Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shaimerdenov, A.*; Gizatulin, Sh.*; Sairanbayev, D.*; Bugybay, Zh.*; Silnyagin, P.*; Akhanov, A.*; Fuyushima, Takumi; Hirota, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 548, p.165235_1 - 165235_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0Compared to conditions in other types of installations, cable insulation in nuclear reactors is exposed to mixed conditions (high temperatures, radiation, pressure, humidity, aggressive environments) and at the same time they must maintain their performance characteristics for a long time (about 40-50 years). As a result of irradiation to such conditions, the electrical properties of the cable insulation are degraded, which leads to an increase in current loss. This is because the charge is induced by radiation into the insulator. At the WWR-K reactor, studies were started on the radiation resistance of signal cables with two types of mineral insulation (MgO and Al O
O ). As part of these studies, new experimental data will be obtained on the behavior of signal cables with mineral insulation of two types in mixed operating conditions (radiation field and high temperature). It is planned to accumulate fluence of fast neutrons
). As part of these studies, new experimental data will be obtained on the behavior of signal cables with mineral insulation of two types in mixed operating conditions (radiation field and high temperature). It is planned to accumulate fluence of fast neutrons  10
10 cm
cm in cables. The irradiation temperature will be (500
in cables. The irradiation temperature will be (500  50)
50) C). The study of the degradation of the electrical properties of the insulation of signal cables will be carried out in real time (in-situ). For this, a special design of the experimental device and a technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics were developed. This paper presents a sketch of the capsule design, the results of complex calculations for the development of the capsule design, the expected neutron fluences, the dpa in steel, the technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics, and a work plan for the future indicating the expected results. The cable irradiation time until the target neutron fluence is reached will be about 100 effective days. This research is funded by the International Scientific-Technical Center.
C). The study of the degradation of the electrical properties of the insulation of signal cables will be carried out in real time (in-situ). For this, a special design of the experimental device and a technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics were developed. This paper presents a sketch of the capsule design, the results of complex calculations for the development of the capsule design, the expected neutron fluences, the dpa in steel, the technique for in-reactor measurement of electrical characteristics, and a work plan for the future indicating the expected results. The cable irradiation time until the target neutron fluence is reached will be about 100 effective days. This research is funded by the International Scientific-Technical Center.
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
Hirota, Noriaki; Funamoto, Kodai*; Tachibana, Yukio
Zairyo, 72(3), p.255 - 261, 2023/03
For the purpose of developing metallic materials with excellent corrosion resistance under boiling sulfuric acid environment, the coated materials were evaluated for their corrosion resistance and the differences in surface morphology were investigated. As a result, the corrosion resistance of SUS304 coated and sintered eight times by chemical densified coating method (S-ZAC) was maintained at the point after 12h corrosion test, but the corrosion rate rapidly increased after 100h corrosion test. The cross-sectional microstructural analysis of the specimens showed that only a small amount of SiO remained on the surface, while Cr
remained on the surface, while Cr O
O completely disappeared. The mechanism of film delamination in S-ZAC is assumed to be due to the thermal expansion caused by heating, which resulted in curvature of the thick film and cracks at the Cr
completely disappeared. The mechanism of film delamination in S-ZAC is assumed to be due to the thermal expansion caused by heating, which resulted in curvature of the thick film and cracks at the Cr O
O and SiO
and SiO interfaces. On the other hand, SUS304 coated with higher density of Cr
interfaces. On the other hand, SUS304 coated with higher density of Cr O
O by repeating the coating and sintering eleven times (MS-ZAC) showed excellent corrosion resistance as well as SiC even after 100h corrosion test. The results of cross-sectional microstructuCr
by repeating the coating and sintering eleven times (MS-ZAC) showed excellent corrosion resistance as well as SiC even after 100h corrosion test. The results of cross-sectional microstructuCr O
O particle layer, in addition to the thinning of the entire film.
particle layer, in addition to the thinning of the entire film.
