Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.1 - 7, 2022/03
Background: In Japan, new regulations that revise the dose limit for the lens of the eye (the lens), operational quantities, and measurement positions for the lens dose were enforced in April 2021. Based on the international safety standards, national guidelines, the results of the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund of the Nuclear Regulatory Authority, and other studies, the Working Group of Radiation Protection Standardization Committee, the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) developed a guideline for radiation dose monitoring for the lens. Materials and Methods: The Working Group of the JHPS discussed the criteria of non-uniform exposure and the management criteria set to not exceed the dose limit for the lens. Results and Discussion: In July 2020, the JHPS guideline was published. The guideline consists of three parts: main text, explanations, and 26 questions. In the questions, the corresponding answers were prepared, and specific examples were provided to enable similar cases to be addressed. Conclusion: With the development of guideline on radiation dose monitoring of the lens, radiation managers and workers will be able to smoothly comply with revised regulations and optimise radiation protection.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Iwai, Satoshi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-15) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
Wada, Seiichi*; Ando, Tatsuhiko*; Watanabe, Aya*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 79, 2015/03
So far, we clarified that X-ray irradiation induced cell killing by bystander effect mediated-secreted factor. This phenomenon was related with sphingomyelinase (SMase). In this study we analyzed mechanism of secreted SMase from irradiated cells after irradiation. SMase was detected in the culture medium after irradiation by SDS-PAGE. Then, SMase was detected in the exosome of culture medium, but not out of exosome after irradiation. This result indicates that SMase was secreted as exosome from the irradiated cells.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Izumo, Hironobu; Hori, Naohiko; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ishihara, Masahiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2011/12
Establishment of a world network is proposed to achieve efficient facility utilization and provide high quality irradiation data by role sharing of irradiation tests with materials testing reactors in the world. As for the first step, mutual understanding among materials testing reactors is thought to be necessary. From this point, an international symposium on materials testing reactors (ISMTR) was held to construct the world network from 2008 every year, and a common understanding of world network has begun to be shared. The ISMTR-5 will be held on USA in 2012, and the ISMTR-6 will be held on Argentine in 2013.
 Mo production plan from
Mo production plan from  Mo by (n,
Mo by (n, ) reaction in JMTR
) reaction in JMTRIzumo, Hironobu; Kimura, Akihiro; Hori, Naohiko; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Ishihara, Masahiro; Tanase, Masakazu*; Fujisaki, Saburo*; Ota, Akio*
Proceedings of 1st Asian Symposium on Material Testing Reactors (ASMTR 2011), p.77 - 82, 2011/02
no abstracts in English
 Tc extraction techniques from
Tc extraction techniques from  Mo by (n,
Mo by (n, ) reaction
) reactionKimura, Akihiro; Hori, Naohiko; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Ishihara, Masahiro; Yamabayashi, Hisamichi*; Tanase, Masakazu*; Fujisaki, Saburo*; Sato, Yuichi*
JAEA-Review 2010-053, 23 Pages, 2010/11
Production techniques of  Mo, parent nuclide of
Mo, parent nuclide of  Tc, have been developed for the industrial utilization as medical diagnosis medicine after the JMTR refurbishment. The (n,
Tc, have been developed for the industrial utilization as medical diagnosis medicine after the JMTR refurbishment. The (n, ) method is proposed in JMTR because of low-amount radioactive wastes and easy
) method is proposed in JMTR because of low-amount radioactive wastes and easy  Tc production process. In this study, the production of the high-density MoO
Tc production process. In this study, the production of the high-density MoO pellet and concentration techniques of
pellet and concentration techniques of  Tc solution were developed. As the trial test, the MoO
Tc solution were developed. As the trial test, the MoO pellets with high density were produced by the SPS (Spark Plasma Sintering) method. On the other hands, it was possible to concentrate
pellets with high density were produced by the SPS (Spark Plasma Sintering) method. On the other hands, it was possible to concentrate  Tc solution by the solvent extraction using Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK). From the result, the
Tc solution by the solvent extraction using Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK). From the result, the  Tc concentrating device with more than 80% concentration efficiency, was performed successfully.
