Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shirai, Nobutoshi; Miura, Yasushi; Tachibana, Ikuya; Omori, Satoru; Wake, Junichi; Fukuda, Kazuhito; Nakano, Takafumi; Nagasato, Yoshihiko
JAEA-Technology 2016-007, 951 Pages, 2016/07
The periodic safety review of TRP is to confirm the safety activities and get effective additional measures the facility safety and its reliability. We implemented 4 items; for (1) evaluation of safety activity implementation, we confirmed we are adequately expanding its safety activities by the necessary documents and schemes. For (2) evaluation of status of safety activities reflecting the latest technical knowledges, we confirmed we reflect latest knowledges for improvement of safety and reliability. For (3) technical evaluation about aging degradation, we can keep the safety of the facilities important to safety and the sea discharge line, under assumption of the present maintenance, because of "focuses for aging degradation". For (4) planning measures about a 10-years-plan that the operator shall implement to keep the facility condition, by the technical evaluation, we found no additional safety plans into maintenance strategies.
Sugawara, Takanori; Kodama, Yasuhiro*; Nishihara, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-016, 27 Pages, 2015/10
The general-purpose reactor analysis code system, MARBLE, has been used to calculate neutron transport and burn-up calculations for Accelerator-Driven System (ADS). In the burn-up calculation of MARBLE, fission product (FP) nuclides had been treated as lump FP in the past. It meant that MARBLE was unable to treat residual nuclides such as rare-earth ones which would be generated by the fuel exchange of the ADS. To treat residual nuclides, ORIGEN2, which was one of the most famous burn-up calculation codes was implemented to MARBLE. By the implementation of ORIGEN2 code, it was available to treat FP nuclides by each nuclide and to consider the residual nuclides in the ADS burn-up calculation.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Jin, Tomoyuki; Hirai, Yasushi*; Hazama, Taira
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-009, 120 Pages, 2015/07
The second version of the versatile reactor analysis code system, MARBLE2, has been developed. A lot of new functions have been added inMARBLE2 by using the base technology developed in the first version (MARBLE1). Introducing the remaining functions of the conventional code system (JOINT-FR and SAGEP-FR), MARBLE2 enables one to execute almost all analysis functions of the conventional code system with the unified user interfaces of its subsystem, SCHEME. In particular, the sensitivity analysis functionality is available in MARBLE2. On the other hand, new built-in solvers have been developed, and existing ones have been upgraded. Furthermore, some other analysis codes and libraries developed in JAEA have been consolidated and prepared in SCHEME. In addition, several analysis codes developed in the other institutes have been additionally introduced as plug-in solvers. Consequently,  -ray transport calculation and heating evaluation become available. As for another subsystem, ORPHEUS, various functionality updates and speed-up techniques have been applied based on user experience of MARBLE1 to enhance its usability.
-ray transport calculation and heating evaluation become available. As for another subsystem, ORPHEUS, various functionality updates and speed-up techniques have been applied based on user experience of MARBLE1 to enhance its usability.
