Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 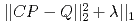 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
Ishikawa, Ryoya*; Suzuki, Masatoshi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Endo, Satoru*; Nakajima, Hiroo*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Shinoda, Hisashi*; et al.
KEK Proceedings 2022-2, p.61 - 66, 2022/11
The balance between oxidative stress and antioxidant activity, which is a defense mechanism against oxidative stress, was investigated in the liver and bladder of wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima Prefecture. No significant induction of oxidative stress by exposure to environmental radionuclides after the Fukushima nuclear accident was observed, suggesting that the stress defense mechanism of the organism is activated in some organs.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Klotz, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Fern ndez-D
ndez-D az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(40), p.e2208717119_1 - e2208717119_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.4(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here we present the first elucidation of the disordered structure of ice VII, the dominant high-pressure form of water, at 2.2 GPa and 298 K from both single-crystal and powder neutron diffraction techniques. We reveal the three-dimensional atomic distributions from the maximum entropy method and unexpectedly find a ring-like distribution of hydrogen in contrast to the commonly-accepted discrete sites. In addition, total scattering analysis at 274 K clarified the difference in the intermolecular structure from ice VIII, the ordered counterpart of ice VII, despite an identical molecular geometry. Our complementary structure analyses robustly demonstrate the unique disordered structure of ice VII. Furthermore, these noble findings are related to the proton dynamics which drastically vary with pressure, and will contribute to an understanding of the structural origin of anomalous physical properties of ice VII under pressures.
Toyoda, Satoshi*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*
Hoshako, 35(3), p.200 - 206, 2022/05
The present status of spatiotemporal depth profiling analysis of the multilayer stacked film interface based on Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (APXPS) is presented. To begin with, depth profiles of the multilayer stacked film interfaces have been achieved by time-division Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved PhotoEmission Spectroscopy data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division angle resolved AP-XPS data including spatial resolution, which enables us to realize spatiotemporal depth profiles of the interfaces under reaction conditions such as oxidation and reduction. In addition, it is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
Kim, M.; Malins, A.; Machida, Masahiko; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshida, Hiroko*; Yanagi, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*
RIST News, (67), p.3 - 15, 2021/09
no abstracts in English
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 Cs and
Cs and  Cs radioactivity measurements
Cs radioactivity measurementsMalins, A.; Imamura, Naohiro*; Niizato, Tadafumi; Takahashi, Junko*; Kim, M.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Shinomiya, Yoshiki*; Miura, Satoru*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 226, p.106456_1 - 106456_12, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.04(Environmental Sciences) U
U O
O
Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kitagaki, Toru; Hoshino, Takanori; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.915 - 921, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)To elucidate the mechanical properties of fuel debris inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, we use first-principles calculations to evaluate mechanical properties of cubic Zr U
U O
O , which is a main component of the fuel debris. We focus on the dependence of mechanical properties on the fraction x of zirconium, compare our results with recent experiment of simulated debris, in which dependences of elastic moduli and fracture toughness on the ZrO
, which is a main component of the fuel debris. We focus on the dependence of mechanical properties on the fraction x of zirconium, compare our results with recent experiment of simulated debris, in which dependences of elastic moduli and fracture toughness on the ZrO content showed deviation from a simple linear relation. We show that elastic moduli drop at around x=0.25 and increase again for larger values of x, as has been observed in experiments. The reason of the drop is a softening owing to disordered atomistic structures induced by the solute zirconium atoms. We also find that stress-strain curves for the x=0.125 case show marked hysteresis owing to the existence of many meta-stable states. We show that this hysteresis leads to slightly increased fracture toughness, but it is not enough to account for the significant increase of fracture toughness observed in experiments.
content showed deviation from a simple linear relation. We show that elastic moduli drop at around x=0.25 and increase again for larger values of x, as has been observed in experiments. The reason of the drop is a softening owing to disordered atomistic structures induced by the solute zirconium atoms. We also find that stress-strain curves for the x=0.125 case show marked hysteresis owing to the existence of many meta-stable states. We show that this hysteresis leads to slightly increased fracture toughness, but it is not enough to account for the significant increase of fracture toughness observed in experiments.
