Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kijima, Jun; Koyama, Hayato; Owada, Mitsuhiro; Hagiwara, Masayoshi; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka
JAEA-Technology 2022-012, 14 Pages, 2022/07
Steam reforming system has been developed for the treatment of organic wastes which are not suitable materials (halogenated oil) for the incineration due to generation of corrosive compounds and plugging materials. The refractory material is cast inside the main reactor, which is a part of the steam reforming system. Since the surface of this refractory material has deteriorated over time, the main reactor was replaced. If the refractory material surface of the used main reactor can be repaired, the used main reactor can be reused as a spare. The refractory material surface was repaired using two types of repair materials ("S" and "P"). Combustion tests were conducted on samples simulating organic wastes to evaluate each repair material. As a result of the combustion test, it was concluded that the repair of the main reactor was possible to use the repair material "P" because no cracks or flakes were observed.
Sakashita, Koichi; Ishii, Naoyuki; Kijima, Jun; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hagiwara, Masayoshi; Fukushima, Mineo
JAEA-Testing 2020-003, 20 Pages, 2020/07
Steam reforming method has been developed for the treatment of organic wastes which are not suitable materials (halogenated oil) for the incineration. This method consists of the gasification process in which organics are vaporized and decomposed with superheated steam and the oxidation process in which vaporized organics are decomposed by oxidizing reaction with heated air. In the gasification process, nonvolatile radionuclides are separated from vaporized waste. Therefore it can be expected that treatment of liquid waste generated from an off-gas treatment system and maintenance operation of the off-gas treatment system become easy to perform. 1,500L of waste oil contaminated with halogen, solvent and uranium was treated using the demonstration scale steam reforming system to examine the performance of the system in 2018. Results obtained this study were as follows; (1) The temperature in the steam reforming system was controlled under the self-regulation temperature. (2) The concentration of CO and NO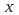 in the off-gas were controlled less than 100 ppm and 250 ppm respectively. (3) The gasification ratio of waste oil was more than 99%. (4) Concentration of fluorine oil in waste oil is needed to be less than 20wt% to perform stable continuance treatment.
in the off-gas were controlled less than 100 ppm and 250 ppm respectively. (3) The gasification ratio of waste oil was more than 99%. (4) Concentration of fluorine oil in waste oil is needed to be less than 20wt% to perform stable continuance treatment.
Unno, Masayoshi*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Fukuyama, Keiichi*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 57(5), p.297 - 303, 2015/10
Bilin compounds are fundamentally important for oxygenic photosynthetic organisms, because they are utilized as pigments for photosynthesis (phycobilins) and photoreceptors (phytochromobilin). Phycocyanobilin (PCB), a phycobilin, comprises the chromophore of algal phytochromes and the core phycobiliprotein antennae of cyanobacteria and red algae. PCB is biosynthesized by a member of the ferredoxin-dependent bilin reductase family, phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA). In the present study, we determined the neutron crystal structure of PcyA in complex with its substrate biliverdin (BV). This neutron structure revealed the protonation state of BV and the surrounding residues. We found that two forms of BV, neutral BV and protonated BVH , were coupled with the two conformation/protonation states of the essential residue Asp105. Further, His88 and His74 near BV were singly protonated and were connected with an intervening hydronium ion. Neutron analysis also revealed how X-ray irradiation of the PcyA-BV crystal altered the structure of the PcyA-BV complex.
, were coupled with the two conformation/protonation states of the essential residue Asp105. Further, His88 and His74 near BV were singly protonated and were connected with an intervening hydronium ion. Neutron analysis also revealed how X-ray irradiation of the PcyA-BV crystal altered the structure of the PcyA-BV complex.
Unno, Masayoshi*; Ishikawa, Kumiko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(16), p.5452 - 5460, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:64.39(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Phycocyanobilin, a light-harvesting and photoreceptor pigment in higher plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is synthesized from biliverdin IX (BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH
(BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH , a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N
, a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H
was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H O
O . These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
. These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
; Omori, Eiichi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Shimoyamada, Tetsuya; Tomiyama, Masahiro; Shimokura, Mitsuharu; Sakuraba, Terumi; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Hagiwara, Masayoshi; et al.
PNC TN8410 98-013, 1028 Pages, 1998/01
None
Kaneko, Yoshihiko; Kawarasaki, Yuki; Kudo, Hiroshi; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Suzuki, Yasuo; Tanaka, Shunichi; Nakamura, Tomoo; Nagashima, Takashi; ; Noda, Kenji; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 32(6), p.578 - 582, 1990/06
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Koki; Koyama, Hayato; Hagiwara, Masayoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kanda, Naoyuki; Hagiwara, Masayoshi; Sakashita, Koichi; Kijima, Jun
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English