Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuru, Tomohito; Lobzenko, I.; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Han, W.-Z.*
Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 28, p.1013 - 1021, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Some solute atoms induce hardening and embrittlement in body-centered-cubic refractory metals. Especially interstitial oxygen has a dramatic hardening effect in Nb, where the yield stress of oxygen-doped Nb alloys becomes more than twice as high as that of pure Nb. Conventional mechanisms cannot explain the oxygen-induced dramatic hardening since the interaction between dislocation and oxygen is relatively weak. Here, we focused on the three-body interaction of a screw dislocation with oxygen and vacancy. Our first-principles calculations revealed that the formation of vacancy-oxygen pair enhances the attractive interaction with a screw dislocation though the interaction between oxygen and dislocation is repulsive. Furthermore, this feature was found to be a unique nature of oxygen in Nb. The vacancy-oxygen pair increases the energy barrier for dislocation motion more significantly than an isolated vacancy and oxygen interstitial. We have discovered a new oxygen-induced mechanism: a unique octahedral-tetrahedral shuffling process of oxygen dominantly contributes to the dramatic hardening. Thus, the widely distributed vacancy-oxygen pairs behave as strong obstacles for dislocation motion that causes damage accumulation and successive hardening in oxygen-doped BCC alloys.
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Kang, Y.-G.*; Avdeev, M.*; Sibille, R.*; Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Lee, K. H.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.8346_1 - 8346_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Ramadhan, R. S.*; Glaser, D.*; Soyama, Hitoshi*; Kockelmann, W.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Pirling, T.*; Fitzpatrick, M. E.*; Tremsin, A. S.*
Acta Materialia, 239, p.118259_1 - 118259_12, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Grsic, Z.*; Halsall, C.*; Heinrich, G.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Ku a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2001, 226 Pages, 2022/06
The IAEA organized a programme from 2012 to 2015 entitled Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA), which aimed to improve capabilities in the field of environmental radiation dose assessment by acquiring improved data, model testing and comparison of model inputs, assumptions and outputs, reaching a consensus on modelling philosophies, aligning approaches and parameter values, developing improved methods and exchanging information. This publication describes the activities of Working Group 2, Exposures in Contaminated Urban Environments and Effect of Remedial Measures.
Thiessen, K. M.*; Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Federspiel, L.; Gra i
i , B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
, B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020502_1 - 020502_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.52(Environmental Sciences) /La
/La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO heterostructures
heterostructuresZhang, J.*; Chen, M.*; Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Wang, H.*; Hamdi, M.*; Sun, Y.*; Wagner, K.*; He, W.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.7258_1 - 7258_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:77.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Yao, Y.*; Cai, R.*; Yang, S.-H.*; Xing, W.*; Ma, Y.*; Mori, Michiyasu; Ji, Y.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Xie, X.-C.*; Han, W.*
Physical Review B, 104(10), p.104414_1 - 104414_6, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) sp
sp HRL LTDE-SD experiments
HRL LTDE-SD experimentsSoler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-20-17, 71 Pages, 2021/07
Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
 clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter
clusters in dilute neutron-rich matterTanaka, Junki*; Yang, Z.*; Typel, S.*; Adachi, Satoshi*; Bai, S.*; van Beek, P.*; Beaumel, D.*; Fujikawa, Yuki*; Han, J.*; Heil, S.*; et al.
Science, 371(6526), p.260 - 264, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:99.12(Multidisciplinary Sciences)By employing quasi-free  -cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of
-cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of  clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between
clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between  -cluster formation and the neutron skin.
-cluster formation and the neutron skin.
Oyanagi, Koichi*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Cornelissen, L. J.*; Shan, J.*; Daimon, Shunsuke*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Van Wees, B. J.*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.4740_1 - 4740_6, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:89.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Han, W.*; Chen, B. J.*; Gu, B.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; 14 of others*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.7490_1 - 7490_6, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.92(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yang, P.-J.*; Li, Q.-J.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Zhang, J.-W.*; Sheng, H.-W.*; Shan, Z.-W.*; Sha, G.*; Han, W.-Z.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 168, p.331 - 342, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:96.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Body-centred-cubic metallic materials, such as niobium (Nb) and other refractory metals, are prone to embrittlement due to low levels of oxygen solutes. The mechanisms responsible for the oxygen-induced rampant hardening and damage are unclear. Here we illustrate that screw dislocations moving through a random repulsive force field imposed by impurity oxygen interstitials readily form cross-kinks and emit excess vacancies in Nb. The vacancies bind strongly with oxygen and screw dislocation in a three-body fashion, rendering dislocation motion difficult and hence pronounced dislocation storage and hardening. This leads to unusually high strain hardening rates and fast breeding of nano-cavities that underlie damage and failure.
