Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

 /
/
 effect on confinement properties
effect on confinement propertiesNarita, Emi*; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Honda, Mitsuru; Isayama, Akihiko; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kamada, Yutaka; Tanaka, Yasuyuki*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403102_1 - 2403102_5, 2012/07
Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 4, p.051_1 - 051_7, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095006_1 - 095006_7, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)H-modes operated at higher 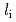 with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The
with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The  -factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on
-factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on 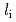 with the relation of
with the relation of 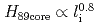 for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high
for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high 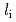 H-modes. The pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high
H-modes. The pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high 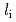 H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and temperature. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high
H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and temperature. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high 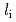 case, resulting in the center peaked
case, resulting in the center peaked 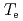 profile while the
profile while the 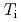 profiles are approximately unchanged.
profiles are approximately unchanged.
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095017_1 - 095017_8, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:74.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reports the recent development of reversed shear plasmas with a high bootstrap current fraction towards reactor relevant regime, especially lower 
 regime. By utilizing large volume configuration close to the conductive wall for wall stabilization, the beta limit of the reversed shear plasmas is significantly improved. As a result, high confinement reversed shear plasmas with high bootstrap current fraction exceeding no-wall beta limit are obtained in reactor relevant regime, where
regime. By utilizing large volume configuration close to the conductive wall for wall stabilization, the beta limit of the reversed shear plasmas is significantly improved. As a result, high confinement reversed shear plasmas with high bootstrap current fraction exceeding no-wall beta limit are obtained in reactor relevant regime, where 
 of 2.7,
of 2.7, 
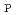 of 2.3 is achieved with reversed
of 2.3 is achieved with reversed  profile with
profile with 
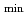 of 2.3, and then HH
of 2.3, and then HH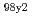 of 1.7,
of 1.7, 
 /
/
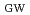 of 0.87 and
of 0.87 and 
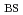 of 0.9 are also obtained at
of 0.9 are also obtained at 
 of 5.3.
of 5.3.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
Suzuki, Takahiro; Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Kamada, Yutaka; Naito, Osamu; Sueoka, Michiharu; Moriyama, Shinichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085003_1 - 085003_8, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:30.72(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Fully non-inductive discharge having a relaxed current profile and high bootstrap current fraction f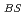 =0.5 has been realized in the high-
=0.5 has been realized in the high-
 ELMy H-mode discharge with weak magnetic-shear having q
ELMy H-mode discharge with weak magnetic-shear having q =5.8, qmin=2.1, and q(0)=2.4, where qmin and q(0) are the safety factor q at the minimum and the plasma center, respectively. The rest of the plasma current is externally driven by neutral beams (NBs) and lower-hybrid (LH) waves. The safety factor profile evaluated by the motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostic is kept unchanged during 0.7 s at the end of the full current drive (CD) sustainment for 2 s (1.5 times the current relaxation time
=5.8, qmin=2.1, and q(0)=2.4, where qmin and q(0) are the safety factor q at the minimum and the plasma center, respectively. The rest of the plasma current is externally driven by neutral beams (NBs) and lower-hybrid (LH) waves. The safety factor profile evaluated by the motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostic is kept unchanged during 0.7 s at the end of the full current drive (CD) sustainment for 2 s (1.5 times the current relaxation time 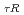 ). The loop voltage profile is spatially uniform at 0 V at the end of the sustainment. This demonstration shows, for the first time, that the steady sustainment of ful-CD plasma is possible at high f
). The loop voltage profile is spatially uniform at 0 V at the end of the sustainment. This demonstration shows, for the first time, that the steady sustainment of ful-CD plasma is possible at high f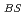 =0.5 and reasonably low q
=0.5 and reasonably low q =5.8 regime and is stably controlled by appropriate external current drivers. On the other hand, when the combination of bootstrap current and externally driven current does not match to the steady current profile, slight change in the current profile due to current relaxation resulted in appearance of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instability, e.g. neo-classical tearing mode (NTM), in a high beta plasma. This discharge clarifies importance of the demonstration of steady current profile developed here. These discharges contribute to the ITER steady-state operation scenario development.
=5.8 regime and is stably controlled by appropriate external current drivers. On the other hand, when the combination of bootstrap current and externally driven current does not match to the steady current profile, slight change in the current profile due to current relaxation resulted in appearance of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instability, e.g. neo-classical tearing mode (NTM), in a high beta plasma. This discharge clarifies importance of the demonstration of steady current profile developed here. These discharges contribute to the ITER steady-state operation scenario development.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(1), p.015005_1 - 015005_7, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:45.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Transport analysis during the transient phase of heating (a dynamic transport study) applied to the plasma with internal transport barriers (ITBs) in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and the JT-60U tokamak is described. In the dynamic transport study the time of transition from the L-mode plasma to the ITB plasma is clearly determined by the onset of flattening of the temperature profile in the core region and a spontaneous phase transition from a zero curvature ITB (hyperbolic tangent shaped ITB) or a positive curvature ITB (concaved shaped ITB) to a negative curvature ITB (convex shaped ITB) and its back-transition are observed. The flattening of the core region of the ITB transition and the back-transition between a zero curvature ITB and a convex ITB suggest the strong interaction of turbulent transport in space.
 plasmas
plasmasMatsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Isayama, Akihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Dependence of the H-mode confinement and pedestal structure on the plasma current is investigated. Higher energy confinement is obtained in higher 
 H-mode. The profiles of the core
H-mode. The profiles of the core 
 and
and 
 are tends to be peaked. The H-factor for the core plasma depends strongly on
are tends to be peaked. The H-factor for the core plasma depends strongly on 
 . Higher energy confinement obtained at higher
. Higher energy confinement obtained at higher 
 is attributed to the core confinement improvement. The edge pedestal pressure is not significantly changed by core current density profile. In both
is attributed to the core confinement improvement. The edge pedestal pressure is not significantly changed by core current density profile. In both 
 ramp and
ramp and 
 scan experiments, the core energy confinement is improved by the increased core
scan experiments, the core energy confinement is improved by the increased core 
 value. The effect of magnetic shear on the confinement should be investigated in next step study.
value. The effect of magnetic shear on the confinement should be investigated in next step study.
Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Oikawa, Toshihiro
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(10), p.10F533_1 - 10F533_5, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:39.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)Motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostics in JT-60U works as polarimeter to measure the pitch angle of magnetic field as well as beam-emission-spectroscopy (BES) monochromator simultaneously at 30 spatial channels. Fluctuation in the BES signal using MSE optics (MSE/BES) contains fluctuations in not only the density but also the pitch angle (or the magnetic field). Correlation analysis of the magnetic fluctuation between two spatial channels have been applied to a high beta plasma with m/n=2/1 MHD activity at frequency of about 0.9 kHz. It has been found that the magnetic fluctuation measured by the MSE/BES is spatially localized near q=2 surface measured by the MSE diagnostic and that the phase of the fluctuation is inverted at about the q=2 surface, suggesting magnetic island-structure by neo-classical tearing mode (NTM). The magnetic fluctuation measured by the MSE/BES at outside of the q=2 surface is consistent with that by the pick-up coil placed outside the plasma.
Ida, Katsumi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ito, Kimitaka*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 101(5), p.055003_1 - 055003_4, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:79.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A spontaneous transition phenomena between two meta-stable states of plasmas with internal transport barrier (ITB), that are characterized by different radial profiles of second derivative of ion temperature inside the ITB region where the ion temperature gradient is large, is observed in the steady-state phase of magnetic shear in the negative magnetic shear plasma in JT-60U tokamak. The curvature asymmetry factor evaluated from the radial profile of second derivative of ion temperature profiles changes from 0.08 (symmetric curvature ITB) to -0.43 (asymmetric curvature ITB) during transition phase.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.465 - 467, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Fujita, Akihiko*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Okuda, Takashi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 113, 2008/03
We have shown that anhydrobiotic larvae of 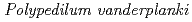 have higher tolerance against both high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation than hydrated larvae. We therefore examined effects of high-LET radiation on four kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae.
have higher tolerance against both high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation than hydrated larvae. We therefore examined effects of high-LET radiation on four kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kubo, Hirotaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 53(1), p.114 - 129, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)We report on the applications of the ECH to the JT-60U tokamak. The ECH contributes to the advanced tokamak study in JT-60U in such respects as (1)NTM suppression, (2)Study on the internal transport barrier, (3)Impurity exhaust, (4)Tokamak start-up without center solenoid, (5)Current hole study, (6)Confinement and transport study, and (7)Start-up and shut-down assist. These contributions comes from the good local coupling of the ECH to the tokamak plasma.
Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(1), p.70 - 72, 2008/01
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takechi, Manabu; Kamada, Yutaka; Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1506 - 1511, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:25.84(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Controllability of plasmas with a large bootstrap current fraction (
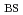 ) has been investigated in JT-60U. Dynamic change in current profile, especially
) has been investigated in JT-60U. Dynamic change in current profile, especially 
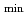 , which was induced by change in pressure profile at the internal transport barrier (ITB) through rotation control, was observed, indicating the strong linkage among the profiles. Response of pressure and current profiles to off-axis neutral beam injection is investigated and found that the alignment of peaks of total current profile and beam driven current profile affects to
, which was induced by change in pressure profile at the internal transport barrier (ITB) through rotation control, was observed, indicating the strong linkage among the profiles. Response of pressure and current profiles to off-axis neutral beam injection is investigated and found that the alignment of peaks of total current profile and beam driven current profile affects to 
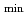 location, and the change in toroidal rotation induces the movement of ITB location. The current profile in strong reversed shear plasma without current hole is largely varied in the core region by electron cyclotron current drive, while the ITB structure is not affected.
location, and the change in toroidal rotation induces the movement of ITB location. The current profile in strong reversed shear plasma without current hole is largely varied in the core region by electron cyclotron current drive, while the ITB structure is not affected.
Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Hosoyama, Hiroki; Kamada, Yutaka; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 933, p.229 - 236, 2007/10
no abstracts in English
Sasao, Mamiko*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mase, Atsushi*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(9), p.779 - 782, 2007/09
This is a report of highlights from 2007 spring meetings of seven Topical Groups (TG) of International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA). In each meeting, high priority issues in physics of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and other burning plasma experiments have been discussed and investigated. Twenty-seven scientists from Japan have participated in those meetings. Dates and places of the meetings are shown below. (1) Diagnostics TG: 26-30 March, Princeton (USA), (2) Transport Physics TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (3) Confinement Database and Modeling TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (4) Edge Pedestal Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany) (5) Steady State Operation TG: 9-11 May, Daejeon (South Korea), (6)MHD TG: 21-24 May, San Diego (USA), (7) Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany).
 larvae
larvaeWatanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Fujita, Akihiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Okuda, Takashi*
Journal of Insect Physiology, 53(6), p.573 - 579, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:65.12(Entomology)We examined effects of high-LET radiation on 4 kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately-rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately-rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae. In addition, almost complete desiccation further enhanced radiation tolerance, possibly in a different way from the hydrated larvae.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(4), p.525 - 534, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English