Sugawara, Takanori; Hirai, Yasushi*; Nishihara, Kenji; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Sambuu, O.*; Ushio, Tadashi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-024, 86 Pages, 2015/02
To investigate an Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) with sub-criticality control mechanism such as control rods or burnable poison, the ADS3D code has been developed on MARBLE which is a next generation reactor analysis code system developed by JAEA. In the past neutronics calculation for the ADS, JAEA employed RZ calculation models to realize efficient investigations. However, it was very difficult to model sub-criticality control mechanisms in RZ calculation models. The ADS3D code system is available to calculate the transportation of protons and neutrons, the burn-up calculation and the fuel exchange in three-dimensional calculation models. It means this code system can treat ADS concepts with sub-criticality control mechanism and makes it possible to investigate a new concept of ADS.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Iwai, Takehiko*; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Hazama, Taira; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Chiba, Go; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-030, 148 Pages, 2011/03
A next generation reactor analysis code system, MARBLE, has been developed. MARBLE is a successor of the fast reactor neutronics analysis code systems, JOINT-FR and SAGEP-FR (conventional system), which were developed for so-called JUPITER standard analysis methods. MARBLE has the equivalent analysis capability to the conventional system. On the other hand, burnup analysis functionality for power reactors as improved compared with the conventional system. In the development of MARBLE, the object oriented technology was adopted. As a result, MARBLE became an assembly of components for building an analysis code (i.e. framework) but not an independent analysis code system which simply receives input and returns output. Furthermore, MARBLE provides some pre-built analysis code systems such as the fast reactor neutronics analysis code system, SCHEME, which corresponds to the conventional code and the fast reactor burnup analysis code system, ORPHEUS.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-015, 218 Pages, 2010/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency promotes development of innovative analysis methods and models in fundamental studies for next-generation nuclear reactor systems. In order to efficiently and effectively reflect the latest analysis methods and models to primary design of prototype reactor and/or in-core fuel management for power reactors, a next-generation analysis system MARBLE has been developed. In the present study, functionalities for debugging have been enhanced by preparing an error handling mechanism in order to provide higher level of usability for users of the framework. Other functionalities have been also developed to deal with complex calculation routes with corrections such as analysis of critical experiments by introducing a mechanism for flexible handling of computational procedures.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-016, 92 Pages, 2010/10
Development of burnup analysis system for fast reactors with modularity and flexibility is being done that would contribute to actual core design work and improvement of prediction accuracy. In this fiscal year the present study, by extending the prototype system, features for handling of control rods and energy collapse of group constants have been designed and implemented. In addition, a mechanism for database management has been developed by extending the idea on restart files in order to help user easily access arbitrary data of the results.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 13(7), p.071304_1 - 071304_7, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:79.43(Physics, Nuclear)A laser-driven repetition-rated 1.9 MeV proton beam line composed of permanent quadrupole magnets (PMQs), a radio frequency (rf) phase rotation cavity, and a tunable monochromator is developed to evaluate and to test the simulation of laser-accelerated proton beam transport through an integrated system for the first time. In addition, the proton spectral modulation and focusing behavior of the rf phase rotationcavity device is monitored with input from a PMQ triplet. In the 1.9 MeV region we observe very weakproton defocusing by the phase rotation cavity. The final transmitted bunch duration and transverse profile are well predicted by the PARMILA particle transport code. The transmitted proton beam duration of 6 ns corresponds to an energy spread near 5% for which the transport efficiency is simulated to be 10%. The predictive capability of PARMILA suggests that it can be useful in the design of future higher energy transport beam lines as part of an integrated laser-driven ion accelerator system.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.88 - 90, 2010/05
The concept of a compact ion particle accelerator has become attractive in view of recent progress in laser-driven ion acceleration. We report here the recent progress in the laser-driven proton beam transport at the Photo Medical Research Center (PMRC) at JAEA, which is established to address the challenge of laser-driven ion accelerator development for ion beam cancer therapy.
 Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O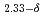 through
through  neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 K
neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 KIto, Takanori*; Hirai, Takene*; Yamashita, Junichi*; Watanabe, Shoji*; Kawata, Etsuya*; Kitamura, Naoto*; Idemoto, Yasushi*; Igawa, Naoki
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 405(8), p.2091 - 2096, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:55.02(Physics, Condensed Matter)We analyze the mechanism of oxygen ion diffusion in (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O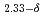 by using the Rietveld refinement, the maximum entropy method (MEM) analysis, and MEM-based pattern fitting (MPF) with
by using the Rietveld refinement, the maximum entropy method (MEM) analysis, and MEM-based pattern fitting (MPF) with  neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 K. We speculate that when
neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 K. We speculate that when 
 and neutron scattering density of O1(4
and neutron scattering density of O1(4 ) site with a large number of vacancies metamorphose into that with anisotropy directed toward the O1(4
) site with a large number of vacancies metamorphose into that with anisotropy directed toward the O1(4 ) and O2(8
) and O2(8 ) sites at 720 K, the oxygen ions diffuse along the paths between O1(4
) sites at 720 K, the oxygen ions diffuse along the paths between O1(4 ) and O1(4
) and O1(4 ), and O1(4
), and O1(4 ) and O2(8
) and O2(8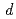 ).