Hirota, Noriaki; Takeda, Kiyoko*; Tachibana, Yukio; Masaki, Yasuhiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(3), p.68 - 76, 2021/03
Corrosion resistance of stainless steels and Ni-based alloys were evaluated in a sulfuric acid decomposition gas at high temperature. The evaluation were carried out in an environment simulated in the sulfuric acid decomposition reaction vessel for thermochemical hydrogen production process (IS process). Their corrosion films were also analyzed for better understanding of the corrosion behavior. As a result, after 100 hour corrosion test, Ni-based alloy containing 2.4% Si showed good corrosion resistance. Ferritic stainless steel containing 3% Al (3Al-Ferrite) showed better corrosion resistance. Its corrosion rate was lower than that of SiC (0.1mm/year), which is a candidate material for the sulfuric acid decomposition reaction vessel. On the other hand, Ni-based alloy pre-filmed with Al O
O is prepared as the relative corrosion film of 3Al-Ferrite. Its corrosion rate was significantly higher than that of 3Al-Ferrite. As the result of EPMA analysis of these oxide films, Ni-based alloy containing 2.4% Si formed Si oxide film which had some cracks after the long term corrosion test. Therefore S penetrated into grain boundaries of the matrix through the oxide film. 3Al-Ferrite formed a thin and uniform Al
is prepared as the relative corrosion film of 3Al-Ferrite. Its corrosion rate was significantly higher than that of 3Al-Ferrite. As the result of EPMA analysis of these oxide films, Ni-based alloy containing 2.4% Si formed Si oxide film which had some cracks after the long term corrosion test. Therefore S penetrated into grain boundaries of the matrix through the oxide film. 3Al-Ferrite formed a thin and uniform Al O
O film, and the penetration of S into the grain boundaries was not observed. Al
film, and the penetration of S into the grain boundaries was not observed. Al O
O pre-film of Ni-based alloy also showed S penetration in the matrix because the Al
pre-film of Ni-based alloy also showed S penetration in the matrix because the Al O
O pre-film had many small defects originally. The corrosion oxide film of 3Al-Ferrite consisted of only
pre-film had many small defects originally. The corrosion oxide film of 3Al-Ferrite consisted of only  -Al
-Al O
O , while the Al
, while the Al O
O pre-film consist of
pre-film consist of  -Al
-Al O
O and
and  -Al
-Al O
O . Those results suggest that the better corrosion resistance of 3Al-Ferrite is due to the uniform formation of dense
. Those results suggest that the better corrosion resistance of 3Al-Ferrite is due to the uniform formation of dense  -Al
-Al O
O film at the early stage of the corrosion.
film at the early stage of the corrosion.
Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1276 - 1286, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of materials of mineral-insulated (MI) cables on their electrical characteristics upon exposure to high-temperature conditions was examined via a transmission test, in the objective of achieving the stability of the potential distribution along the cable length. Occurrence of a voltage drop along the cable was confirmed for aluminum oxide (Al O
O ) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al
) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al O
O and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires (
and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires ( ) and the distance between them (
) and the distance between them ( ) were varied. Considering the variation of
) were varied. Considering the variation of  , the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio
, the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio 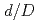 of 0.35, obtained by dividing
of 0.35, obtained by dividing  with that of the insulating material (
with that of the insulating material ( ). In case of varying
). In case of varying  , a minimum voltage drop was l/
, a minimum voltage drop was l/ of 0.5.
of 0.5.
Kataoka, Noriaki*; Nakajima, Junya; Miwa, Kazuji; Hirota, Seiko*; Tsubota, Yoichi; Yamada, Ryohei; Fujimichi, Yuki*; Ishikawa, Junya*; Sunaoshi, Masaaki*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 54(2), p.140 - 145, 2019/06
It is the written report of the joint meeting of young researchers in the field of radiation protection and radiation biology.
Hirota, Noriaki; Kasahara, Seiji; Iwatsuki, Jin; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.; Tachibana, Yukio
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(6), p.137 - 142, 2019/06
New corrosion test equipment for high temperature gas of decomposed sulfuric acid was manufactured in order to ascertain flow rate of sulfuric acid in the piping, occurrence of sulfuric acid decomposition reaction in the equipment, and temperature distribution inside the furnace tube. The flow rate of the sulfuric acid solution was constantly measured using an ultrasonic flowmeter. The SO concentration at the inlet of the test equipment was almost the same as that at the inlet of the sulfuric acid decomposer in the hydrogen production plant assuming a high-temperature gas cooled reactor hydrogen-power cogeneration system (GTHTR300C). On the other hand, during a test, leakage of sulfuric acid occurred from the fitting part at the outlet side. Hence the temperature distribution of the fitting part at the outlet side was investigated using fluid analysis. As a result, it was found that the temperature at the fitting was low enough to use fluorine joint grease when the distance was 0.05 m or more away from the outlet side pipe. An improved furnace tube was manufactured and the temperature was measured again at fitting part of the outlet side. The temperature was lower that the temperature limit of the joint grease and almost the same as the temperature distribution in the fluid analysis, and leakage of sulfuric acid has not occurred to date.