Tc concentrating device with more than 80% concentration efficiency, was performed successfully.
 Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents for (n,
Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents for (n, ) method; Joint experiment report on irradiation technology of RI production (STC No.2
) method; Joint experiment report on irradiation technology of RI production (STC No.2 II) (Joint research)
II) (Joint research)Kimura, Akihiro; Izumo, Hironobu; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Hori, Naohiko; Ishihara, Masahiro; Bannykh, V.*; Gluschenko, N.*; Chakrova, Y.*; Chakrov, P.*
JAEA-Testing 2010-002, 20 Pages, 2010/08
JMTR has a plan to produce  Mo, which is the parent nuclide of radiopharmaceutical
Mo, which is the parent nuclide of radiopharmaceutical  Tc, by (n,
Tc, by (n, ) method. The cooperation experiments for
) method. The cooperation experiments for  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution with the Poly-Zirconium Compound (PZC) and the Molybdate Zirconium Gel (Zr-gel) methods were carried out at Kazakhstan National Nuclear Energy Center (NNC) in October, 2009. The
Tc elution with the Poly-Zirconium Compound (PZC) and the Molybdate Zirconium Gel (Zr-gel) methods were carried out at Kazakhstan National Nuclear Energy Center (NNC) in October, 2009. The  Mo adsorption capability was the same level as reference data, however the
Mo adsorption capability was the same level as reference data, however the  Tc elution capability with PZC was lower than reference data in this test. Therefore, re-experiments of
Tc elution capability with PZC was lower than reference data in this test. Therefore, re-experiments of  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution with both methods were carried out at NNC. As a result, the
Tc elution with both methods were carried out at NNC. As a result, the  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution capabilities were obtained as the same levels as reference data. Additionally,
Tc elution capabilities were obtained as the same levels as reference data. Additionally,  Tc solution was high purity by the elution method connected with alumina column.
Tc solution was high purity by the elution method connected with alumina column.
 ) cross-sections of a nucleus in the range 0.008
) cross-sections of a nucleus in the range 0.008 
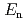
 20 MeV
20 MeVSegawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Fukahori, Tokio; Matsue, Hideaki; Oshima, Masumi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 618(1-3), p.153 - 159, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new measurement system to determine the neutron-capture cross section of a nucleus at 0.008 
 20 MeV has been installed at the 4 MV Pelletron accelerator laboratory at the facility of radiation standards at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Pulsed neutrons are produced by bombarding a pulsed proton beam on
20 MeV has been installed at the 4 MV Pelletron accelerator laboratory at the facility of radiation standards at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Pulsed neutrons are produced by bombarding a pulsed proton beam on  Li (or
Li (or  H) or a deuteron beam on
H) or a deuteron beam on  H. The performance of the new system was studied by measuring discrete
H. The performance of the new system was studied by measuring discrete  rays from neutron capture by
rays from neutron capture by  Pb and
Pb and  Pb to their low-lying states at several resonances at 10
Pb to their low-lying states at several resonances at 10 
 110 keV using neutrons from
110 keV using neutrons from  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be. The
Be. The  rays were detected with a good signal-to-noise ratio by means of a highly sensitive anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer combined with a time-of-flight method. The present study demonstrated good sensitivity of the new system to determine the neutron-capture cross section of a nucleus at keV neutron energy.
rays were detected with a good signal-to-noise ratio by means of a highly sensitive anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer combined with a time-of-flight method. The present study demonstrated good sensitivity of the new system to determine the neutron-capture cross section of a nucleus at keV neutron energy.
