Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
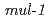 , induced by ionizing radiation in
, induced by ionizing radiation in 
Kimura, Takafumi*; Takanami, Takako*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Higashitani, Atsushi*
Radiation Research, 178(4), p.313 - 320, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:41.9(Biology)Here, we found that exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) induce certain innate immune response gene of 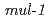 in the intestine. Pre-treatment with IR before seeding on
in the intestine. Pre-treatment with IR before seeding on 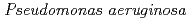 lawn plate, significantly increased survival rate in the nematode. IR induction of
lawn plate, significantly increased survival rate in the nematode. IR induction of 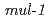 gene was highly dependent on the ELT-2 transcription factor and p38 MAPK. Moreover, the insulin/IGF-1 signal pathway works as an enhancer of induction of this gene. Silencing of the
gene was highly dependent on the ELT-2 transcription factor and p38 MAPK. Moreover, the insulin/IGF-1 signal pathway works as an enhancer of induction of this gene. Silencing of the 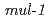 gene led to growth retardation after IR irradiation. Finally, we describe the cross-tolerance between the responses to radiation exposure and innate immune system.
gene led to growth retardation after IR irradiation. Finally, we describe the cross-tolerance between the responses to radiation exposure and innate immune system.
 ; Germ cell response, aging and behavior
; Germ cell response, aging and behaviorSakashita, Tetsuya; Takanami, Takako*; Yanase, Sumino*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Kimura, Takafumi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ishii, Naoaki*; Higashitani, Atsushi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(2), p.107 - 121, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:63.91(Biology)The study of radiation effect in 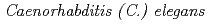 have been carried out over three decades and now allow for understanding at the molecular, cellular and individual levels. This review describes the current knowledge of the biological effects of ionizing irradiation with a scope of the germ line, aging and behavior.
have been carried out over three decades and now allow for understanding at the molecular, cellular and individual levels. This review describes the current knowledge of the biological effects of ionizing irradiation with a scope of the germ line, aging and behavior.  may be a good
may be a good  model system in the field of radiation biology.
model system in the field of radiation biology.

Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yanase, Sumino*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Oba, Hirofumi; Higashitani, Atsushi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Fukamoto, Kana; Tsuji, Toshio*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(2), p.119 - 125, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:29.52(Biology)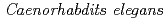
Higashitani, Atsushi*; Mori, Chihiro*; Kimura, Takafumi*; Ikenaga, Takahiko*; Takanami, Takako*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 112, 2008/03
We investigated the gene expression of  following carbon and
following carbon and  irradiation using DNA microarray analysis. We observed the 187 and 297 upregulated genes after
irradiation using DNA microarray analysis. We observed the 187 and 297 upregulated genes after  and carbon irradiation with 100 Gy, respectively, in which 51 genes were upregulated following both irradiations. On the other hand, the 358 and 388 genes were downregulated after
and carbon irradiation with 100 Gy, respectively, in which 51 genes were upregulated following both irradiations. On the other hand, the 358 and 388 genes were downregulated after  and carbon irradiation, respectively.
and carbon irradiation, respectively.

Higashitani, Atsushi*; Sugimoto, Tomoko*; Mori, Chihiro*; Suzuki, Yoko*; Saito, Rumiko*; Ichishi, Eiichiro*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 113, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
 germline cells following heavy-ion microbeam irradiation
germline cells following heavy-ion microbeam irradiationSugimoto, Tomoko*; Dazai, Kumiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Higashitani, Atsushi*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 82(1), p.31 - 38, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:93.12(Biology)no abstracts in English

Maehira, Takahiro; Higashitani, Atsushi*; Higuchi, Masahiko*; Yasuhara, Hiroshi*; Hasegawa, Akira*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 312-313(1-4), p.103 - 105, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:53.21(Physics, Condensed Matter)UBe is a typical heavy-fermion superconductor compound. The lowtemperature electronic specific heat coefficient has the anomalous large value,
is a typical heavy-fermion superconductor compound. The lowtemperature electronic specific heat coefficient has the anomalous large value, 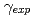 =1.1J/K
=1.1J/K mol, which is the largest among the heavy fermion uranium compounds. It also becomes the superconductor below T
mol, which is the largest among the heavy fermion uranium compounds. It also becomes the superconductor below T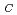 =0.85K. Therefore, UBe
=0.85K. Therefore, UBe is an important material as a strongly correlated electron system, and it is necessary to study from both sides of the theory and the experiment. The measurement suggests that the Fermi surface of UBe
is an important material as a strongly correlated electron system, and it is necessary to study from both sides of the theory and the experiment. The measurement suggests that the Fermi surface of UBe may consist of small sheets. The energy band structure and the Fermi surface for UBe
may consist of small sheets. The energy band structure and the Fermi surface for UBe are calculated by the relativistic linear APW method.
are calculated by the relativistic linear APW method.
 germ cell development
germ cell developmentHigashitani, Atsushi*; Sugimoto, Tomoko*; Dazai, Kumiko*; Mori, Chihiro*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Mori, Chihiro*; Sugimoto, Tomoko*; Dazai, Kumiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ichishi, Eiichiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Higashitani, Atsushi*; Mori, Chihiro*; Sugimoto, Tomoko*; Dazai, Kumiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 using heavy-ion microbeam
using heavy-ion microbeamSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ikeda, Daisuke*; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanase, Sumino*; Higashitani, Atsushi*; Ishii, Naoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Using  as a model multicellular organism, we push forward a heavy-ion microbeam irradiation individual-study. As for about 1.2 mm in a range of carbon ions in water, all cells and tissues of
as a model multicellular organism, we push forward a heavy-ion microbeam irradiation individual-study. As for about 1.2 mm in a range of carbon ions in water, all cells and tissues of  are microbeam irradiation objects. Sugimoto et al. showed DNA-damage-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in locally irradiated areas of
are microbeam irradiation objects. Sugimoto et al. showed DNA-damage-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in locally irradiated areas of  . We focus the nervous system of
. We focus the nervous system of  and study the effects of localized irradiation on salt chemotaxis learning behavior. However, the anesthetic method for fixation of animals is not usable because the whole body irradiation of
and study the effects of localized irradiation on salt chemotaxis learning behavior. However, the anesthetic method for fixation of animals is not usable because the whole body irradiation of  Co
Co  rays affected only transition stage of the conditioning for salt chemotaxis learning. Thus, now we are constructing the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation system for living target
rays affected only transition stage of the conditioning for salt chemotaxis learning. Thus, now we are constructing the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation system for living target  .
.