concentration at the inlet of the test equipment was almost the same as that at the inlet of the sulfuric acid decomposer in the hydrogen production plant assuming a high-temperature gas cooled reactor hydrogen-power cogeneration system (GTHTR300C). On the other hand, during a test, leakage of sulfuric acid occurred from the fitting part at the outlet side. Hence the temperature distribution of the fitting part at the outlet side was investigated using fluid analysis. As a result, it was found that the temperature at the fitting was low enough to use fluorine joint grease when the distance was 0.05 m or more away from the outlet side pipe. An improved furnace tube was manufactured and the temperature was measured again at fitting part of the outlet side. The temperature was lower that the temperature limit of the joint grease and almost the same as the temperature distribution in the fluid analysis, and leakage of sulfuric acid has not occurred to date.
Nishihara, Tetsuo; Yan, X.; Tachibana, Yukio; Shibata, Taiju; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Kubo, Shinji; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; Ueta, Shohei; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2018-004, 182 Pages, 2018/07
Research and development on High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in Japan started since late 1960s. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in cooperation with Japanese industries has researched and developed system design, fuel, graphite, metallic material, reactor engineering, high temperature components, high temperature irradiation and post irradiation test of fuel and graphite, high temperature heat application and so on. Construction of the first Japanese HTGR, High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), started in 1990. HTTR achieved first criticality in 1998. After that, various test operations have been carried out to establish the Japanese HTGR technologies and to verify the inherent safety features of HTGR. This report presents several system design of HTGR, the world-highest-level Japanese HTGR technologies, JAEA's knowledge obtained from construction, operation and management of HTTR and heat application technologies for HTGR.
Hirota, Noriaki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Yan, X.; Tanaka, Kohei*; Otani, Akihito*
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2018/07
Nakano, Hiroko; Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 5(2), p.17-00594_1 - 17-00594_12, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Hiroshi; Nakano, Hiroko; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Otsuka, Noriaki; Nishikata, Kaori; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Hirota, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Testing 2017-002, 138 Pages, 2017/12
From the viewpoints of utilization improvement of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), the experimental devices have been established for the out-pile tests in the irradiation technology development building. The devices for the irradiation capsule assembly, material tests and inspections were established at first and experimental data were accumulated before the neutron irradiation tests. On the other hand, after the Great East Japan Earthquake, the repairs and earthquake-resistant measures of the existing devices were carried out. New devices and equipments were also established for the R&D program for power plant safety enhancement of the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc production development under the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone. This report describes the outline and basic operation manuals of the devices established from 2011 to 2016 and the management points for the safety works in the irradiation technology development building.
Tc production development under the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone. This report describes the outline and basic operation manuals of the devices established from 2011 to 2016 and the management points for the safety works in the irradiation technology development building.
Hirota, Noriaki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Yan, X.
JAEA-Technology 2017-027, 19 Pages, 2017/12
In this study, austenitic Fe-based alloys and Ni based alloys was developed as candidate structural materials for equipment operated in sulfuric acid and hydrogen iodide (HI) environment, which exists in various industrial processes including iodine-sulfur (IS) hydrogen production process and geothermal power generation process. The objectives of the study are to achieve the corrosion resistance performance sufficient under the working condition of these processes and to overcome the practical scale-up difficulty of the ceramic (SiC) material that is presently used in the processes due to the manufacturing size limitation of the ceramic. The chemical composition development plan for the austenitic Fe-based alloys is threefold: reinforcement of matrix by addition of Cu and Ta, strength compensation of the surface film by addition of Si and Ti, and prevention of peeling of surface oxide by addition of rare earth elements. Because addition of Cu and Si is known to reduce the ductility of the material and thus manufacturability of the component, it is important to determine the allowable amount of each element to be added. On the other hand, the chemical composition development plan for the Ni based alloys is reinforcement of matrix by addition of Mo, W and Ta, strength compensation of the surface film by addition of Ti, and prevention of peeling of surface oxide by addition of rare earth elements. In particular, the addition of Mo and W to the Ni based alloy is expected to be effective in preventing dimensional deviation of structures from increasing during heating and cooling of process equipment. Various material specimens will be fabricated based on the above chemical composition development plans and tests on these specimens will then be carried out to confirm the corrosion resistance performance under the fluid conditions simulating each industrial processes.