Yada, Hiroki; Takaya, Shigeru; Wakai, Takashi; Nakai, Satoru; Machida, Hideo*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 84(859), p.17-00389_1 - 17-00389_15, 2018/03
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Matsunami, Noriaki*; Ito, M.*; Kato, M.*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sataka, Masao*; Kakiuchida, Hiroshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part A), p.191 - 195, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have studied ion impact effects on atomic structure in terms of X-ray diffraction (XRD), optical absorption and electrical resistivity of Mn (6%)-doped ZnO films under 100 MeV Xe ion impact at room temperature. We find the monotonic reduction of the XRD intensity to 1/50 of that of unirradiated film at 5  10
10 cm
cm , little bandgap change (
, little bandgap change ( 0.02 eV) and decrease of the resistivity by 4 order of magnitude. The resistivity modification has been compared with that by irradiations of low energy ions such as 100 keV Ne and N, which show more effective decrease of resistivity. We also find that temperature (T) dependence of the magnetic susceptibility (
0.02 eV) and decrease of the resistivity by 4 order of magnitude. The resistivity modification has been compared with that by irradiations of low energy ions such as 100 keV Ne and N, which show more effective decrease of resistivity. We also find that temperature (T) dependence of the magnetic susceptibility ( ) of Mn-doped ZnO follows the Curie law:
) of Mn-doped ZnO follows the Curie law:  =
= 
 + C/T (i.e., paramagnetic) and the Curie constant C decreases to a half of that before irradiation (C
+ C/T (i.e., paramagnetic) and the Curie constant C decreases to a half of that before irradiation (C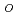 = 0.012 emu cm
= 0.012 emu cm K) at 100 MeV Xe ion fluence of 10
K) at 100 MeV Xe ion fluence of 10 cm
cm .
.
Rouault, J.*; Le Coz, P.*; Garnier, J.-C.*; Hamy, J.-M.*; Hayafune, Hiroki; Iitsuka, Toru*; Mochida, Haruo*
Proceedings of 2015 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2015) (CD-ROM), p.832 - 837, 2015/05
The French and international industrial partners already joined the project from 2010 to 2013 and many others are also effective in the Research and Development in support of ASTRID. A new partnership is now effective on both topics with Japan. This collaboration on the ASTRID Program and Sodium Fast Reactor is now fully integrated in the ASTRID program organization. In addition a specific Joint Team, CEA, AREVA, JAEA, MHI and MFBR, has been created to follow specifically Japanese contribution and develop evaluations of a common interest to orientate future work and contribute to ASTRID options confirmation and be of an interest for the future Japanese Fast Breeder reactor.
Rouault, J.*; Abonneau, E.*; Settimo, D.*; Hamy, J.-M.*; Hayafune, Hiroki; Gefflot, R.*; Benard, R.-P.*; Mandement, O.*; Chauveau, T.*; Lambert, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 2015 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2015) (CD-ROM), p.824 - 831, 2015/05
The Preconceptual Design phase of the ASTRID Project ended late 2012, the main goal was to evaluate innovative options. It is now followed by the AVP2 phase planned until the end of 2015 whose objectives are both to focus the design in order to finalize a coherent reactor outline and to finalize by December 2015 the Safety Option Report. The CEA acts as the industrial architect of the project. In 2014, Japan which participates now in the design studies and also in Research and Development in support of the ASTRID Project and VELAN are the latest partners to join the Project. The next important milestone is at the end of 2015 with the release by the Project team of a convincing and coherent Conceptual Design file.
Takaya, Shigeru; Asayama, Tai; Kamishima, Yoshio*; Machida, Hideo*; Watanabe, Daigo*; Nakai, Satoru; Morishita, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 1(1), p.011004_1 - 011004_9, 2015/01
A new process for determination of inservice inspection (ISI) requirements was proposed based on the System Based Code concept to realize effective and rational ISI by properly taking into account plant specific features. The proposed process consists of two complementary evaluations, one focusing on structural integrity and the other one on detectability of defects before they would grow to an unacceptable size in light of plant safety. If defect detection was not feasible, structural integrity evaluation would be required under sufficiently conservative hypothesis. The applicability of the proposed process was illustrated through an application to the existing prototype fast breeder reactor, Monju.
Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Ikeda, Takashi; Matsumura, Daiju; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki
Hoshako, 27(6), p.315 - 322, 2014/11
no abstracts in English