 Pt
PtTsekhanovich, I.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Denis-Petit, D.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Matheson, Z.*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Nazarewicz, W.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 790, p.583 - 588, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:94.9(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Bandodkar, A. J.*; Gutruf, P.*; Choi, J.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Reeder, J. T.*; Jeang, W. J.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Lee, S. P.*; Model, J. B.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 5(1), p.eaav3294_1 - eaav3294_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:446 Percentile:99.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Interest in advanced wearable technologies increasingly extends beyond systems for biophysical measurements to those that enable continuous, non-invasive monitoring of biochemical markers in biofluids. Here, we introduce battery-free, wireless microelectronic platforms that perform sensing via schemes inspired by the operation of biofuel cells. Combining these systems in a magnetically releasable manner with chrono-sampling microfluidic networks that incorporate assays based on colorimetric sensing yields thin, flexible, lightweight, skin-interfaced technologies with broad functionality in sweat analysis. A demonstration device allows simultaneous monitoring of sweat rate/loss, along with quantitative measurements of pH and of lactate, glucose and chloride concentrations using biofuel cell and colorimetric approaches.
Finsterle, S.*; Lanyon, B.*;  kesson, M.*; Baxter, S.*; Bergstr
kesson, M.*; Baxter, S.*; Bergstr m, M.*; Bockg
m, M.*; Bockg rd, N.*; Dershowitz, W.*; Dessirier, B.*; Frampton, A.*; Fransson,
rd, N.*; Dershowitz, W.*; Dessirier, B.*; Frampton, A.*; Fransson,  .*; et al.
.*; et al.
Geological Society, London, Special Publications, No.482, p.261 - 283, 2019/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:70.92(Geology)Nuclear waste disposal in geological formations relies on a multi-barrier concept that includes engineered components which in many cases includes a bentonite buffer surrounding waste packages and the host rock. An SKB's (Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.) Modelling Task Force project facilitated to improve the overall understanding of rock - bentonite interactions, as 11 teams used different conceptualisations and modelling tools to analyse the in-situ experiment at the  ps
ps Hard Rock Laboratory. The exercise helped identify conceptual uncertainties that led to different assessments of the relative importance of the engineered and natural barrier subsystems and of aspects that need to be better understood to arrive at reliable predictions of bentonite wetting.
Hard Rock Laboratory. The exercise helped identify conceptual uncertainties that led to different assessments of the relative importance of the engineered and natural barrier subsystems and of aspects that need to be better understood to arrive at reliable predictions of bentonite wetting.
Phan, L. H. S.*; Ohara, Yohei*; Kawata, Ryo*; Liu, X.*; Liu, W.*; Morita, Koji*; Guo, L.*; Kamiyama, Kenji; Tagami, Hirotaka
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2018/10
Self-leveling behavior of core fuel debris beds is one of the key phenomena for the safety assessment of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The SIMMER code has been developed for CDA analysis of SFRs, and the code has been successfully applied to numerical simulations for key thermal-hydraulic phenomena involved in CDAs as well as reactor safety assessment. However, in SIMMER's fluid-dynamics model, it is always difficult to represent the strong interactions between solid particles as well as the discrete particle characteristics. To solve this problem, a new method has been developed by combining the multi-fluid model of the SIMMER code with the discrete element method (DEM) for the solid phase to reasonably simulate the particle behaviors as well as the fluid-particle interactions in multi-phase flows. In this study, in order to validate the multi-fluid model of the SIMMER code coupled with DEM, numerical simulations were performed on a series of self-leveling experiments using a gas injection method in cylindrical particle beds. The effects of friction coefficient on the simulation results were investigated by sensitivity analysis. Though more extensive validations are needed, the reasonable agreement between simulation results and corresponding experimental data preliminarily demonstrates the potential ability of the present method in simulating the self-leveling behaviors of debris bed. It is expected that the SIMMER code coupled with DEM is a prospective computational tool for analysis of safety issues related to solid particle debris bed in SFRs.
Tang, C.*; Song, Q.*; Chang, C.-Z.*; Xu, Y.*; Onuma, Yuichi; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Liu, Y.*; Yuan, W.*; Yao, Y.*; Moodera, J. S.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 4(6), p.eaas8660_1 - eaas8660_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:84.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Zr(
Zr( )
)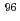 Zr cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on
Zr cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on  -process nucleosynthesis
-process nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Karakas, A. I.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mohr, P.*; Su, J.*; Li, Y. J.*; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 848(2), p.98_1 - 98_8, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)