Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Minamikawa, Takuya*; Gao, B.*; Kojo, Toru*; Harada, Masayasu*
Symmetry (Internet), 15(3), p.745_1 - 745_30, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Harada, Takuya*; Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori
Chigaku Zasshi, 132(1), p.57 - 65, 2023/02
The Harachiyama Formation is Lower Cretaceous volcanic rocks, distributed in the eastern margin of the Kitakami Mountains in northeastern Japan. We performed whole-rock chemical analysis, zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analysis from the Harachiyama Formation to constrain the formation age and discuss the origin of magma. The lava and tuff samples of the Harachiyama Formation from the Omoto and Tsukue areas support island-arc rhyolitic rocks (SiO content
content  70%), and yielded the weighted mean U-Pb ages of 127.8
70%), and yielded the weighted mean U-Pb ages of 127.8  3.4 Ma and 129.2
3.4 Ma and 129.2  2.6 Ma (2
2.6 Ma (2 ), respectively. Eighteen zircon grains from two samples, dated between 141.6 Ma and 123.9 Ma, yielded positive
), respectively. Eighteen zircon grains from two samples, dated between 141.6 Ma and 123.9 Ma, yielded positive  Hf(t) values between +5.0 and +8.7. These ages and values are consistent with those of the Kitakami Granititods reported in previous studies. Therefore, it is suggested that the Harachiyama Formation have the same magmatic origin as the Kitakami Granitoid.
Hf(t) values between +5.0 and +8.7. These ages and values are consistent with those of the Kitakami Granititods reported in previous studies. Therefore, it is suggested that the Harachiyama Formation have the same magmatic origin as the Kitakami Granitoid.
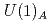 anomaly on nuclear and neutron star equation of state based on a parity doublet model
anomaly on nuclear and neutron star equation of state based on a parity doublet modelGao, B.*; Minamikawa, Takuya*; Kojo, Toru*; Harada, Masayasu*
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.065205_1 - 065205_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kikkawa, Nobuaki*; Yoneyama, Hiroaki*; Takahashi, Naoko*; Minami, Saori*; Akimoto, Yusuke*; Mitsuoka, Takuya*; Kawaura, Hiroyuki*; Harada, Masashi*; Yamada, Norifumi*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 14(48), p.53744 - 53754, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.75(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 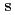 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 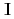 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 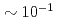 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (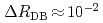 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Uchiya, Naoyuki*; Harada, Takuya*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Haga, Junji; Sakai, Takuro; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Uchiya, Naoyuki*; Harada, Takuya*; Murai, Masato*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Haga, Junji; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sakai, Takuro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsui, Hiroki; Toyokawa, Takuya; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Akio; Kurosaki, Ken*; Konashi, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Harada, Masahide; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Okudaira, Takuya*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Ino, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
In neutron fundamental physics, a study of correlation term  of a neutron spin s and a target nuclear spin
of a neutron spin s and a target nuclear spin 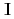 is important because the
is important because the  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving (TRNC) terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving (TRNC) terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 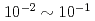 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We attempted to develop a polarized Xe target in a compact
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We attempted to develop a polarized Xe target in a compact  SEOP system and measure neutron polarizing ability caused by the
SEOP system and measure neutron polarizing ability caused by the  term at a 9.6 eV
term at a 9.6 eV  -wave resonance peak of
-wave resonance peak of  Xe, by detecting change
Xe, by detecting change 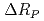 of a ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. As preliminary results, we observed a signified value of
of a ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. As preliminary results, we observed a signified value of 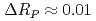 after demonstrating that our apparatus could distinguish Doppler broadening effect as systematic error.
after demonstrating that our apparatus could distinguish Doppler broadening effect as systematic error.