 Mo-production facility in JMTR
Mo-production facility in JMTRKimura, Akihiro; Iimura, Koichi; Hosokawa, Jinsaku; Izumo, Hironobu; Hori, Naohiko; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Kanno, Masaru; Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-072, 18 Pages, 2010/03
JAEA has a plan to produce  Mo, a parent nuclide of
Mo, a parent nuclide of  Tc. At present, radioisotopes are indispensable for a diagnosis and treatment in the medical field. Demand of
Tc. At present, radioisotopes are indispensable for a diagnosis and treatment in the medical field. Demand of  Tc (half life 6h) used as a radiopharmaceutical increases up year by year. Moreover, the expansion of demand will be expected in future. However, the supply of
Tc (half life 6h) used as a radiopharmaceutical increases up year by year. Moreover, the expansion of demand will be expected in future. However, the supply of  Mo in Japan depends fully on the import from foreign countries. Therefore, it is necessary to supply
Mo in Japan depends fully on the import from foreign countries. Therefore, it is necessary to supply  Mo stably by the domestic production. There are two methods of
Mo stably by the domestic production. There are two methods of  Mo (half life 65.9h) production; the one is the nuclear fission (n,fiss) method, and the other is the (n,
Mo (half life 65.9h) production; the one is the nuclear fission (n,fiss) method, and the other is the (n, ) method using the
) method using the  Mo target.
Mo target.  Mo production in the JMTR with the (n,
Mo production in the JMTR with the (n, ) method was studied and evaluated. As a result, it was found that the partial amount of
) method was studied and evaluated. As a result, it was found that the partial amount of  Mo demand is possible to supply stably if a new hydraulic-rabbit-irradiation-facility (HR) is used.
Mo demand is possible to supply stably if a new hydraulic-rabbit-irradiation-facility (HR) is used.
 Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents for (n,
Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents for (n, ); Method-joint experiment report on irradiation technology of RI production (STC No. 2-II) (Joint research)
); Method-joint experiment report on irradiation technology of RI production (STC No. 2-II) (Joint research)Kimura, Akihiro; Izumo, Hironobu; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Hori, Naohiko; Ishihara, Masahiro; Bannykh, V.*; Gluschenko, N.*; Chakrova, Y.*; Chakrov, P.*
JAEA-Technology 2009-075, 23 Pages, 2010/02
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has a plan to produce  Mo, which is the parent nuclide of radiopharmaceutical
Mo, which is the parent nuclide of radiopharmaceutical  Tc, by (n,
Tc, by (n, ) method. The
) method. The  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents should be evaluated since the specific activity of
Tc elution characteristics of molybdenum adsorbents should be evaluated since the specific activity of  Mo obtained by (n,
Mo obtained by (n, ) method is low. Therefore,
) method is low. Therefore,  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution tests with molybdenum adsorbents for the (n,
Tc elution tests with molybdenum adsorbents for the (n, ) method such as poly-zirconium compound (PZC) and molybdate zirconium gel were carried out under cooperation with the Kazakhstan National Nuclear Energy Center (NNC). As a result, the
) method such as poly-zirconium compound (PZC) and molybdate zirconium gel were carried out under cooperation with the Kazakhstan National Nuclear Energy Center (NNC). As a result, the  Mo adsorption performance of the adsorbents was the same level as conventional data, whereas the
Mo adsorption performance of the adsorbents was the same level as conventional data, whereas the  Tc elution performance of the adsorbents was lower than conventional data. The
Tc elution performance of the adsorbents was lower than conventional data. The  Mo adsorption and
Mo adsorption and  Tc elution performance will be investigated again in future.
Tc elution performance will be investigated again in future.
Kaminaga, Masanori; Niimi, Motoji; Hori, Naohiko; Takahashi, Kunihiro; Kanno, Masaru; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-056, 20 Pages, 2010/02
The JMTR is a light water moderated and cooled, beryllium reflected tank- type reactor using LUE silicide plate-type fuels. Its thermal power is 50 MW, maximum thermal and fast neutron flux is 4  10
10 m
m s
s . First criticality was achieved in March 1968, and its operation was stopped from August, 2006 for the refurbishment. The refurbishment is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. The renewed and upgraded JMTR will be re-started from FY2011. An investigation on aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, etc., and for tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out at the beginning of FY2007. As a result, some components were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability, and some components or structures were decided to repair. A visual inspection of inner side of the pressure vessel was carried out using an underwater camera in FY2008, and no serious damage was observed. Up to now, refurbishment works are in progress according to the planned schedule. In this paper, current status of JMTR refurbishment project is presented.
