Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ratliff, H.; McGirl, N. A.*; Beach, M. R.*; Castellanos, L. A.*; Clowdsley, M. S.*; Heilbronn, L. H.*; LaTessa, C.*; Norbury, J. W.*; Rusek, A.*; Sivertz, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 542, p.87 - 94, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)Tsai, P.-E.; Heilbronn, L. H.*; Lai, B.-L.*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Sheu, R.-J.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 449, p.62 - 70, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)The secondary neutrons produced from 100- and 230-MeV/nucleon He ions, respectively, stopping in the thick iron, PMMA and water targets are measured by the time of flight method combined with the pulse shape discrimination of liquid scintillators. The experimental data show that the secondary neutrons were contributed from breakup of projectiles, emission from overlap regions of projectile nuclei and target nuclei, and evaporation of projectiles and target nuclei. The measured double-differential thick target neutron yields, angular distributions, and total neutron yields per ion, were benchmarked by the PHITS, FLUKA, and MCNP model calculations. The default models in these codes agree the experimental data well at intermediate-to-large angles in the low-to-intermediate energy range. However, the physics models implemented in PHITS need further improvement for some particular nuclear interaction mechanisms, and this work can be an importance reference for future model development.
Tsai, P.-E.; Lai, B.-L.*; Heilbronn, L. H.*; Sheu, R.-J.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 416, p.16 - 29, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fifteen thin target experiments were selected for this benchmark study of the neutron production cross sections. The studied cases include a mix combination of  C,
C,  Ne
Ne  Ar,
Ar, 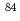 Kr, and
Kr, and  Xe ions bombarding
Xe ions bombarding  Li,
Li,  C,
C,  Al,
Al,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Pb target with projectile energies between 135 and 600 MeV/nucleon. The experimental data were compared to the model calculations performed by (1) PHITS version 2.73 with JQMD and GEM model, (2) PHITS version 2.82 with revised JQMD 2.0 and GEM model, (3) FLUKA version 2011.2c with RQMD 2.4 and FLUKA's own de-excitation model, and (4) MCNP6 version 1.0 with LAQGSM 03.03 and GEM2 model. This study provides useful information not only for code users but also for model developers, and it will lead to future improvements of the PHITS - JQMD model for heavy-ion induced reactions, which is important for accelerator facilities, heavy-ion radiotherapy, and space radiation.
Pb target with projectile energies between 135 and 600 MeV/nucleon. The experimental data were compared to the model calculations performed by (1) PHITS version 2.73 with JQMD and GEM model, (2) PHITS version 2.82 with revised JQMD 2.0 and GEM model, (3) FLUKA version 2011.2c with RQMD 2.4 and FLUKA's own de-excitation model, and (4) MCNP6 version 1.0 with LAQGSM 03.03 and GEM2 model. This study provides useful information not only for code users but also for model developers, and it will lead to future improvements of the PHITS - JQMD model for heavy-ion induced reactions, which is important for accelerator facilities, heavy-ion radiotherapy, and space radiation.
Mancusi, D.*; Sihver, L.*; Gustafsson, K.*; La Tessa, C.*; Guetersloh, S.*; Zeitlin, C.*; Miller, J.*; Heilbronn, L.*; Niita, Koji*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 254(1), p.30 - 38, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:73.75(Instruments & Instrumentation)The PHITS code is a three-dimensional Monte Carlo code that is able to simulate the transport of nuclei and other particles in complicated geometries. As a part of a comprehensive benchmarking program, we have investigated the possibility of using PHITS to calculate partial charge-changing cross sections and we have compared the results with measurements. The results suggest that the current reaction-cross-section models might be inadequate for use in space radiation protection: We therefore claim the need for a thorough benchmarking of the models and for new reaction-cross-section measurements and experimental techniques.
Tsai, P.-E.; Heilbronn, L.*; Lai, B. L.*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Sheu, R.-J.*
no journal, ,
The thick target neutron yields from 100- and 230-MeV/nucleon helium ions bombarding water, PMMA, and iron targets were measured by using the time-of-flight technique at 0 to 121
to 121 . The experimental data were compared with INCL-4.6, RQMD, and ISABEL model calculations respectively by the PHITS, FLUKA, and MCNP6 codes. The model calculations of the neutron yields generally agree with the measurements, especially in the intermediate and low energy regions at angles at and above 30 degrees. However, some disagreements exist not only between the data and the simulations but also between models. The benchmark results will be used for further improvement of the PHITS code in the future.
. The experimental data were compared with INCL-4.6, RQMD, and ISABEL model calculations respectively by the PHITS, FLUKA, and MCNP6 codes. The model calculations of the neutron yields generally agree with the measurements, especially in the intermediate and low energy regions at angles at and above 30 degrees. However, some disagreements exist not only between the data and the simulations but also between models. The benchmark results will be used for further improvement of the PHITS code in the future.
Tsai, P.-E.; Lai, B. L.*; Heilbronn, L.*; Sheu, R.-J.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko
no journal, ,
Fifteen thin target experiments were selected for this benchmark study of the neutron production cross sections. The studied cases include a mix combination of  C,
C,  Ne
Ne  Ar,
Ar, 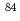 Kr, and
Kr, and  Xe ions bombarding
Xe ions bombarding  Li,
Li,  C,
C,  Al,
Al,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Pb target with projectile energies between 135 and 600 MeV/nucleon. The experimental data were compared to the model calculations performed by (1) PHITS version 2.73 with JQMD and GEM model, (2) PHITS version 2.82 with revised JQMD 2.0 and GEM model, (3) FLUKA version 2011.2c with RQMD 2.4 and FLUKA's own de-excitation model, and (4) MCNP6 version 1.0 with LAQGSM 03.03 and GEM2 model. This study provides useful information not only for code users but also for model developers, and it will lead to future improvements of the PHITS - JQMD model for heavy-ion induced reactions, which is important for accelerator facilities, heavy-ion radiotherapy, and space radiation.
Pb target with projectile energies between 135 and 600 MeV/nucleon. The experimental data were compared to the model calculations performed by (1) PHITS version 2.73 with JQMD and GEM model, (2) PHITS version 2.82 with revised JQMD 2.0 and GEM model, (3) FLUKA version 2011.2c with RQMD 2.4 and FLUKA's own de-excitation model, and (4) MCNP6 version 1.0 with LAQGSM 03.03 and GEM2 model. This study provides useful information not only for code users but also for model developers, and it will lead to future improvements of the PHITS - JQMD model for heavy-ion induced reactions, which is important for accelerator facilities, heavy-ion radiotherapy, and space radiation.
Ratliff, H.; McGirl, N.*; Castellanos, L.*; Wang, H.-C.*; Srikrishna, A.*; Heilbronn, L.*
no journal, ,