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi; Seko, Noriaki; Oto, Keisuke*
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology (CEST 2011), p.B835 - B842, 2011/09
Cotton consisting of nearly 100% cellulose is one of the widely available natural polymers with versatile applications. In order to know the possibility of using cellulosic materials for the development of functional adsorbents by radiation induced vinyl graft modification method, cotton was studied as a representative natural material. In the present study, cotton was pre-irradiated with electron beam and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was grafted onto it. Various parameters like irradiation dose, solvent system, monomer concentration, grafting time, etc were studied to achieve the optimum graft yield. Once GMA containing reactive epoxy group was grafted onto the cotton matrix, various functional groups possessing different selectivity behavior for different metals were introduced by simple chemical reaction. The newly developed functional-cotton derivatives were studied for their ion exchange performances and selectivity patterns mainly for palladium in HCl and HCl-HNO systems.
systems.
Hirota, Koichi; Parajuli, D.; Seko, Noriaki
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Radiation Curing in Asia (RadTech Asia 2011) (Internet), p.136 - 137, 2011/06
Conventional methods for the recovery of precious metals are solvent extraction, chemical precipitation, and use of ion exchange resins. However these methods are facing to significant disadvantages like high capital costs, large chemical and energy requirements, and generation of toxic sludge or other waste products creating additional burden. Development of biomass based sorbents is a better, probably the best, option with lower capital cost and higher efficiency. Although the biomass-sorbents are better than the existing methods, the methods of preparing sorbents from them usually use several kinds of chemicals. In the present work, biomass has been modified with functional groups after electron beam irradiation and its performance for the recovery of precious metals has been studied. The obtained results are compared with that of chemically modified derivative.
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi; Seko, Noriaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 288(1), p.53 - 58, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:78.83(Chemistry, Analytical)
Aso, Naofumi*; Owada, Kenji; Watanuki, Tetsu; Machida, Akihiko; Omura, Ayako; Inami, Toshiya; Homma, Yoshiya*; Shiokawa, Yoshinobu*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Sato, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(Suppl.), p.88 - 90, 2006/08
no abstracts in English
Hirota, Koichi; Parajuli, D.; Seko, Noriaki
no journal, ,
Lignin in Japanese cedar wood powder was extracted in the form of lignophenol and was modified with ethylenediamine and trimethylamine groups using Electron-beam technology. The functionalized lignophenol adsorbents were then studied for the recovery of precious metals: Au, Pt, and Pd from urban mine. From the batch test of mixture solution containing equal molar concentration of various metal ions, the sorbent was found to hold selectivity for Au(III), Pd(II), and Pt(IV) ions only with negligible sorption for other metal ions like Cu(II), Co(II), Fe(III), Ni(II), and Zn(II). The biomass sorbent is expected to be an excellent material for recovering the precious metal from urban mine.
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi; Seko, Noriaki
no journal, ,
Hirota, Koichi; Parajuli, D.; Seko, Noriaki
no journal, ,
High level radioactive waste contains precious metals like Pd, Rh, and Ru. Biomass sorbents were synthesized using Japanese cedar wood and tested its adsorption performance. The results showed that the sorbents functionalize with thioamide group exhibit high adsorption ability for Pd(II) under  -ray irradiation.
-ray irradiation.
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi; Seko, Noriaki
no journal, ,
Wood derived lignin was modified with ethylenediamine after electron beam irradiation and its performance for the recovery of precious metals was compared to that modified by chemicals. The results showed that the sorbents obtained by the irradiation had higher sorption ability for precious metals. Electron beam has an advantage for creating high performance biomass absorbents for precious metals such as Au, Pt, and Pd.