Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:79.13(Instruments & Instrumentation) -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Mishima, Kenji*; Ino, Takashi*; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Sato, Hiromi*; Otake, Yoshie*; Omori, Hitoshi*; Muto, Suguru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.342 - 345, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:85.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new beamline for a fundamental physics experiment is under construction at BL05 port in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), this beamline is designed using novel techniques of neutron optics and it is termed "Neutron Optics and Physics". The beam from the moderator is deflected by multi-channel supermirrors and split into three branches for individual experiments. In this study, we have optimized the design of the beam optics and shields using the Monte Carlo simulation package PHITS. The neutron fluxes of beams are expected to be 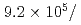 cm
cm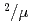 str
str s
s MW,
MW, 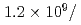 cm
cm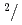 s
s MW,
MW, 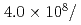 cm
cm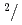 s
s MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
 Am lung monitoring system using an imaging plate
Am lung monitoring system using an imaging plateHirota, Masahiro*; Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Momose, Takumaro; Deji, Shizuhiko*; Ito, Shigeki*; Saze, Takuya*; Nishizawa, Kunihide*
Health Physics, 93(1), p.28 - 35, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.41(Environmental Sciences)A new  Am lung monitoring system without shielding was devised by using an imaging plate system. The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's realistic torso phantom containing a
Am lung monitoring system without shielding was devised by using an imaging plate system. The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's realistic torso phantom containing a  Am lung was covered by imaging plates sealed in lightproof bags. The imaging plate system displayed
Am lung was covered by imaging plates sealed in lightproof bags. The imaging plate system displayed  Am lung images characteristic of the lung shape of the torso phantom. The imaging plate system's lower detection limits of 14 Bq for 60 min exposure and 6 Bq for 300 min were the same levels as those of the phoswich detectors and the germanium detectors placed in shielded rooms. The imagingplate system for 60 min exposure detected about 2% of the annual limit of 740 Bq for
Am lung images characteristic of the lung shape of the torso phantom. The imaging plate system's lower detection limits of 14 Bq for 60 min exposure and 6 Bq for 300 min were the same levels as those of the phoswich detectors and the germanium detectors placed in shielded rooms. The imagingplate system for 60 min exposure detected about 2% of the annual limit of 740 Bq for  Am inhalation. A lung monitoring system using imaging plates is applicable for
Am inhalation. A lung monitoring system using imaging plates is applicable for  Am lung monitoring.
Am lung monitoring.
Shinohara, Nobuo; Asano, Yoshie; Hirota, Naoki*; Hokida, Takanori; Inoue, Yoji; Kumata, Masahiro; Nakahara, Yoshinori*; Oda, Tetsuzo*; Uchikoshi, Takako*; Yamamoto, Yoichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2005/10
Research activities of JAERI related to the CTBT verification regime are presented in the International Conference. The subjects of this presentation are (1) an overview of the CTBT verification regime, (2) construction and operation of the radionuclide monitoring stations of Okinawa (RN37) and Takasaki (RN38) and the certified radionuclide laboratory (RL11), and (3) preparation of the National Data Center at Tokai (JAERI NDC) for radionuclide data. The RN38 station has been certified by the CTBTO/PrepCom and sending the measured data every day. The infrastructures and operational manuals for RN37 and RL11 are now preparing for their operations. The JAERI NDC has experimentally analyzed and evaluated the radionuclide data from all over the world through International Data Center (IDC). As an example of the JAERI NDC works, atmospheric dispersion backtracking system has been developing by using WSPEEDI (Worldwide Version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information) code to estimate a source location of radionuclide release by nuclear explosion/accident.
Shinohara, Nobuo; Inoue, Yoji; Uchikoshi, Takako*; Oda, Tetsuzo*; Kumata, Masahiro; Kurosawa, Yoshiaki; Hirota, Naoki*; Hokida, Takanori; Nakahara, Yoshinori*; Yamamoto, Yoichi
Dai-25-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.51 - 58, 2005/00
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) conducts researches and developments related to Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) on the basis of Japan's pragmatic and progressive efforts toward peaceful use of atomic energy and non-proliferation with the goal of realizing a peaceful and safe world free from nuclear weapons. The Treaty aims for the establishment of a global verification regime comprising an International Monitoring System (IMS) and the JAERI has engaged in the following activities: construction and operation of the radionuclide monitoring stations at Okinawa (RN37) and Takasaki (RN38) and the certified radionuclide laboratory at Tokai (RL11) as specified in Annex 1 of CTBT Protocol, and preparation of the National Data Center at Tokai (JAERI NDC). Research activities of JAERI related to the CTBT verification regime are presented in the paper. The subjects of this presentation are (1) an overview of the CTBT verification regime, (2) construction and operation of RN37, RN38 and RL11, and (3) preparation of the JAERI NDC for radionuclide data.