).
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-016, 100 Pages, 2010/02
Development of burnup analysis system for fast reactors with modularity and flexibility is being done that would contribute to actual core design work and improvement of prediction accuracy. In the present study, we implemented functions for cell calculations and burnup calculations. With this, whole steps in analysis can be carried out with only this system. In addition, we modified the specification of user input to improve the convenience of this system. Since implementations being done so far had some bottlenecks to be resolved; we have realized the improvement on efficiency and amount of memory usage with modification on actual implementation.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-012, 208 Pages, 2010/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency promotes development of innovative analysis methods and models in fundamental studies for next-generation nuclear reactor systems. In order to efficiently and effectively reflect the latest analysis methods and models to primary design of prototype reactor and/or in-core fuel management for power reactors, a next-generation analysis system MARBLE has been developed. In the present study, we examined in detail the existing design and implementation of ZPPR critical experiment analysis database followed by unification of models within the framework of the next-generation analysis system by extending to various critical experiment analysis. Furthermore, we examined requirements for functions of analysis results correction which is indispensable for critical analysis system, and designed and implemented an analysis system for various critical experiments including ZPPR.
Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Yokoyama, Kenji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-021, 110 Pages, 2008/10
Development of burnup analysis system for fast reactors with modularity and flexibility is being done that would contribute to actual core design work and improvement of prediction accuracy. In the previous study on "Development of Burnup Analysis System for Fast Reactors (2)" in FY2006, design and implementation of models for detailed geometry of assembly, fuel loading pattern and so on, accompanied with specification and implementation of input file handling to construct data models. In this study, a prototype system has been implemented in which functionalities are embedded for calculation of macroscopic cross section, core calculation and burnup calculation applying the fruits of the study "Development of a Framework for the Neutronics Analysis System for Next Generation (2)". It also implements a fuel reloading/shuffling function controlled with simple description in user input for multi-cycle burnup analysis.
Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-020, 188 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency promotes development of innovative analysis methods and models in fundamental studies for next-generation nuclear reactor systems. In order to efficiently and effectively reflect the latest analysis methods and models to primary design of prototype reactor and/or in-core fuel management for power reactors, a next-generation analysis system MARBLE has been developed. In this study, detailed design of a framework, its implementation and tests are conducted so that a Python system layer can drive calculation codes written in C++ and/or Fortran. It is confirmed that various type of calculation codes such as diffusion, transport and burnup codes can be treated in the same manner on the platform for unified management system for calculation codes with a data exchange mechanism for abstracted data model between the Python and the calculation code layers.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hirai, Yasushi*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Chiba, Go; Hazama, Taira; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Ishikawa, Makoto
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
A development project of the next generation neutronics analysis code system, MARBLE, has been launched in JAEA. A software platform and common data models for fast reactor neutronics analysis were developed to realize the new system. At present, a fast reactor burnup calculation system, ORPHEUS, has been implemented in the MARBLE system. The new system reproduced benchmark results by the conventional code system and it reduced input data preparation works with the help of the capabilities supported by common data model packages. The new system was validated in an analysis of a burnup reactivity coefficient measured in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. These results show that MARBLE/ORPHEUS can be adopted as a new standard neutronics analysis system for fast reactors.
Hirai, Yasushi*; Hyodo, Hideaki*; Tatsumi, Masahiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2007-019, 133 Pages, 2007/11
There is a problem that analysis work tends to become inefficient for lack of functionality suitable for analysis of composition change due to burnup since the conventional analysis system is targeted to critical assembly systems. Therefore development of burnup analysis system for fast reactors with modularity and flexibility can contribute actual core design work and improvement of prediction accuracy. In the previous study on "Development of Burnup Analysis System (for Fast Reactors)" in FY2005, basic design was conducted to define each component in the system(input, solver, edit) and how to drive them. In this study, detailed design of the system and implementation of the I/O component were conducted according to the results in the basic design followed by proto-typing implementation.
