Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -rays and internal exposure to
-rays and internal exposure to  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  I
ISato, Tatsuhiko; Manabe, Kentaro; Hamada, Nobuyuki*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 9(6), p.e99831_1 - e99831_10, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.9(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The RBEs of the internal exposure to  Cs,
Cs,  Cs and
Cs and 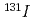 were evaluated on the basis of the microdosimetric analysis.
were evaluated on the basis of the microdosimetric analysis.
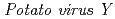 -resistance in the progeny of haploid mutants obtained by the culture of
-resistance in the progeny of haploid mutants obtained by the culture of  L. Anthers exposed to ion beams
L. Anthers exposed to ion beamsHamada, Kentaro*; Inoue, Masayoshi*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Plant Biotechnology, 18(4), p.251 - 257, 2001/04
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Manabe, Kentaro; Hamada, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Biological effectiveness of internal exposure relative to external Exposures was estimated from microdosimetry analysis. It can be concluded from the analysis that the risk from internal exposures to Cs-137, Cs-134, and I-131 should be nearly equivalent to that of external exposure to  -rays at the same absorbed dose level, as suggested in the current recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection.
-rays at the same absorbed dose level, as suggested in the current recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Manabe, Kentaro
no journal, ,
The risk of internal exposure to  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  I is of great public concern after the accident at the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The relative biological effectiveness (RBE, defined herein as effectiveness of internal exposure relative to the external exposure to
I is of great public concern after the accident at the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The relative biological effectiveness (RBE, defined herein as effectiveness of internal exposure relative to the external exposure to  -rays) is occasionally believed to be much greater than unity due to insufficient discussions on the difference of their microdosimetric profiles. We therefore performed a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation in ideally aligned cell systems to calculate the probability densities of absorbed doses in subcellular and intranuclear scales for internal exposures to electrons emitted from
-rays) is occasionally believed to be much greater than unity due to insufficient discussions on the difference of their microdosimetric profiles. We therefore performed a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation in ideally aligned cell systems to calculate the probability densities of absorbed doses in subcellular and intranuclear scales for internal exposures to electrons emitted from  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  I, as well as the external exposure to 662 keV photons. The RBE due to the high ionization density and that for the bystander effect were very close to 1, because the microdosimetric probability densities were nearly identical between the internal exposures and the external exposure from the 662 keV photons. On the other hand, the RBE due to the RI inhomogeneity largely depended on the intranuclear RI concentration and cell size, but their maximum possible RBE was only 1.04 even under conservative assumptions. Thus, it can be concluded from the microdosimetric viewpoint that the risk from internal exposures to
I, as well as the external exposure to 662 keV photons. The RBE due to the high ionization density and that for the bystander effect were very close to 1, because the microdosimetric probability densities were nearly identical between the internal exposures and the external exposure from the 662 keV photons. On the other hand, the RBE due to the RI inhomogeneity largely depended on the intranuclear RI concentration and cell size, but their maximum possible RBE was only 1.04 even under conservative assumptions. Thus, it can be concluded from the microdosimetric viewpoint that the risk from internal exposures to  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  I should be nearly equivalent to that of external exposure to
I should be nearly equivalent to that of external exposure to  -rays at the same absorbed dose level, as suggested in the current recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection.
-rays at the same absorbed dose level, as suggested in the current recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection.