of hydrophilic regions phase-separated from the surrounding hydrophobic polymers.
/s despite of its low IEC. The lower Dw in the cPTFE PEMs is probably attributed to the geometry of hydrophilic regions phase-separated from the surrounding hydrophobic polymers.
 -ray pre-irradiation grafting
-ray pre-irradiation graftingKoshikawa, Hiroshi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Yamamoto, Kazuya*; Asazawa, Koichiro*; Yamada, Koji*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Radiation Curing in Asia (RadTech Asia 2011) (Internet), p.240 - 241, 2011/06
The anion-exchange membranes (AEM) for fuel cells were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization of chloromethylstyrene into poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films and subsequent quaternization of the grafts with trimethylamine. When the AEM were treated in 1M-KOH and washed with N -saturated water, the membranes with chloride form can be converted quantitatively to hydroxide form. However, the hydroxide form was easily converted to the bicarbonate form by the treatment in non-bubbled (CO
-saturated water, the membranes with chloride form can be converted quantitatively to hydroxide form. However, the hydroxide form was easily converted to the bicarbonate form by the treatment in non-bubbled (CO dissolved) water. When we introduced the crosslinkers in polymer grafts, which is proved to be very effective in the proton conducting PEM having a poly(styrenesulfonic acid) grafts, the grafted AEM with both chloride and hydroxide forms showed only slight decrease of water uptake. It should be noted that AEM with hydroxide form showed very high tendency to absorb water.
dissolved) water. When we introduced the crosslinkers in polymer grafts, which is proved to be very effective in the proton conducting PEM having a poly(styrenesulfonic acid) grafts, the grafted AEM with both chloride and hydroxide forms showed only slight decrease of water uptake. It should be noted that AEM with hydroxide form showed very high tendency to absorb water.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
ECS Transactions, 35(24), p.1 - 12, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.05(Electrochemistry)Our focus has been placed on ion track membranes of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF), a type of fluoropolymer, because of their superior chemical, mechanical and ferro-electric properties. The aim of this study is to investigate the formation of the PVDF track membranes in more detail by electrolytic conductometry. Interestingly, application of a higher voltage to the conductometry cell as well as irradiation with a higher-LET beam promoted track etching up to breakthrough probably because electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
Chen, J.; Li, D.; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari
Journal of Membrane Science, 362(1-2), p.488 - 494, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:75.41(Engineering, Chemical)An aromatic hydrocarbon polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) was prepared by direct modification of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) film using the radiation-induced crosslinking and grafting techniques. The crosslinking structure induced by the electron-beam irradiation enhanced the insolubility of the PEEK base film. The film shape of the crosslinked PEEK (cPEEK) was well maintained under sulfonation. A small amount of divinylbenzene was introduced into the cPEEK film to enhance the radiation-induced styrene-grafting. The styrene-grafted film was sulfonated under a mild sulfonation condition to obtain the PEM. The PEM with different ion exchange capacity was prepared by changing the grafting yield of styrene. The new PEM exhibited lower methanol permeability and higher mechanical properties, and was proven to be durable in a direct methanol fuel cell at high temperature, reaching a high maximum power density.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Misaki*; Asano, Masaharu; Nomura, Kumiko*; Takagi, Shigeharu*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru*
Proceedings of Sadoway 60 Symposium, p.114 - 120, 2010/06
My presentation deals with the application of high-energy heavy ion beams from the cyclotron accelerator of Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA), JAEA. Our strategic focus is centered on using nano-scale controllability of the ion-beam processing; the membrane preparation involves (1) the irradiation of commercially-available base polymer films with hundreds of MeV ions, (2) graft polymerization of vinyl monomers into electronically-excited parts along the ion trajectory, called latent tracks, and (3) sulfonation of the graft polymers. Interestingly, the resulting membranes exhibited anisotropic proton transport, i.e., higher conductivity in the thickness direction. According to microscopic observations, this is probably because the columnar electrolyte phase extended, with a width of tens-to-hundreds nanometers, through the membrane.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2010/05
For concentrating of HI in HI-I -H
-H O mixture by electro-electrodialysis (EED) in the thermochemical water-splitting IS process, an application of self-made polymer electrolyte membranes fabricated by radiation-induced graft polymerization and cross-linking method has been studied. In order to bring the EED technology into practical application, stability of membrane is required in the severe environments of high temperature and strongly acidic solution. The present study examined thermal, chemical and electrochemical stability of the grafted membranes in the service environments by performing the EED operation over 100 hours at 373 K, while measuring the evolution of cell voltage and the change of ion exchange capacity. The results showed that chemical cross-linking could largely improve the membrane stability.
O mixture by electro-electrodialysis (EED) in the thermochemical water-splitting IS process, an application of self-made polymer electrolyte membranes fabricated by radiation-induced graft polymerization and cross-linking method has been studied. In order to bring the EED technology into practical application, stability of membrane is required in the severe environments of high temperature and strongly acidic solution. The present study examined thermal, chemical and electrochemical stability of the grafted membranes in the service environments by performing the EED operation over 100 hours at 373 K, while measuring the evolution of cell voltage and the change of ion exchange capacity. The results showed that chemical cross-linking could largely improve the membrane stability.
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Enomoto, Kazuyuki; Sawada, Shinichi; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Trautmann, C.*; Neumann, R.*
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 78(2), p.146 - 149, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:13.71(Electrochemistry)Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes with conical and cylindrical nanopores were prepared in a controlled manner by the ion-track technique, which involved heavy ion beam irradiation and the subsequent alkaline etching. Etching behavior mainly depended on energy deposition of ion beams, and thus its depth distribution, estimated by theoretical simulation, was successfully applied to control the shapes and diameters of the etched pores. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electrolytic conductometry then gave an insight into critical experimental parameters. Interestingly, applying a higher voltage to the conductometry cell promoted track etching up to breakthrough probably because electrophoretic migration of dissolved products occurred out of each pore.
 -H
-H O mixture using radiation-grafted polymer electrolyte membranes
O mixture using radiation-grafted polymer electrolyte membranesTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Onuki, Kaoru
Journal of Membrane Science, 346(1), p.136 - 142, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:56.37(Engineering, Chemical)In the thermochemical water-splitting Iodine-Sulfur process used to produce hydrogen new polymer electrolyte membranes were applied in an electro-membrane process (Electro-electrodialysis, EED) to increase the HI molality of HIx solution (HI-I -H
-H O mixture) to be over quasi-azeotropic. Radiation grafting of a styrene monomer into a poly (ethylene-
O mixture) to be over quasi-azeotropic. Radiation grafting of a styrene monomer into a poly (ethylene-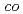 -tetrafluoroethylene) base film and subsequent sulfonation provided electrolyte membranes that had ion exchange capacities (IECs) of 1.1-1.6 mmol/g. With the EED of the HIx solutions using [HI]=[I
-tetrafluoroethylene) base film and subsequent sulfonation provided electrolyte membranes that had ion exchange capacities (IECs) of 1.1-1.6 mmol/g. With the EED of the HIx solutions using [HI]=[I ]=10 mol/kg at 40
]=10 mol/kg at 40  C the transport number of protons, ratio of permeated quantities of water to the protons, and current efficiency all appeared to depend on the IEC of the resulting membranes. When compared to Nafion the tested membranes exhibited lower electric cell resistance, and thereby decreasing the overall energy required in the concentration operation.
C the transport number of protons, ratio of permeated quantities of water to the protons, and current efficiency all appeared to depend on the IEC of the resulting membranes. When compared to Nafion the tested membranes exhibited lower electric cell resistance, and thereby decreasing the overall energy required in the concentration operation.