Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Gulden, W.*; Watanabe, Kazuhito*; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Matsumiya, Hisato*; Ishii, Kyoko*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2028 - 2032, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident, a social need for assuring safety of fusion energy has grown gradually in the Japanese (JA) fusion research community. DEMO safety research has been launched as a part of BA DEMO Design Activities (BA-DDA). This paper reports progress in the fusion DEMO safety research conducted under BA-DDA. Safety requirements and evaluation guidelines have been, first of all, established based on those established in the Japanese ITER site invitation activities. The amounts of radioactive source terms and energies that can mobilize such source terms have been assessed for a reference DEMO, in which the blanket technology is based on the Japanese fusion technology R&D programme. Reference event sequences expected in DEMO have been analyzed based on the master logic diagram and functional FMEA techniques. Accident initiators of particular importance in DEMO have been selected based on the event sequence analysis.
Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Gulden, W.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Watanabe, Kazuhito*; Matsumiya, Hisato*; Ishii, Kyoko*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9, p.1405139_1 - 1405139_11, 2014/10
Key aspects of the safety study of a water-cooled fusion DEMO reactor is reported. Safety requirements, dose target, DEMO plant model and confinement strategy of the safety study are briefly introduced. The internal hazard of a water-cooled DEMO, i.e. radioactive inventories, stored energies that can mobilize these inventories and accident initiators and scenarios, are evaluated. It is pointed out that the enthalpy in the first wall/blanket cooling loops, the decay heat and the energy potentially released by the Be-steam chemical reaction are of special concern for the water-cooled DEMO. An ex-vessel loss-of-coolant of the first wall/blanket cooling loop is also quantitatively analyzed. The integrity of the building against the ex-VV LOCA is discussed.
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Kazuo; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tokuda, Shinji
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.1138 - 1142, 2009/09
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:139 Percentile:97.7(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
 B
B C
CNagai, Yuki*; Kato, Yusuke*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Yamauchi, Kunihiko*; Harima, Hisatomo*
Physical Review B, 76(21), p.214514_1 - 214514_8, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:60.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To determine the superconducting gap function of YNi B
B C, we calculate the local density of states around a single vortex core with the use of Eilenberger theory and the band structure calculated by local density approximation, assuming various gap structures with point nodes at different positions. We also calculate the angular-dependent heat capacity in the vortex state on the basis of the Doppler-shift method. Comparing our results with the scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy experiment, the angular-dependent heat capacity and thermal conductivity, we propose the gap structure of YNi
C, we calculate the local density of states around a single vortex core with the use of Eilenberger theory and the band structure calculated by local density approximation, assuming various gap structures with point nodes at different positions. We also calculate the angular-dependent heat capacity in the vortex state on the basis of the Doppler-shift method. Comparing our results with the scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy experiment, the angular-dependent heat capacity and thermal conductivity, we propose the gap structure of YNi B
B C, which has the point nodes and gap minima along
C, which has the point nodes and gap minima along 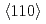 . Our gap structure is consistent with all results of angular-resolved experiments.
. Our gap structure is consistent with all results of angular-resolved experiments.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.892 - 899, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:86.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The concept for a compact DEMO reactor named "SlimCS" is presented. Distinctive features of the concept is low aspect ratio ( = 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low-
= 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low- , i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
, i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Sakurai, Shinji; Fujita, Takaaki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nakano, Tomohide; Kubo, Hirotaka; Higashijima, Satoru; Hayashi, Takao; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 31F, 4 Pages, 2007/00
Divertor design for the JT-60 SA has been progressing in order to handle large heat flux during full pulse duration of 100 s. Divertor should be suitable for single null plasma experiments with the full power injection of 41 MW. The simulation results using 2D fluid (plasma) and Monte-Carlo (neutral) code are summarized. Lower single-null divertor is designed for ITER-like plasma configuration in order to study physics concept of the ITER divertor: control of the plasma detachment. Simulation results for various divertor geometries showed that the vertical target with V-shaped corner can produce plasma detachment near the outer strike-point for medium edge plasma density. It was also demonstrated that the divertor plasma became attached to move the outer strike point above the V-corner, suggesting that recover from sever detachment can be achieved by changing the plasma location. USN divertor will be designed for high- plasma experiments with the highest shaping plasma of S=6.
plasma experiments with the highest shaping plasma of S=6.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Clozel, B.*; Komuro, Kosei; Nakashima, Satoru*; Nagano, Tetsushi*; Masaki, Nobuyuki*; Hayashi, Hisato*
PNC TN6410 92-004, 32 Pages, 1992/03
Rock samples from different world U deposits mainly in sedimentary rocks have been studied by Electron Spin Resonancc (ESR) spectroscopy and Cathodoluminescence (CL) measurement in order to characterize radiation damage centers in clays and quartz. The presence of kaolinite-like radiation centers ill ESR spectra in some of the samples containing kaolin group minerals suggests that this type of radiation damages can be used as an indicator of U behavior during supergene and hydrothermal alteration of U ores. Other clay minerals such as smectite and illite were not found to exhibit radiation damage centers by ESR. CL measurement on quartz grains iadicated the presence of radiation damage rims for the samples containing high U content. These rims can also be recognized for older samples with low U cocentration because of the longer contact of quartz with U. Although much more systematic studies are need for the reconstruction of the U behavior, these two methods have been proven useful for the characterization of radiation damage histories recorded in minerals.
Takizuka, Tomonori; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosokawa, Masanari*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takizuka, Tomonori; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosokawa, Masanari*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Parchamy, H.*; Peterson, B. J.*; Hayashi, Hiromi*; Konoshima, Shigeru; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Seo, D. C.*; Kawashima, Hisato; JT-60 Team
no journal, ,
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Yamada, Masao*; Kakudate, Satoshi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Enoeda, Mikio; Tsuru, Daigo; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Maintenance is one of critical issues that determines the torus configuration of a fusion reactor. For high availability of operation, in-vessel components should be replaceable easily. On the other hand, the in-vessel components must be supported robustly enough to withstand the electromagnetic forces acting on a disruption. In addition, the fraction of the structural material of blanket should be reduced to keep the breeding region high as possible. In order to meet these requirements, JAEA has attempted to find a sector transport maintenance scheme based on the existing technologies in industries. Possible ideas on transportation of the sector, cask and support structure of toroidal field coils for the sector transport maintenance will be presented.
Sakurai, Shinji; Higashijima, Satoru; Kawashima, Hisato; Shibama, Yusuke; Hayashi, Takao; Ozaki, Hidetsugu; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Masaki, Kei; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Ide, Shunsuke; et al.
no journal, ,
Lower single null closed divertor with vertical target will be installed at the start of the experiment phase for JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA). Reproducibility of brazed CFC (carbon fiber composite) monoblock targets for a divertor target has been significantly improved by precise control of tolerances and metallization inside CFC blocks. Divertor cassette with fully water cooled plasma facing components and remote handling (RH) system shall be employed to allow long pulse high performance discharges with large neutron yield and they are designed compatible with limited position and size of maintenance ports. Static structural analysis for dead weight, coolant pressure and electromagnetic forces shows that displacement and stress in the divertor module are generally small.
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
no journal, ,