Hirota, Naoki*; Hokida, Takanori; Inoue, Yoji; Kumata, Masahiro; Kurosawa, Yoshiaki; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Oda, Tetsuzo; Shinohara, Nobuo; Uchikoshi, Takako*; et al.
JAERI-Review 2003-021, 68 Pages, 2003/08
This report describes research activities of the R & D Group for Non-Proliferation Technology related to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) verification regime. The main subjects of this report are (1) an overview of the CTBT verification regime, (2) preparation of the National Data Center for radionuclide data, (3) construction and operation of the radionuclide monitoring stations at Takasaki and Okinawa and the certified rarionuclide laboratory at Tokai in Japan. We have participated in an intercomparison test internationally organized for the certified laboratories and the test results are given here. Scientific application of the CTBT-related technologies to environmental researches is also depicted.
Yamamoto, Yoichi; Hokida, Takanori; Hirota, Naoki*; Oda, Tetsuzo; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Kumata, Masahiro; Inoue, Yoji; Uchikoshi, Takako*; Shinohara, Nobuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Dai-23-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.53 - 60, 2002/12
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) has developed the National Data Center (NDC) for radionuclide as part of the international monitoring regime related to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT). JAERI NDC already started to input gamma-ray spectrum data obtained from several International Monitoring System (IMS) stations into a database. Data analysis reports made by the International Data Center (IDC) are also stored in the database. Some software tools are under development for the NDC's independent analysis such as investigation of existence of the radionuclides derived from nuclear explosion and presumptive analysis of source location of radionuclide release. The NDC system will also be able to post IMS data and analysis results to the authorized users on the Internet. This paper presents the role, current state of system development and future plan of JAERI NDC.
Oda, Tetsuzo; Kumata, Masahiro; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Hokida, Takanori; Hirota, Naoki*; Uchikoshi, Takako*; Inoue, Yoji; Shinohara, Nobuo
Dai-23-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.29 - 37, 2002/12
The Comprehensive nuclear Test-Ban Treaty(CTBT) bans all nuclear explosions and also calls for a verification regime, which consists of the International Monitoring System(IMS) and On-site Inspection. The primary objectives of the IMS are to deter nuclear explosions in all environments and, if such an explosion does occur, to detect, locate, and identify its source. The CTBT was opened for signature on September 24, 1996 and the Preparatory Commission(PrepCom) for the CTBT Organization was established to prepare for the verification regime in order to monitor compliance with the Treaty. The Preparatory Commission comprises two main organs: a plenary body of all the States Signatories as the highest policy-making organ, and the Provisional Technical Secretariat(PTS). The plenary body has three subsidiary bodies: Working Group A(administrative matters and legal issues), Working Group B(verification issues), and an Advisory Group. This paper presents an overview and mandate of the PrepCom, and status of verification regime, and discusses future activities.
Kumata, Masahiro; Oda, Tetsuzo; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Uchikoshi, Takako*; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Hokida, Takanori; Hirota, Naoki*; Inoue, Yoji; Shinohara, Nobuo
Dai-23-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.39 - 44, 2002/12
The International Monitoring System (IMS) will be established across the world to verify compliance with the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT). The IMS will be capable of detecting and identifying nuclear explosions of detonated within the atmosphere, underwater and underground. 321 monitoring stations will be set around the world as a monitoring network of the IMS. The four technologies of seismology, hydroacoustic, infrasound, and radionuclide will be used for monitoring purposes. In order to build the radionuclide monitoring network, 80 radionuclide stations were chosen. Particles in the atmosphere are collected on a filter at each station to measure radioactivity by a HP-Ge detector. Further, 40 out of these 80 stations will be equipped with an automatic radioactive noble gas sampler/analyzer. The JAERI is establishing infrastructure to host radionuclide air monitoring equipment for two raionuclide stations in Japan. This paper presents the current status of the establishment and promising performance of the stations in Japan.
Shinohara, Nobuo; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Inoue, Yoji; Kumata, Masahiro; Oda, Tetsuzo; Uchikoshi, Takako*; Hokida, Takanori; Hirota, Naoki*; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Usuda, Shigekazu
Dai-23-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu, p.45 - 52, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
 Pu distribution in the lung
Pu distribution in the lungHirota, Masahiro; Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Momose, Takumaro; Deji, Shizuhiko*; Ito, Shigeki*; Saze, Takuya*; Nishizawa, Kunihide*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Pu distribution in the lung by an imaging plate
Pu distribution in the lung by an imaging plateHirota, Masahiro; Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Momose, Takumaro; Deji, Shizuhiko*; Ito, Shigeki*; Saze, Takuya*; Nishizawa, Kunihide*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English