Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hamada, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Kawano, Katsumi; Ebisawa, Noboru; Oshikiri, Masayuki; Tsutsumi, Fumiaki; Saito, Toru*; Nakajima, Hideo; Matsuda, Hidemitsu*; et al.
Teion Kogaku, 47(3), p.153 - 159, 2012/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has the responsibility to procure 25% of the ITER Toroidal Field coil conductors as the Japanese Domestic Agency (JADA) in the ITER project. The TF conductor is a circular shaped, cable-in-conduit conductor, composed of a cable and a stainless steel conduit (jacket). The outer diameter and maximum length of the TF conductor are 43.7 mm and 760 m, respectively. JAEA has constructed newly conductor manufacturing facility. Prior to starting conductor, JAEA manufactured a 760-m long Cu dummy conductor as process qualification of dummy cable, the jacket sections and fabrication procedures, such as welding, cable insertion, compaction and spooling. Following qualification of all manufacturing processes, JAEA has started to fabricate superconducting conductors for the TF coils.
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Tasaki, Seiji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 634(1, Suppl.), p.S90 - S93, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)In a neutron spin interferometer (NSI), incident neutrons are in states of up- and down-spin eigenstates and a phase difference between the eigenstates is observed after transmission through a magnetic sample. Since the phase difference is proportional to an integral of magnetic field along a trajectory of neutrons, NSI imaging provides projection images of a distribution of magnetic field in the sample. We tried to visualize magnetic field in permalloy film with and without stress as a demonstration of the NSI imaging. An experiment was carried out at C3-1-2-2, MINE2 port at the neutron guide hall of JRR-3M with wavelength of 0.88nm and wavelength resolution of 0.3% in FWHM. Permalloy film with thickness of 0.1 mm was used as a sample and was stressed by bending with angles of 45 and 180  . As a result, images of decrease of a saturated magnetization and an increase of leak magnetic field with increasing the bending angle were obtained.
. As a result, images of decrease of a saturated magnetization and an increase of leak magnetic field with increasing the bending angle were obtained.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Hino, Masahiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Achiwa, Norio*; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2594 - 2599, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.82(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron resonance spin echo (NRSE) is one of the most useful techniques for quasi-elastic scattering with high energy resolution. The path length variation due to the beam divergence has to be corrected in high resolution NRSE measurement because it gives the limit in the energy resolution. A neutron focusing technique using neutron supermirrors is effective to overcome this problem. When a cylindrical shaped neutron supermirror placed in the center of the flight path with a pair of RSFs has the object and the image plane corresponding to the each coil plane of the first and the second RSF, the path length difference can be corrected for the neutron beam with large divergent angle, which leads to the realization of high intensity as well as high resolution in NRSE measurement. In this study, the correction method of the beam divergence with a cylindrical shaped supermirror and its experimental results are discussed.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Journal of Applied Physics, 105(8), p.083527_1 - 083527_8, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:62.26(Physics, Applied)Neutron supermirrors are one of the most useful multilayer devices in neutron experiments since a polychromatic neutron beam can be reflected. The diffuse intensity from a supermirror has to be suppressed since it causes a serious problem of low signal to background noise in focusing systems. The diffuse intensity can be decreased by more than an order of magnitude by adopting NiC/Ti multilayers instead of conventional Ni/Ti multilayers, which leads to a high performance focusing system with a diffuse intensity down to the order of 10 of the specular intensity. In this study, in order to obtain the mechanism that controls the diffuse intensity from a supermirror, we investigated the crystal structure of Ni and NiC monolayers and the interface structure of Ni/Ti and NiC/Ti multilayers and demonstrated that a multilayer with a large vertical correlation length and a small lateral correlation length effectively suppresses the diffuse intensity from a supermirror.
of the specular intensity. In this study, in order to obtain the mechanism that controls the diffuse intensity from a supermirror, we investigated the crystal structure of Ni and NiC monolayers and the interface structure of Ni/Ti and NiC/Ti multilayers and demonstrated that a multilayer with a large vertical correlation length and a small lateral correlation length effectively suppresses the diffuse intensity from a supermirror.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.68 - 70, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron supermirrors have been utilized as reflective optical devices at many neutron sources for transporting, focusing, polarizing neutron beam. In order to produce such devices for the new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), an ion beam sputtering system with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m has been installed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The fabrication methods and the performance of the supermirrors are discussed.
