Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsubota, Yoichi; Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Suteau, C.*; Lallot, Y.*; Bouland, A.*; Roulet, D.*; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
In order to safely remove fuel debris from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), it is necessary to quantitatively evaluate radioactive airborne particulate generated by the cutting of nuclear fuel debris. We fabricated Uranium-bearing simulated fuel debris (SFD) with In/Ex-Vessel compositions and evaluated the physical and chemical properties of aerosols generated by heating the SFDs. Based on these results, we estimated the isotopic composition and radioactivity of aerosols produced when 1F-Unit2 fuel debris is laser cut, which is a typical example of a heating method. Plutonium, mainly  Pu,
Pu, Am, and
Am, and  Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and
Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and  Pu,
Pu,  Cs-Ba, and
Cs-Ba, and  Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Tsubota, Yoichi; Ikeda, Atsushi; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
Results of the URASOL project aimed at evaluating the generation and dispersion of radioactive aerosols during the cutting of fuel debris, a key issue in the decommissioning of the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), are presented in this report. Characterization of aerosols generated during heating and mechanical cutting of simulated fuel debris in terms of mass concentration, real-time number density, mass-based particle size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties is reported. In the heating tests, an increase in particle size with increasing temperature was observed, and in terms of particle number density, the case using depleted uranium simulated fuel debris had a smaller number density than the test using Hf-containing simulated fuel debris. In mechanical cleavage, the aerodynamic median mass diameter of the aerosol was almost the same for the radioactive and non-radioactive samples (about 3.7 4.4
4.4  m).
m).
Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Gu var, C.*; Testud, V.*; Brackx, E.*; Porcheron, E.*; Bouland, A.*; Berlemont, R.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
var, C.*; Testud, V.*; Brackx, E.*; Porcheron, E.*; Bouland, A.*; Berlemont, R.*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Science Talks (Internet), 6, p.100215_1 - 100215_9, 2023/05
Porcheron, E.*; Leblois, Y.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Molina, D.*; Suteau, C.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Roulet, D.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
One of the important challenges for the decommissioning of the damaged reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is the fuel debris retrieval. The URASOL project, which is undertaken by a French consortium consisting of ONET Technologies, CEA, and IRSN for JAEA/CLADS, is dedicated to acquiring basic scientific data on the generation and characteristics of radioactive aerosols from the thermal or mechanical processing of fuel debris simulant. Heating process undertaken in the VITAE facility simulates some representative conditions of thermal cutting by LASER. For mechanical cutting, the core boring technique is implemented in the FUJISAN facility. Fuel debris simulants have been developed for inactive and active trials. The aerosols are characterized in terms of mass concentration, real time number concentration, mass size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties. The chemical characterization aims at identifying potential radioactive particles released and the associated size distribution, both of which are important information for assessing possible safety and radioprotection measures during the fuel debris retrieval operations at 1F.
P rez S
rez S nchez, R.*; Jurado, B.*; M
nchez, R.*; Jurado, B.*; M ot, V.*; Roig, O.*; Dupuis, M.*; Bouland, O.*; Denis-Petit, D.*; Marini, P.*; Mathieu, L.*; Tsekhanovich, I.*; et al.
ot, V.*; Roig, O.*; Dupuis, M.*; Bouland, O.*; Denis-Petit, D.*; Marini, P.*; Mathieu, L.*; Tsekhanovich, I.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 125(12), p.122502_1 - 122502_5, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:70.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:98.06(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides ( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 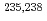 U and
U and  Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
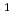 H,
H,  O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 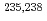 U, and
U, and  Pu
PuChadwick, M. B.*; Dupont, E.*; Bauge, E.*; Blokhin, A.*; Bouland, O.*; Brown, D. A.*; Capote, R.*; Carlson, A. D.*; Danon, Y.*; De Saint Jean, C.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.1 - 25, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:98.48(Physics, Nuclear)CIELO (Collaborative International Evaluated Library Organization) provides a new working paradigm to facilitate evaluated nuclear reaction data advances. It brings together experts from across the international nuclear reaction data community to identify and document discrepancies among existing evaluated data libraries, measured data, and model calculation interpretations, and aims to make progress in reconciling these discrepancies to create more accurate ENDF-formatted files. The focus will initially be on a small number of the highest-priority isotopes, namely  H,
H,  O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 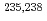 U, and
U, and  Pu. This paper identifies discrepancies between various evaluations of the highest priority isotopes. The evaluated data for these materials in the existing nuclear data libraries are reviewed, and some integral properties are given. The paper summarizes a program of nuclear science and computational work needed to create the new CIELO nuclear data evaluations.
Pu. This paper identifies discrepancies between various evaluations of the highest priority isotopes. The evaluated data for these materials in the existing nuclear data libraries are reviewed, and some integral properties are given. The paper summarizes a program of nuclear science and computational work needed to create the new CIELO nuclear data evaluations.