Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Honda, Maki
Journal of the Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan, 70(4), p.282 - 283, 2022/12
The development of measurement and chemical separation techniques in the accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) method has enabled highly sensitive analysis of  Pu (half-life 8.1
Pu (half-life 8.1 10
10 years),
years),  Fe (half-life 2.62
Fe (half-life 2.62 10
10 years), and
years), and  Sr (half-life 28.9 years) in AMS. For example, the study analyzing
Sr (half-life 28.9 years) in AMS. For example, the study analyzing  Pu in ferromanganese crust samples successfully quantified
Pu in ferromanganese crust samples successfully quantified  Pu from outside the solar system, which had been hidden by
Pu from outside the solar system, which had been hidden by  Pu from nuclear tests. Furthermore, the research has revealed that
Pu from nuclear tests. Furthermore, the research has revealed that  Pu is produced in neutron star mergers, etc., leading to unraveling the production sites where the heavy elements originate. This topic highlights the frontline of studies on
Pu is produced in neutron star mergers, etc., leading to unraveling the production sites where the heavy elements originate. This topic highlights the frontline of studies on  Pu,
Pu,  Fe, and
Fe, and  Sr utilizing AMS.
Sr utilizing AMS.
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs by AMS
Cs by AMSHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Wieser, A.*; Marchhart, O.*; Lachner, J.*; Priller, A.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.85 - 90, 2022/11
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is an analytical method that combines mass spectrometry with a tandem accelerator, which has been used mainly in nuclear physics experiments. AMS is used to measure radionuclides with half-lives of 10 -10
-10 years. For radionuclides with half-lives of this order, the method of measuring their mass is 10
years. For radionuclides with half-lives of this order, the method of measuring their mass is 10 -10
-10 times more sensitive than measuring their activity. Because of this advantage, AMS has been widely applied in Earth and planetary sciences, atomic energy research, and other fields. Among the various studies, Wallner et al. (2021, 2016) have achieved excellent work in Earth and planetary sciences. For example, they have attained the ultra-sensitive analysis of
times more sensitive than measuring their activity. Because of this advantage, AMS has been widely applied in Earth and planetary sciences, atomic energy research, and other fields. Among the various studies, Wallner et al. (2021, 2016) have achieved excellent work in Earth and planetary sciences. For example, they have attained the ultra-sensitive analysis of  Fe and
Fe and  Pu in environmental samples. These are radionuclides produced by rapid-neutron-capture (r-process) nucleosynthesis. Our recent work shows that a new AMS system (VERA, University of Vienna), which combines laser isobaric separation and a typical AMS system, has been successfully applied to the ultra-sensitive determination of
Pu in environmental samples. These are radionuclides produced by rapid-neutron-capture (r-process) nucleosynthesis. Our recent work shows that a new AMS system (VERA, University of Vienna), which combines laser isobaric separation and a typical AMS system, has been successfully applied to the ultra-sensitive determination of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in environment. For
Cs in environment. For  Sr in environmental samples, the
Sr in environmental samples, the  -ray measurement by the milking of the daughter nuclide
-ray measurement by the milking of the daughter nuclide  Y is still the principal method, which takes 3-6 weeks. The new AMS method has a detection limit of
Y is still the principal method, which takes 3-6 weeks. The new AMS method has a detection limit of  0.1 mBq, which is comparable to that of
0.1 mBq, which is comparable to that of  -ray measurement, with a more straightforward chemical treatment than
-ray measurement, with a more straightforward chemical treatment than  -measurement. Our achievement demonstrates that AMS can be a practical new method for determining
-measurement. Our achievement demonstrates that AMS can be a practical new method for determining  Sr in the environment.
Sr in the environment.
