Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
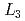 -edge jump and shift on white-line of Pd interlayer for trilaminar neutron production target under H
-edge jump and shift on white-line of Pd interlayer for trilaminar neutron production target under H
 irradiation
irradiationIshiyama, Shintaro; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 8(9), p.870 - 875, 2014/09
Interlayer Pd for the Li/Pd/Cu neutron target for BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) was characterized after 0.1-5 keV H
 irradiation by XAFS technique, and following conclusions were derived; (1) From the XAFS observation of white line of Pd, remarkable Pd
irradiation by XAFS technique, and following conclusions were derived; (1) From the XAFS observation of white line of Pd, remarkable Pd 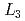 Edge jump was found in 1.1-3 times higher than before irradiation in low irradiation fluence. (2) This fact indicates increase of hole density in Pd 4d-band, whereas no change was observed for XASF spectra of Ag sample under the same irradiation conditions. (3) Remarkable Pd
Edge jump was found in 1.1-3 times higher than before irradiation in low irradiation fluence. (2) This fact indicates increase of hole density in Pd 4d-band, whereas no change was observed for XASF spectra of Ag sample under the same irradiation conditions. (3) Remarkable Pd 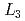 Edge shift of 0.12-0.66 eV was also found with increase of H
Edge shift of 0.12-0.66 eV was also found with increase of H
 irradiation energy in low fluence, and drastically decreased after peak in high irradiation energy and fluence.(4)Implanted protons deposited in Pd as negative under the balance of electron population enhanced by proton irradiation and charge transfer.
irradiation energy in low fluence, and drastically decreased after peak in high irradiation energy and fluence.(4)Implanted protons deposited in Pd as negative under the balance of electron population enhanced by proton irradiation and charge transfer.
 O addition on lithium target for BNCT
O addition on lithium target for BNCTIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(8), p.317 - 321, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Low temperature synthesis of lithium-nitride compound was conducted on the lithium target for BNCT by N /H
/H O mixing gas squirt in the ultra high vacuum chamber, and the following results were derived; (1) Lithium-nitride compound was synthesized on the lithium target under 101.3 Pa N
O mixing gas squirt in the ultra high vacuum chamber, and the following results were derived; (1) Lithium-nitride compound was synthesized on the lithium target under 101.3 Pa N gas squirt at room temperature and in the ultra high vacuum chamber under the pressure of 1
gas squirt at room temperature and in the ultra high vacuum chamber under the pressure of 1 10
10 Pa. (2) Remarkable contamination by O and C was observed on the lithium-nitride compound synthesized under the squirt pressure of 13.3-80 Pa/1.33-4.7 Pa N
Pa. (2) Remarkable contamination by O and C was observed on the lithium-nitride compound synthesized under the squirt pressure of 13.3-80 Pa/1.33-4.7 Pa N /H
/H O mixing gas. (3) No contamination and synthesis of Li-N compound was observed under the squirt pressure of 0.013-0.027 Pa/0-0.005 Pa N
O mixing gas. (3) No contamination and synthesis of Li-N compound was observed under the squirt pressure of 0.013-0.027 Pa/0-0.005 Pa N /H
/H O mixing gas. (4) Contamination by O and C was enhanced with excessive addition of H
O mixing gas. (4) Contamination by O and C was enhanced with excessive addition of H O at the pressure of over 1.33 Pa.
O at the pressure of over 1.33 Pa.
 N synthesized on lithium target for boron neutron capture therapy
N synthesized on lithium target for boron neutron capture therapyIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(8), p.322 - 325, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To remove high level of contaminants by O and C from Li N surface for boron neutron capture therapy target, high temperature thermal desorption was conducted up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum and the following results were derived; (1) During thermal desorption up to 1023 K, typical three peaks of vacuum pressure disturbance due to vaporization of contaminants were observed in vacuum pressure-temperature curve. (2) Over-layered contaminants with high melting temperature below 1023 K on Li
N surface for boron neutron capture therapy target, high temperature thermal desorption was conducted up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum and the following results were derived; (1) During thermal desorption up to 1023 K, typical three peaks of vacuum pressure disturbance due to vaporization of contaminants were observed in vacuum pressure-temperature curve. (2) Over-layered contaminants with high melting temperature below 1023 K on Li N surface is completely removed by high temperature thermal desorption up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum. (3) From these desorption results, it is suggested that these contaminants corresponding to these vaporization peaks are H
N surface is completely removed by high temperature thermal desorption up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum. (3) From these desorption results, it is suggested that these contaminants corresponding to these vaporization peaks are H O and Li compounds with high melting temperature below 1023 K, of which LiOH and Li
O and Li compounds with high melting temperature below 1023 K, of which LiOH and Li CO
CO were synthesized by decomposition process of Li
were synthesized by decomposition process of Li N with residual H
N with residual H O and CO
O and CO in low temperature.
in low temperature.
 N thin layer on lithium target surface for BNCT in N
N thin layer on lithium target surface for BNCT in N gaseous conditions
gaseous conditionsIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(4), p.137 - 141, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To prevent vaporization damage of BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) lithium target during operation, direct synthesis of Li N thin layer on lithium target surface was demonstrated in 0.1 MPa N
N thin layer on lithium target surface was demonstrated in 0.1 MPa N gas at temperature below 548 K and the following conclusions were derived; (1) Synthesis of Li
gas at temperature below 548 K and the following conclusions were derived; (1) Synthesis of Li N thin layer on lithium surface was confirmed after nitridation at 276
N thin layer on lithium surface was confirmed after nitridation at 276 548 K with surface contamination by oxygen and carbon. (2) Rapid nitridation over 1-5wt.%/min was observed above Li melting temperature, whereas slow reaction under 0.02-0.5 wt.%/min below melting temperature. (3) During nitridation, removal of oxygen contamination on Li
548 K with surface contamination by oxygen and carbon. (2) Rapid nitridation over 1-5wt.%/min was observed above Li melting temperature, whereas slow reaction under 0.02-0.5 wt.%/min below melting temperature. (3) During nitridation, removal of oxygen contamination on Li N thin layer is taken place by nitrogen below Li melting temperature.
N thin layer is taken place by nitrogen below Li melting temperature.

 irradiation to Li/Pd/Cu trilaminar neutron production target for BNCT
irradiation to Li/Pd/Cu trilaminar neutron production target for BNCTIshiyama, Shintaro; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Materials Transactions, 55(4), p.658 - 663, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The Li/Pd/Cu trilaminar structures of the synthesized target for BNCT were characterized under 3keV H
 irradiation by XPS and XAFS technique, which provides structural/electronic properties of solids, and information about the local structure, such as the nature and number of surrounding atoms and inter-atomic distances. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Pd-Cu physical bonding was produced between the Pd and Cu interface by electro-less plating Pd deposition on a high purity Cu plate (2) From the XAFS observation of white line of Pd, the Pd
irradiation by XPS and XAFS technique, which provides structural/electronic properties of solids, and information about the local structure, such as the nature and number of surrounding atoms and inter-atomic distances. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Pd-Cu physical bonding was produced between the Pd and Cu interface by electro-less plating Pd deposition on a high purity Cu plate (2) From the XAFS observation of white line of Pd, the Pd  3 Edge jump was found after H
3 Edge jump was found after H
 irradiation, this fact indicates increase of hole density in Pd 4
irradiation, this fact indicates increase of hole density in Pd 4 -band. (3) 0.9 eV chemical shift was also observed in Pd
-band. (3) 0.9 eV chemical shift was also observed in Pd  3 white line for Pd/Cu samples, which will affect the quality of the Li/Pd/Cu target due to the formation of PdH
3 white line for Pd/Cu samples, which will affect the quality of the Li/Pd/Cu target due to the formation of PdH in palladium insert layer.
in palladium insert layer.