has been installed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The fabrication methods and the performance of the supermirrors are discussed.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Thin Solid Films, 515(14), p.5704 - 5706, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:81.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The development of neutron supermirrors is important for neutron scattering experiments since it offers a considerable increase in the available neutron intensity. Up to now, many studies have been carried out to realize high reflectivity and large  , where
, where  is the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel. We have developed neutron supermirrors by employing the ion beam sputtering (IBS) technique because it enables the production of layers with high density and small grain size. Although the IBS technique produces high quality layers, its disadvantage is that the deposition area is relatively small. In order to produce the optical devices using supermirrors, which is planned in the project of a new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), a new IBS instrument with a large deposition area whose diameter is 500 mm has been designed and installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The deposition rate has been confirmed to be almost uniform over the entire deposition area. We have carried out the development of Ni/Ti supermirror with large
is the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel. We have developed neutron supermirrors by employing the ion beam sputtering (IBS) technique because it enables the production of layers with high density and small grain size. Although the IBS technique produces high quality layers, its disadvantage is that the deposition area is relatively small. In order to produce the optical devices using supermirrors, which is planned in the project of a new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), a new IBS instrument with a large deposition area whose diameter is 500 mm has been designed and installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The deposition rate has been confirmed to be almost uniform over the entire deposition area. We have carried out the development of Ni/Ti supermirror with large  . In this presentation, the performance of those supermirrors fabricated with the IBS instrument is discussed.
. In this presentation, the performance of those supermirrors fabricated with the IBS instrument is discussed.
Yamazaki, Dai; Moriai, Atsushi; Tamura, Itaru; Maruyama, Ryuji; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2007-030, 21 Pages, 2007/03
A new neutron reflectometer "SUIREN" has been developed and started its operation at the research reactor JRR-3 of JAEA in 2006. SUIREN (Apparatus for Surface and Interface investigations with Reflection of Neutrons) provides monochromatic neutron beam with wavelength of 3.8  and vertical sample geometry, which is suitable for studies on interfaces involving solid layers of soft materials, magnetic materials, neutron mirrors and many other things. Collimated neutron intensity is about 2.1
and vertical sample geometry, which is suitable for studies on interfaces involving solid layers of soft materials, magnetic materials, neutron mirrors and many other things. Collimated neutron intensity is about 2.1 10
10
 2.6
2.6 10
10 n/s/cm
n/s/cm with =0.08 deg at the sample position. Background is as low as 4.5
with =0.08 deg at the sample position. Background is as low as 4.5 10
10 n/s when a local beam shutter is closed. A demonstration experiment showed that specular reflectivity of a silicon substrate of 3 inches in diameter can be measured down to 10
n/s when a local beam shutter is closed. A demonstration experiment showed that specular reflectivity of a silicon substrate of 3 inches in diameter can be measured down to 10 over 0
over 0  Qz
Qz  0.22
0.22 
 in 27 hours. This paper describes the beam-line and components of the SUIREN reflectometer, some results of test measurements and future plans.
in 27 hours. This paper describes the beam-line and components of the SUIREN reflectometer, some results of test measurements and future plans.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 18th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-18) (CD-ROM), p.197 - 200, 2007/00
The development of high performance neutron supermirrors with high reflectivity and large  , the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel, is important for the J-PARC project since it greatly increases the available neutron intensity. Neutron supermirrors consist of alternating layers of two materials with different refractive indices for neutrons. An ion beam sputtering instrument with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m
, the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel, is important for the J-PARC project since it greatly increases the available neutron intensity. Neutron supermirrors consist of alternating layers of two materials with different refractive indices for neutrons. An ion beam sputtering instrument with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m has been installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in order to produce neutron guides, benders, and other neutron optical devices, which are planned for application in the J-PARC project. We have succeeded in fabricating the supermirror with large critical angle of
has been installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in order to produce neutron guides, benders, and other neutron optical devices, which are planned for application in the J-PARC project. We have succeeded in fabricating the supermirror with large critical angle of 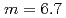 and that with high reflectivity (
and that with high reflectivity ( 85%) for
85%) for 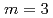 .
.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1256 - 1258, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:70.4(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron supermirror has become an important device to transport, bending and focusing a neutron beam. We have developed it using ion beam sputtering (IBS) instrument since it enables us to produce good quality layers with high density and small grain size. We have also investigated ion-polishing technique, which suppresses the interface roughness of multilayers. We have now installed new IBS instrument with effective deposit area of 500 mm in diameter for the realization of supermirror guide and bender with large effective critical angle. In this presentation, the performance of the supermirrors fabricated with it and the future development of neutron optical devices using supermirrors will be discussed.