 Sr analysis of environmental samples by ion-laser interaction mass spectrometry
Sr analysis of environmental samples by ion-laser interaction mass spectrometryHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Marchhart, O.*; Priller, A.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakaguchi, Aya*
Analytical Methods, 14(28), p.2732 - 2738, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:45.92(Chemistry, Analytical)The sensitive  Sr analysis with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was developed for the advances of environmental radiology. One advantage of AMS is the ability to analyze various environmental samples with
Sr analysis with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was developed for the advances of environmental radiology. One advantage of AMS is the ability to analyze various environmental samples with  Sr/
Sr/ Sr atomic ratios of 10
Sr atomic ratios of 10 in a simple chemical separation. Three different IAEA samples with known
in a simple chemical separation. Three different IAEA samples with known  Sr concentrations (moss-soil, animal bone, Syrian soil: 1 g each) were analyzed to assess the validity of the chemical separation and the AMS measurement. The
Sr concentrations (moss-soil, animal bone, Syrian soil: 1 g each) were analyzed to assess the validity of the chemical separation and the AMS measurement. The  Sr measurements were conducted on the AMS system combined with the Ion Laser InterAction MasSpectrometry (ILIAMS) setup at the University of Vienna, which has excellent isobaric separation performance. The isobaric interference of
Sr measurements were conducted on the AMS system combined with the Ion Laser InterAction MasSpectrometry (ILIAMS) setup at the University of Vienna, which has excellent isobaric separation performance. The isobaric interference of  Zr in the
Zr in the  Sr AMS was first removed by chemical separation. The separation factor of Zr in two-step column chromatography with Sr resin and anion exchange resin was 10
Sr AMS was first removed by chemical separation. The separation factor of Zr in two-step column chromatography with Sr resin and anion exchange resin was 10 . The
. The  Zr remaining in the sample was removed by ILIAMS effectively. This simple chemical separation achieved a limit of detection
Zr remaining in the sample was removed by ILIAMS effectively. This simple chemical separation achieved a limit of detection  0.1 mBq in the
0.1 mBq in the  Sr AMS, which is lower than typical
Sr AMS, which is lower than typical  -ray detection. The agreement between AMS measurements and nominal values for the
-ray detection. The agreement between AMS measurements and nominal values for the  Sr concentrations of IAEA samples indicated that the new highly-sensitive
Sr concentrations of IAEA samples indicated that the new highly-sensitive  Sr analysis in the environmental samples with AMS is reliable even for high matrix samples of soil and bone.
Sr analysis in the environmental samples with AMS is reliable even for high matrix samples of soil and bone.
 (Copepoda) from a deep sediment-trap; Abundance and implications for ecological and biogeochemical studies
(Copepoda) from a deep sediment-trap; Abundance and implications for ecological and biogeochemical studiesIkenoue, Takahito*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Honda, Makio*; Kitamura, Minoru*; Mino, Yoshihisa*; Narita, Hisashi*; Kobayashi, Takuya
Frontiers in Marine Science (Internet), 9, p.884320_1 - 884320_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We studied seasonal variations of the mesozooplankton swimmer community collected by a sediment trap moored at 873 m in the Kuroshio & Oyashio Transition region off the east coast of Japan from 5 August 2011 to 23 June 2013. The total flux of mesozooplankton swimmers varied between 0 and 11.1 individuals m-2 d-1, with a mean of 3.1 individuals m-2 d-1 during the sampling period. Among the Copepoda, Neocalanus cristatus was the most dominant taxon. The species composition of the swimmers closely reflected the mid-depth mesozooplankton of the Oyashio region. The fluxes of Neocalanus species reflected ontogenetic vertical migration, but may have been overestimates of active fluxes if they included dormant individuals that accidentally entered the sediment trap.
Hain, K.*; Martschini, M.*; G lce, F.*; Honda, Maki; Lachner, J.*; Kern, M.*; Pitters, J.*; Quinto, F.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Steier, P.*; et al.
lce, F.*; Honda, Maki; Lachner, J.*; Kern, M.*; Pitters, J.*; Quinto, F.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Steier, P.*; et al.
Frontiers in Marine Science (Internet), 9, p.837515_1 - 837515_17, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:96.12(Environmental Sciences)Recent major advances in accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) at the Vienna Environmental Research Accelerator (VERA) regarding detection efficiency and isobar suppression have opened possibilities for the analysis of additional long-lived radionuclides at ultra-low environmental concentrations. These radionuclides, including  U,
U,  Cs,
Cs,  Tc and
Tc and  Sr, will become important for oceanographic tracer application due to their generally conservative behavior in ocean water. In particular, the isotope ratios
Sr, will become important for oceanographic tracer application due to their generally conservative behavior in ocean water. In particular, the isotope ratios  U/
U/ U and
U and  Cs/
Cs/ Cs have proven to be powerful fingerprints for emission source identification as they are not affected by elemental fractionation. Improved detection efficiencies allowed us to analyze all major long-lived actinides, i.e.