. First criticality was achieved in March 1968, and its operation was stopped from August, 2006 for the refurbishment. The refurbishment is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. The renewed and upgraded JMTR will be re-started from FY2011. An investigation on aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, etc., and for tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out at the beginning of FY2007. As a result, some components were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability, and some components or structures were decided to repair. A visual inspection of inner side of the pressure vessel was carried out using an underwater camera in FY2008, and no serious damage was observed. Up to now, refurbishment works are in progress according to the planned schedule. In this paper, current status of JMTR refurbishment project is presented.
Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Niimi, Motoji; Kaminaga, Masanori; Hori, Naohiko; Nagao, Yoshiharu
Proceedings of 12th International Group on Research Reactors (12th IGORR) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2009/10
The JMTR is a light water cooling tank typed reactor with first criticality in March 1968. The JMTR has been applied to fuel/material irradiation tests for LWRs, HTGR, fusion reactor and RI production. However, the JMTR operation was once stopped at August 2006, and the refurbishment works are now conducting. The reactor facilities will be renewed taking four years from the beginning of FY 2007, and necessary examination and works are carrying out on schedule. The renewed JMTR will be started from FY 2011, and be operated for a period of about 20 years until around FY 2030. The usability improvement of the JMTR, e.g. higher reactor availability-factor, shortening turnaround time to get irradiation results, attractive irradiation cost, business confidence, is also discussing with users as the preparations for re-operation. In the paper, status of the refurbishment of reactor facilities are introduced, moreover the future program using the JMTR will be prescribed.
Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hodatsu, Tsutomu*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Sano, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 69(6), p.605 - 609, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.67(Veterinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Sano, Tadashi*; Wada, Seiichi*; Suzuki, Keiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Ito, Takashi*; Nakazawa, Konomi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ito, Nobuhiko*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 115, 2007/02
 -rays and energetic carbon ions
-rays and energetic carbon ionsKakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Hodatsu, Tsutomu*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Sano, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ito, Nobuhiko*
Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 68(12), p.1269 - 1273, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.41(Veterinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hodatsu, Tsutomu*; Sano, Tadashi*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ito, Nobuhiko*
Journal of Radiation Research, 47(3-4), p.237 - 243, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Wada, Seiichi; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Ito, Nobuhiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.553 - 556, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)Determining the biological effects of a very low number of charged particles crossing the cell nucleus is interest for estimating the risk due to environmental exposure to charged particles. Especially it is necessary to detect the radiation damage induced by a precise number of charged particles in the individual cells. To compare the number of ions traversing the cell and the DNA damage produced by the hit ions, we applied comet assay. Cells attached on the ion track detector CR-39 were irradiated with 17.3 MeV/u 12C, 15.7 MeV/u, 10.4 MeV/u 20Ne and 6.9 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams at TIARA, JAERI-Takasaki. After irradiation, CR-39 was covered with 1 % agarose. After electrophoresis the CR-39 was taken off from the slide glass. The agarose gel on the CR-39 was stained with ethidium bromide and the opposite side of the CR-39 was etched with KOH-ethanol solution at 37  . We observed that the ion particles with higher LET value induced the heavier DNA damage, even by the same number of ion-hits within the irradiated cells.
. We observed that the ion particles with higher LET value induced the heavier DNA damage, even by the same number of ion-hits within the irradiated cells.
Wada, Seiichi*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Yamamoto, Kazuo; Ito, Nobuhiko*
JAERI-Review 2000-024, TIARA Annual Report 1999, p.80 - 82, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Katsuyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi; Abe, Ichiro*; Kuno, Tetsuya; Hori, S.*; Oi, Masahiro*
Proceedings of 12th World Conference in Earthquake Engineering (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2000/01
no abstracts in English