 N synthesized on lithium target for boron neutron capture therapy
N synthesized on lithium target for boron neutron capture therapyIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Materials Transactions, 55(3), p.539 - 542, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To remove high level of contaminants by O and C from Li N surface for BNCT target, high temperature thermal desorption was conducted up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum and the following results were derived; (1) During thermal desorption up to 1023 K, typical three peaks of vacuum pressure disturbance due to vaporization of contaminants were observed in vacuum pressure-temperature curve. (2) Over-layered contaminants with high melting temperature below 1023 K on Li
N surface for BNCT target, high temperature thermal desorption was conducted up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum and the following results were derived; (1) During thermal desorption up to 1023 K, typical three peaks of vacuum pressure disturbance due to vaporization of contaminants were observed in vacuum pressure-temperature curve. (2) Over-layered contaminants with high melting temperature below 1023 K on Li N surface is completely removed by high temperature thermal desorption up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum. (3) From these desorption results, it is suggested that these contaminants corresponding to these vaporization peaks are H
N surface is completely removed by high temperature thermal desorption up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum. (3) From these desorption results, it is suggested that these contaminants corresponding to these vaporization peaks are H O and Li compounds with high melting temperature below 1023 K, of which LiOH and Li
O and Li compounds with high melting temperature below 1023 K, of which LiOH and Li CO
CO were synthesized by decomposition process of Li
were synthesized by decomposition process of Li N with residual H
N with residual H O and CO
O and CO in low temperature.
in low temperature.
 O addition on lithium target for BNCT
O addition on lithium target for BNCTIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Materials Transactions, 54(12), p.2233 - 2237, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Low temperature synthesis of lithium-nitride compound was conducted on the lithium target for BNCT by N /H
/H O mixing gas squirt in ultra high vacuum chamber, and the following results were derived; (1) Lithium-nitride compound was synthesized on lithium target under 101.3 PaN
O mixing gas squirt in ultra high vacuum chamber, and the following results were derived; (1) Lithium-nitride compound was synthesized on lithium target under 101.3 PaN gas squirt at room temperature and 1
gas squirt at room temperature and 1 10
10 Pa in ultra high vacuum chamber. (2) Remarkable contamination by O and C was observed on the lithium-nitride compound synthesized by 13.3
Pa in ultra high vacuum chamber. (2) Remarkable contamination by O and C was observed on the lithium-nitride compound synthesized by 13.3  80 Pa/1.33
80 Pa/1.33  4.7 Pa N
4.7 Pa N /H
/H O mixing gas squirt. (3) No contamination and synthesis of Li-N compound was observed at 0.013
O mixing gas squirt. (3) No contamination and synthesis of Li-N compound was observed at 0.013  0.027 Pa/0
0.027 Pa/0  0.005 Pa N
0.005 Pa N /H
/H O squirt. (4) Contamination by O and C is enhanced with excessive addition of over 1.33 Pa H
O squirt. (4) Contamination by O and C is enhanced with excessive addition of over 1.33 Pa H O addition.
O addition.
 lithium deposition and ion implantation
lithium deposition and ion implantationIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 77(11), p.509 - 513, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.47(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To testify thermal stability of the BNCT neutron target synthesized by  lithium deposition and ion implantation, laser heating test of the Li
lithium deposition and ion implantation, laser heating test of the Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target was conducted in high vacuum chamber of 10
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target was conducted in high vacuum chamber of 10 Pa and thermal stability of the tri-layered target was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Following conclusions were derived; (1) The Li
Pa and thermal stability of the tri-layered target was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Following conclusions were derived; (1) The Li N/Li/Cu tri- layered target with very low oxide and carbon contamination was synthesized by
N/Li/Cu tri- layered target with very low oxide and carbon contamination was synthesized by  lithium deposition and ion implantation techniques without H
lithium deposition and ion implantation techniques without H O and O
O and O additions (2) The starting temperature of evaporation of the Li
additions (2) The starting temperature of evaporation of the Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target increased by 120 K compared to that of the Li/Cu target and (3) frequent repair synthesis of the damaged Li
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target increased by 120 K compared to that of the Li/Cu target and (3) frequent repair synthesis of the damaged Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target caused by evaporation is possible.