Matsuyama, Shinichiro*; Ishii, Katsunori; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Tsuboi, Yasushi*; Kihara, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(3), p.317 - 322, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing vibro-packed fuel as one candidate for commercial fast breeder reactor fuels. In this study, vibro-packing experiments were carried out to investigate particle behavior during vibro-packing and particle distribution after vibro-packing in a cladding tube. Non-spherical uranium dioxide particles and spherical metallic uranium particles were used to simulate mixed oxide particles and oxygen getter particles. These experiments revealed that it is important to feed each size of fuel particles uniformly into a cladding tube without size segregation in order to obtain a vibro-packed fuel pin with oxygen getter particles uniformly dispersed. "Simultaneous feeding" with volumetric powder feeders is useful to obtain a vibro-packed fuel pin with oxygen getter particles uniformly dispersed.
 with uranium particles
with uranium particlesMatsuyama, Shinichiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Tsuboi, Yasushi*; Kihara, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
In the vipac fuel, it is considered that spherical metallic particles mainly consisting of uranium are added as an oxygen getter into vipac MOX fuel for FBR to prevent cladding inner corrosion by fuel-cladding chemical interaction (FCCI). In this study, vibro-packing experiments of granular UO particles and spherical metallic uranium particles and post-packing examinations such as destructive experiment were carried out. This study revealed that that it is important to feed particles uniformly into a cladding tube to obtain a vipac fuel with getter particles uniformly dispersed. Constant-volume feeder seems to be useful to obtain a vipac fuel with getter particles uniformly dispersed.
particles and spherical metallic uranium particles and post-packing examinations such as destructive experiment were carried out. This study revealed that that it is important to feed particles uniformly into a cladding tube to obtain a vipac fuel with getter particles uniformly dispersed. Constant-volume feeder seems to be useful to obtain a vipac fuel with getter particles uniformly dispersed.
 Compacts with/without Uranium Particles
Compacts with/without Uranium ParticlesIshii, Tetsuya; Yuda, Ryoichi*; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Tsuboi, Yasushi*; Ukai, Shigeharu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1204 - 1210, 2004/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal conductivities of granular UO compacts with and without uranium particles were measured to evaluate the thermal performance of vibro-packed granular MOX fuels containing metallic fine particle oxygen getters. The thermal conductivity of the compact with 10wt.% of the uranium particles was higher than without uranium particles and after heating beyond 1408K, the melting point of the uranium particle, the thermal conductivity further increased..The evaluation model for analyzing such phenomena were developed and it was revealed that once the UO
compacts with and without uranium particles were measured to evaluate the thermal performance of vibro-packed granular MOX fuels containing metallic fine particle oxygen getters. The thermal conductivity of the compact with 10wt.% of the uranium particles was higher than without uranium particles and after heating beyond 1408K, the melting point of the uranium particle, the thermal conductivity further increased..The evaluation model for analyzing such phenomena were developed and it was revealed that once the UO compact with the uranium particles was exposed to the temperature beyond 1408K, the uranium particle should melt and provide interconnect area between the UO
compact with the uranium particles was exposed to the temperature beyond 1408K, the uranium particle should melt and provide interconnect area between the UO granules and uranium particles, and between the uranium particles with each other. The resulting increase of the thermal conductivity was reasonably expressed by the effect of necks in the compact on the heat conduction.
granules and uranium particles, and between the uranium particles with each other. The resulting increase of the thermal conductivity was reasonably expressed by the effect of necks in the compact on the heat conduction.
JRR-2 Control Office; Kambara, Toyozo; Shoda, Katsuhiko; Hirata, Yutaka; Shoji, Tsutomu; Kohayakawa, Toru; Morozumi, Minoru; Kambayashi, Yuichiro; Shitomi, Hajimu; Kokanezawa, Takashi; et al.
JAERI 1027, 57 Pages, 1962/09
no abstracts in English