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Maruyama, Ryuji*; Tasaki, Seiji*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 356(1-4), p.174 - 177, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.23(Physics, Condensed Matter)Drabkin energy filter could be used as a fast chopper for pulsed neutrons by varying the resonant wavelength 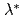 fast in such a way that resonant wavelength matches neutron wavelength at a small time region. The faster
fast in such a way that resonant wavelength matches neutron wavelength at a small time region. The faster 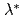 are varied, the smaller time window we could obtain. Neutron pulses could be sharpened much more effectively for a small wavelength band than in the wide-band pulse-shaping mode in which
are varied, the smaller time window we could obtain. Neutron pulses could be sharpened much more effectively for a small wavelength band than in the wide-band pulse-shaping mode in which 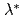 is varied in synchronization with the time-of-flight from the moderator. In our preliminary test of a chopper-mode with a prototype Drabkin energy filter, time-window of 0.21 ms was obtained while it was 1.08 ms with the filter driven stationary. Narrower time-window could have been obtained if we had more beam-time and it could be also narrowed with higher-resolution Drabkin filters.
is varied in synchronization with the time-of-flight from the moderator. In our preliminary test of a chopper-mode with a prototype Drabkin energy filter, time-window of 0.21 ms was obtained while it was 1.08 ms with the filter driven stationary. Narrower time-window could have been obtained if we had more beam-time and it could be also narrowed with higher-resolution Drabkin filters.
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Torikai, Naoya*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Matsuoka, Hideki*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 356(1-4), p.229 - 233, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.23(Physics, Condensed Matter)The application of neutron reflectometry to study dynamic phenomena at surface and interfaces have been restricted so far. It was mainly due to the low intensity of neutron sources, but now high-intensity spallation neutron sources are under construction in Japan (J-PARC) and U.S. (SNS). We have a plan to install a spin-echo option on the J-PARC neutron reflectometer with horizontal sample geometry for studies on dynamics of surfaces and interfaces. This option is based on the resonance spin-echo method and aimed at dynamics upto hundreds of nanoseconds. In this contribution, the plan and status of development are introduced together with the principle and characteristics of this option.
Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*
Hamon, 15(1), p.51 - 54, 2005/01
Neutron spin handling could be used for beam control and spectroscopy. Energy analysis could be performed with Drabkin energy filters, by which inelastic component with a 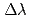 , a
, a 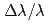 or a
or a 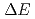 could be extracted for all incident wavelength. Pulsed spin-flipper and polarization analyzer could be used as a neutron chopper (spin-flip chopper) whose opening time, number of windows and phase are controlled independently. It was demonstrated that S/N ratio can be enhanced up to 1.5
could be extracted for all incident wavelength. Pulsed spin-flipper and polarization analyzer could be used as a neutron chopper (spin-flip chopper) whose opening time, number of windows and phase are controlled independently. It was demonstrated that S/N ratio can be enhanced up to 1.5  10
10 by installing three spin-flip choppers in sequence.
by installing three spin-flip choppers in sequence.
Maruyama, Ryuji*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Takeda, Masayasu; Ebisawa, Toru*; Kawabata, Yuji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 530(3), p.505 - 512, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.72(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron resonance spin echo (NRSE) spectroscopy enables us to measure neutron quasielastic scattering with high energy resolution. It is desirable to apply NRSE spectroscopy to pulsed neutron sources because this application allows a very wide range of the spin echo time. We have already developed the neutron resonance spin flipper applicable to a polychromatic pulsed neutron beam, which is necessary for the TOF-NRSE method. Using this flipper, we have succeeded in observing spin echo signals with visibility higher than 0.65 for the pulsed neutron beam with wavelength from 0.3 to 0.9 nm. We discuss the prospect of the NRSE spectrometer with high energy resolution on the basis of the present result.
Oku, Takayuki*; Sakai, Kenji*; Adachi, Tomohiro*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Maruyama, Ryuji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 335(1-4), p.226 - 229, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.38(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tamura, Itaru; Tasaki, Seiji*
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.407 - 415, 2003/06
Drabkin energy filters extract neutrons of required wavelength using spatial neutron spin resonance. If they are applied to pulsed neutrons, they could sharpen pulse width and cut tail neutrons without reducing band-width or peak-intensity. Shaping of J-PARC coupled-moderator pulse by a Drabkin energy filter was simulated. In the simulation, discrete field gradient to Bx is introduced and total field B is varied in accordance with the dominant wavelength at each moment at the filter position. The results suggest that about 90 % or more of tail neutrons from coupled moderator are cut and a fliter with fields of 200 periods could reduce pulse width up to that of decoupled moderator. Effects of fluctuations of width of each half period were studied and it was found that fluctuation within  1 % are tolerable for a flipper with field of 100 or 200 periods.
1 % are tolerable for a flipper with field of 100 or 200 periods.
Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*
JAERI-Research 2003-009, 29 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Junichi; Tasaki, Seiji*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Ebisawa, Toru*
Applied Physics A, 74(Suppl.1), p.S308 - S310, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Junichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Tasaki, Seiji*; Ebisawa, Toru*
JAERI-Conf 2001-002, p.547 - 550, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Kawabata, Yuji*; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*; Suzuki, Masatoshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAERI-Research 2000-019, p.20 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Soyama, Kazuhiko; ; *; Ebisawa, Toru*; Tasaki, Seiji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 35(11), p.750 - 758, 1998/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English