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target caused by evaporation is possible.
 lithium deposition and ion implantation
lithium deposition and ion implantationIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Materials Transactions, 54(9), p.1760 - 1764, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Li N synthesis on Li deposition layer was conducted without H
N synthesis on Li deposition layer was conducted without H O and O
O and O by
by  lithium deposition in high vacuum chamber of 10
lithium deposition in high vacuum chamber of 10 Pa and ion implantation techniques and the thermo-chemical stability of the Li
Pa and ion implantation techniques and the thermo-chemical stability of the Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target under laser heating and air exposure was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Li
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target under laser heating and air exposure was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Li N/Li/Cu tri- layered target with very low oxide and carbon contamination was synthesized by
N/Li/Cu tri- layered target with very low oxide and carbon contamination was synthesized by  lithium deposition and ion implantation techniques without H
lithium deposition and ion implantation techniques without H O and O
O and O additions and frequent synthesis of the target is possible. (2) The evaporating temperature of Li deposited layer increased by 120 K after forming the Li
additions and frequent synthesis of the target is possible. (2) The evaporating temperature of Li deposited layer increased by 120 K after forming the Li N layer on the surface of Li. (3) Remarkable oxidation and carbon contamination were observed on the surfaces of Li/Cu and Li
N layer on the surface of Li. (3) Remarkable oxidation and carbon contamination were observed on the surfaces of Li/Cu and Li N/Li/Cu after air exposure and these contaminated compositions formed on the surface of Li
N/Li/Cu after air exposure and these contaminated compositions formed on the surface of Li N/Li/Cu was not removed by Ar heavy sputtering.
N/Li/Cu was not removed by Ar heavy sputtering.
 N thin layer on lithium target surface for BNCT in N
N thin layer on lithium target surface for BNCT in N gaseous conditions
gaseous conditionsIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Materials Transactions, 54(9), p.1765 - 1769, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To prevent vaporization damage of BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) lithium target during operation, direct synthesis of Li N thin layer on lithium target surface was demonstrated in 0.1 MPa N
N thin layer on lithium target surface was demonstrated in 0.1 MPa N gas at temperature below 548 K and the following conclusions were derived; (1)Synthesis of Li
gas at temperature below 548 K and the following conclusions were derived; (1)Synthesis of Li N thin layer on lithium surface was confirmed after nitridation at 276
N thin layer on lithium surface was confirmed after nitridation at 276 548 K with surface contamination by oxygen and carbon. (2) Rapid nitridation over 1
548 K with surface contamination by oxygen and carbon. (2) Rapid nitridation over 1 5wt.%/min was observed above Li melting temperature, whereas slow reaction under 0.02
5wt.%/min was observed above Li melting temperature, whereas slow reaction under 0.02 0.5wt.%/min below melting temperature. (3) During nitridation, removal of oxygen contamination on Li
0.5wt.%/min below melting temperature. (3) During nitridation, removal of oxygen contamination on Li N thin layer is taken place by nitrogen below Li melting temperature.
N thin layer is taken place by nitrogen below Li melting temperature.
 lithium deposition and ion implantation
lithium deposition and ion implantationIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 293, p.42 - 47, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)To achieve high performance of BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) device, lithium nitride target for neutron production was synthesized by in-situ vacuum deposition and nitridation techniques. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Uniform lithium layer of a few hundreds nanometer was formed on Pd/Cu multilayer surface by  vacuum deposition technique using metallic lithium as a source material. (2) Lithium nitrides were formed by
vacuum deposition technique using metallic lithium as a source material. (2) Lithium nitrides were formed by  nitridation by the implantation of low-energy nitrogen ions on the deposited lithium layer surface. The chemical states of the nitridated zone were close to the stoichiometric lithium nitride, Li
nitridation by the implantation of low-energy nitrogen ions on the deposited lithium layer surface. The chemical states of the nitridated zone were close to the stoichiometric lithium nitride, Li N. (3) This nitridated zone formed on surface of four layered lithium target is stable for three months in air condition. The
N. (3) This nitridated zone formed on surface of four layered lithium target is stable for three months in air condition. The  nitridation is effective to protect lithium target from degradation by unfavourable reactions.
nitridation is effective to protect lithium target from degradation by unfavourable reactions.
Ishiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 288, p.18 - 22, 2012/10
To achieve high performance of BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) device, lithium target for neutron production was redesigned, and the layered structures of the synthesized target were characterized. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Uniform lithium layers with the thickness from 1.6 nm to a few hundreds nanometer were formed on Pd/Cu multilayer surface by in-situ vacuum deposition technique using metallic lithium as a source material. (2) Re-deposition of lithium layer on Li surface can be achieved by in-situ vacuum deposition technique. (3) Small amount of water and carbonate was observed on the top surface of Li. But the thickness of the adsorbed layer was less than monolayer, which will not affect the quality of the Li target. (4) The formation of Pd-Li alloy layer was observed at the Pd and Li interface. The alloy layer would contribute to the stability of the Li layer.
Ishiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 288, p.18 - 22, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)For the purpose of avoiding the radiation blistering of the lithium target for neutron production in BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) device, trilaminar Li target, of which palladium thin layer was inserted between cupper substrate and Li layer, was newly designed. In-situ vacuum deposition and electrolytic coating techniques were applied to validate the method of fabrication of the Li/Pd/Cu target, and the layered structures of the synthesized target were characterized. In-situ vacuum re-deposition technique was also established for repairing and maintenance for lithium target damaged. Following conclusions were derived; (1) Uniform lithium layers with the thickness from 1.6 nm to a few hundreds nanometer were formed on Pd/Cu multilayer surface by in situ vacuum deposition technique using metallic lithium as a source material. (2) Re-deposition of lithium layer on Li surface can be achieved by in situ vacuum deposition technique.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Matsuda, Makoto; Fujii, Yoshio*
Proceedings of 2nd Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 30th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.729 - 730, 2005/07
TRIAC (Tokai Radioactive Ion Accelerator Complex) facility can accelerate both radioactive and stable ion beams up to 1.1Mev/u. In this facility, an ECR ion source is used for production of stable ion beams. Stable ion beams are used mainly as a pilot beam for radioactive ion beam. ECR ion source is required to produce many kinds of ion species, not only gas state elements. So, we developed a high temperature oven for obtaining metal ion beams. This paper describes the design and detail of the oven and experimental results.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
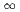 estimator for VHTRC experiment
estimator for VHTRC experimentSuzuki, Katsuo; Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Yamane, Tsuyoshi; Fujii, Yoshio*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(4), p.408 - 417, 2003/12
On-line and real-time estimation of time-varying reactivity in a nuclear reactor is necessary for early detection of reactivity anomaly and safe operation. Using a digital nonlinear H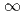 estimator, an experiment of real-time dynamic reactivity estimation was carried out in the VHTRC of JAERI. Some technical issues of the experiment are described, such as reactivity insertion, data sampling frequency, anti-aliasing filter, experimental circuit and digitalizing nonlinear H
estimator, an experiment of real-time dynamic reactivity estimation was carried out in the VHTRC of JAERI. Some technical issues of the experiment are described, such as reactivity insertion, data sampling frequency, anti-aliasing filter, experimental circuit and digitalizing nonlinear H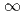 reactivity estimator, and so on. Then, we discussed the experimental results obtained by the digital nonlinear H
reactivity estimator, and so on. Then, we discussed the experimental results obtained by the digital nonlinear H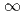 estimator with sampled data of the nuclear instrumentation signal for the power responses under various reactivity insertions. Good performances of estimated reactivity were observed, with almost no delay to the true reactivity and sufficient accuracy between 0.05cent and 0.1cent. From the results of the experiment, it is concluded that the digital nonlinear H
estimator with sampled data of the nuclear instrumentation signal for the power responses under various reactivity insertions. Good performances of estimated reactivity were observed, with almost no delay to the true reactivity and sufficient accuracy between 0.05cent and 0.1cent. From the results of the experiment, it is concluded that the digital nonlinear H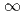 reactivity estimator can be applied as on-line real-time reactivity meter for actual nuclear plants.
reactivity estimator can be applied as on-line real-time reactivity meter for actual nuclear plants.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.14(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English