Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Doi, Daisuke
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2022/08
Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(2), p.198 - 206, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.521 - 532, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.2098 - 2107, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)A sodium concrete reaction (SCR) is one of the important phenomena to cause the structural concrete ablation and the release of H gas in the case of sever accident of sodium cooled fast reactors. In this study, the long-time SCR test had been carried out to investigate the self-termination mechanism. The results showed the SCR terminated even if the enough amount of Na remained on the concrete. The quantitative data were collected on the SCR terminating such as temperature and H
gas in the case of sever accident of sodium cooled fast reactors. In this study, the long-time SCR test had been carried out to investigate the self-termination mechanism. The results showed the SCR terminated even if the enough amount of Na remained on the concrete. The quantitative data were collected on the SCR terminating such as temperature and H generation. The reaction products, which became the small solids in liquid Na were transferred with slurry state by generated H
generation. The reaction products, which became the small solids in liquid Na were transferred with slurry state by generated H bubbles. Though the Na transfers actively and ablated the concrete surface with the high H
bubbles. Though the Na transfers actively and ablated the concrete surface with the high H generation rate, the mass exchange coefficient defined as
generation rate, the mass exchange coefficient defined as 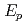 decreased and the reaction products settled gradually with decreasing the H
decreased and the reaction products settled gradually with decreasing the H generation rate. Therefore, the Na concentration decreased at the reaction front and resulted in the SCR terminating naturally.
generation rate. Therefore, the Na concentration decreased at the reaction front and resulted in the SCR terminating naturally.
Doi, Daisuke; Ono, Isao*; Seino, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
CONTAIN-LMR code is an integrated analysis tool to predict the consequence of severe accident in a liquid metal fast reactor. A sodium-concrete reaction is one of the most important phenomena, and Sodium-Limestone Concrete Ablation Model (SLAM) has been installed into the original CONTAIN code. The SLAM treats chemical reaction kinetics between the sodium and the concrete compositions mechanistically, the application is limited to the limestone concrete. In order to apply SLAM to the siliceous concrete which is an ordinary structural concrete in Japan, the chemical reaction kinetics model has been improved. The improved model was validated to analyze a series of sodium-concrete experiments which were conducted in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It has been found that relatively good agreement between calculation and experimental results is obtained and the CONTAIN-LMR code has been validated with regard to the sodium-concrete reaction phenomena.
Doi, Daisuke; Nakagiri, Toshio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(3), p.343 - 349, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)
Doi, Atsunori*; Fujioka, Jun*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Arima, Takahisa*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 90(8), p.081109_1 - 081109_4, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Doi, Daisuke; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2012/07
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Wataru; Yamakami, Mitsunori; Fujikawa, Daisuke; Orukawa, Go*; Kitagawa, Yoshito*; Doi, Takashi*; Saito, Ryosuke*
Doboku Gakkai Heisei-20-Nendo Zenkoku Taikai Dai-63-Kai Nenji Gakujutsu Koenkai Koen Rombunshu, p.453 - 454, 2008/09
no abstracts in English
Doi, Daisuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Doi, Daisuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Masuyama, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Konishi, Kensuke; Miyahara, Shinya
no journal, ,
As the purpose of investigation on terminating mechanism of Na-concrete reaction, the long-time test in which Na continued to be heated than threshold temperature was conducted. Under the condition that enough amount of Na existed and continued to be heated, we confirmed that the reaction stopped.
Doi, Daisuke; Ito, Kei; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Uno, Masayoshi*; Ohno, Shuji; Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Kei; Doi, Daisuke; Ohno, Shuji; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
The authors have been developing a volume-of-fluid based numerical simulation method for hydrogen diffusion flame which may be generated under the severe accident condition of a sodium-cooled fast reactor. Here, the simulation strategy is briefly presented.
Doi, Daisuke; Ito, Kei; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Doi, Daisuke; Ito, Kei; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Kei; Doi, Daisuke; Takata, Takashi; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
Development of numerical simulation method of hydrogen combustion in containment vessel of fast reactor has been developed, in order to establish the estimation technology for availability of measure for failure of containment vessel in sodium cooled fast reactors. In this presentation, estimation results on influence of hydrogen combustion on the structure are reported based on the analysis by using numerical simulations.
Doi, Daisuke; Kondo, Toshiki; Kikuchi, Shin; Seino, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
As part of the source term study for sodium-cooled fast reactors, we have focused on the formation behavior of gaseous iodine in the gas phase. In this report, we will present the results of chemical equilibrium calculations based on the Gibbs free energy minimization method with various parameters, such as ambient oxygen concentrations and temperature for the formation behavior of gaseous iodine.