Cs have proven to be powerful fingerprints for emission source identification as they are not affected by elemental fractionation. Improved detection efficiencies allowed us to analyze all major long-lived actinides, i.e.  U,
U,  Np,
Np, 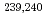 Pu,
Pu,  Am as well as the very rare
Am as well as the very rare  U, in the same 10 L water samples of an exemplary depth profile from the northwest Pacific Ocean. Especially for
U, in the same 10 L water samples of an exemplary depth profile from the northwest Pacific Ocean. Especially for  Sr analysis, our new approach has already been validated for selected reference materials (e.g. IAEA-A-12) and is ready for application in oceanographic studies. We estimate that a sample volume of only (1-3) L ocean water is sufficient for
Sr analysis, our new approach has already been validated for selected reference materials (e.g. IAEA-A-12) and is ready for application in oceanographic studies. We estimate that a sample volume of only (1-3) L ocean water is sufficient for  Sr as well as
Sr as well as  Cs analysis, respectively.
Cs analysis, respectively.
 I in the terrestrial environment after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
I in the terrestrial environment after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentHonda, Maki
Chikyu Kagaku, 55(4), p.176 - 192, 2021/12
Iodine 129 ( I) is a radionuclide that decays to
I) is a radionuclide that decays to  Xe with a half-life of 15.7 million years. The analysis of
Xe with a half-life of 15.7 million years. The analysis of  I in the environment has played an important role not only in the fields of planetary science and earth science, but also in the nuclear field in recent years. Particularly, in the case of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in March, 2011, the scientists estimated the distribution and soil deposition of
I in the environment has played an important role not only in the fields of planetary science and earth science, but also in the nuclear field in recent years. Particularly, in the case of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in March, 2011, the scientists estimated the distribution and soil deposition of  I over a wide area, and contributed to the assessment of internal exposure doses in the early stage of the accident. This is one of the most significant achievements in recent
I over a wide area, and contributed to the assessment of internal exposure doses in the early stage of the accident. This is one of the most significant achievements in recent  I-related studies. Future studies are expected to be conducted to elucidate the transport mechanism of
I-related studies. Future studies are expected to be conducted to elucidate the transport mechanism of  I from land to river and sea, and to investigate the possible accumulation of
I from land to river and sea, and to investigate the possible accumulation of  I in aquatic organisms. The mobility of
I in aquatic organisms. The mobility of  I in the soil studied by the author during the 10-years since the accident has been mainly reviewed in this manuscript.
I in the soil studied by the author during the 10-years since the accident has been mainly reviewed in this manuscript.
 Fe and
Fe and  Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovae
Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovaeWallner, A.*; Froehlich, M. B.*; Hotchkis, M. A. C.*; Kinoshita, N.*; Paul, M.*; Martschini, M.*; Pavetich, S.*; Tims, S. G.*; Kivel, N.*; Schumann, D.*; et al.
Science, 372(6543), p.742 - 745, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:96.93(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Half of the chemical elements heavier than iron are produced by the rapid neutron capture process (r-process). The sites and yields of this process are disputed, with candidates including some types of supernovae (SNe) and mergers of neutron stars. We search for two isotopic signatures in a sample of Pacific Ocean crust-iron-60 ( Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and
Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and  Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of
Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of  Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of
Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of  Pu. The
Pu. The  Pu/
Pu/ Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The
Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The  Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Sasa, Kimikazu*; Honda, Maki; Hosoya, Seiji*; Takahashi, Tsutomu*; Takano, Kenta*; Ochiai, Yuta*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Kurita, Saori*; Satou, Yukihiko; Sueki, Keisuke*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.72 - 79, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
 Cl in soil near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cl in soil near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantOta, Yuki*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Sasa, Kimikazu*; Takahashi, Tsutomu*; Matsunaka, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Masumi*; Tosaki, Yuki*; Honda, Maki*; Hosoya, Seiji*; Takano, Kenta*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2018-002, p.99 - 102, 2019/02
no abstracts in English
Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Arai, Takehiko*; Arai, Tomoko*; Hirata, Naru*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Honda, Chikatoshi*; Imae, Naoya*; et al.
Space Science Reviews, 208(1-4), p.317 - 337, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:71.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)NIRS3: The Near Infrared Spectrometer is installed on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to observe the target C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu at near infrared wavelengths of 1.8 to 3.2 micrometer. It aims to obtain reflectance spectra in order to detect absorption bands of hydrated and hydroxide minerals in the 3 micrometer-band. We adopted a linear-image sensor with indium arsenide (InAs) photo diodes and a cooling system with a passive radiator to achieve an optics temperature of 188 K, which enables to retaining sufficient sensitivity and noise level in the 3 micrometer wavelength region. We conducted ground performance tests for the NIRS3 flight model (FM) to confirm its baseline specifications. The results imply that the properties such as the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conform to scientific requirements to determine the degree of aqueous alteration, such as CM or CI chondrite, and the stage of thermal metamorphism on the asteroid surface.
Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 58(4), p.225 - 228, 2016/04
, 58(4), p.225 - 228, 2016/04
Transport processes of particulate radiocesium obtained from a three year time-series sediment trap experiments at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant off Fukushima are expounded. Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material in sinking particles, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. In particular, we found that accident-derived radiocesium associate with slope and shelf sediments were resuspended and transported laterally to the offshore regions in typhoon seasons in 2013. Continuous observation of such transport processes of particulate radiocesium near the seabed would be significant for better understanding of the fate of accident-derived radiocesium.
Buesseler, K. O.*; German, C. R.*; Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Black, E. E.*; Kawakami, Hajime*; Manganini, S. M.*; Pike, S.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(16), p.9807 - 9816, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.84(Engineering, Environmental)A three year time-series of particle fluxes is presented from sediment traps deployed at 500 and 1000 m at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. The accident-derived radiocesium were enhanced in flux peaks that, given variations in trap  Cs/
Cs/ Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from
Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from  120 to
120 to  500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
 Zn
Zn (T: Rh and Ir)
(T: Rh and Ir)Honda, Fuminori*; Hirose, Yusuke*; Miyake, Atsushi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Watanabe, Shinji*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 592(1), p.012021_1 - 012021_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.17(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Kaori*; Kawachi, Naoki; Ishii, Satomi; Suzui, Nobuo; Ito, Sayuri; Ishioka, Noriko; Honda, Ichiro*; Fujimaki, Shu
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 105, 2009/12
Honda, Akira; Masuda, Kaoru*; Imakita, Tsuyoshi*; Kato, Osamu*; Nishimura, Tsutomu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 58(5), p.182 - 189, 2009/05
Interaction between carbon steel and nitrate was modeled using the mixed potential concept. Carbon steel was selected as an example of metal components in the repository of radioactive waste. The nitrate reduction accompanied by the corrosion of carbon steel was modeled as a reaction series such as nitrate - nitrite - ammonia. The sum of the current of the reaction series of nitrate - nitrite - ammonia and that of water reduction was assumed to balance with the corrosion current of carbon steel. The input parameters for this kinetic model were determined by electrochemical measurement and immersion test. The results of the immersion test can be interpreted by the analyses of the model.
 CO
CO and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system
and a positron-emitting tracer imaging systemKikuchi, Kaori*; Ishii, Satomi; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Honda, Ichiro*; Kawachi, Naoki
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 110, 2008/11
 CO
CO and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system
and a positron-emitting tracer imaging systemKikuchi, Kaori*; Ishii, Satomi; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Honda, Ichiro*; Shishido, Yoshihiro*; Kawachi, Naoki
Journal of the Japanese Society for Horticultural Science, 77(2), p.199 - 205, 2008/04
To clarify the mechanism of growth and development of the fruit of eggplant, CO
CO was fed to a leaf and the translocation of
was fed to a leaf and the translocation of  C-labeled photoassimilate into the fruit was monitored by PETIS. Continuous images of the translocation of
C-labeled photoassimilate into the fruit was monitored by PETIS. Continuous images of the translocation of  C-photoassimilate from the leaf to the fruit were successfully made, with a shorter time resolution than ever reported before. The PETIS images indicated that translocation of photoassimilate within the fruit was not uniform. The velocity of photoassimilate translocation in the peduncle and the changes in the rate of translocation of photoassimilate in the fruit were estimated by analysis of the PETIS data. The advantages of PETIS measurements in physiological studies of source sink relationships are discussed.
C-photoassimilate from the leaf to the fruit were successfully made, with a shorter time resolution than ever reported before. The PETIS images indicated that translocation of photoassimilate within the fruit was not uniform. The velocity of photoassimilate translocation in the peduncle and the changes in the rate of translocation of photoassimilate in the fruit were estimated by analysis of the PETIS data. The advantages of PETIS measurements in physiological studies of source sink relationships are discussed.
Sekimoto, Hitoshi*; Kawachi, Naoki; Honda, Shuzo*; Yamaguchi, Yoshie*; Kato, Shota*; Yoneyama, Kaori*; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishii, Satomi; Watanabe, Satoshi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 124, 2008/03
no abstracts in English