Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toyoda, Shin*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Yamaguchi, Ichiro*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Hirota, Seiko*; Oka, Toshitaka; Shimazaki, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Hideyuki*; Tani, Atsushi*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Interlaboratory comparison studies are important for radiation dosimetry in order to demonstrate how the technique is universally available. The set of standard samples are examined in each participating laboratory in the present study. After a set of standard samples together with the samples with unknown doses, which were prepared in the same laboratory as the standard samples, are measured at a participating laboratory, those samples are sent to another participating laboratory for next measurement. There is some small difference observed in the sensitivity (the slope of the dose response line) of the standard samples while the differences in the obtained doses for the samples with unknown doses are rather systematic, implying that the difference is mostly due to the samples but not to measurements.
Yada, Hiroki; Takaya, Shigeru; Morohoshi, Kyoichi*; Yokoi, Shinobu*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.23-00044_1 - 23-00044_13, 2023/08
To develop rationalized maintenance plans for nuclear power plants, the characteristics of each plant must be considered. For sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) plants, constraints on inspections exist due to the specialty that equipment retaining sodium must be handled, which is one of the important points that must be considered in maintenance rationalization. In this study, we propose a maintenance optimization scheme, which is a design support tool, using risk information to develop a maintenance strategy based on the system based code (SBC) concept. The SBC concept intends to provide a theoretical procedure to optimize the reliability of structure, system and components (SSCs) by administrating every related engineering requirements throughout the life of the SSCs from design to decommissioning. ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Code Case, N-875 was developed based on the SBC concept. The purpose of this study is to establish detailed procedures for the maintenance optimization scheme based on the procedure in Code Case N-875. Furthermore, a quantitative trial evaluation of the core support structure of the next SFR under development in Japan is also performed using the maintenance optimization scheme.
Morishita, Yuki; Takasaki, Koji; Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Tagawa, Akihiro; Shibata, Takuya; Hoshi, Katsuya; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Oura, Masatoshi*
Radiation Measurements, 160, p.106896_1 - 106896_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study proposes a newly developed phoswich alpha/beta detector that can discriminate alpha and beta particles emitted from the alpha and beta contaminations in the FDNPS site. The phoswich alpha/beta detector is made up of two layers of scintillators that detect alpha and beta particles. The pulse shape discrimination (PSD) method was used to detect alpha particles in high beta particle and high gamma-ray (comparable to gamma-ray dose rate near the FDNPS reactor building) environments. Due to a 23.3% full width at half maximum (FWHM) energy resolution for alpha particles, the detector can be used to distinguish between nuclear fuel materials such as plutonium and its radon progeny (Po-214). Moreover, the detector could distinguish alpha particles from  Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Niwa, Masakazu; Ueki, Tadamasa*; Hoshi, Hiroyuki*; Sugisaki, Yuichi*; Yagi, Koshi*; Tozawa, Terumasa
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 126(9), p.543 - 548, 2020/09
A large number of paleomagnetic and chronological studies have contributed to the elucidation of the early Miocene clockwise rotation of Southwest Japan associated with the major opening of back-arc basins of the Japan Sea. Paleomagnetic data from an andesitic parallel dike swarm in the Takane area, Takayama City, Gifu Prefecture, Central Japan, were previously reported, showing the easterly deflection of the observed magnetization direction compared to an early Miocene expected paleomagnetic direction. This must represent the clockwise rotation during the opening of the Japan Sea, if the dike swarm was intruded before the opening event. Here, we report new K-Ar hornblende ages from an andesite dike of the dike swarm. These ages are statistically indistinguishable, indicating emplacement of the dike swarm before the clockwise rotation.
Niwa, Masakazu; Ueki, Tadamasa*; Hoshi, Hiroyuki*; Sugisaki, Yuichi*
JAEA-Research 2020-003, 33 Pages, 2020/07
Ages of volcanic rocks are helpful information to understand the impact of volcanism concerning a site characterization and a safety assessment for geological disposal. In this study, mineralogical and geochemical data of altered volcanic rocks were collected using a polarizing microscope, X-ray diffractometer, X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, X-ray analytical microscope, and electron probe microanalyzer, to select targets suitable for reliable K-Ar dating. In addition, sample preparation procedures such as freeze-thawing and HCl treatment were examined to concentrate unaltered plagioclase which is one of major phenocrysts in volcanic rocks. These data and procedures were compiled in this report.
Morishita, Yuki; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 966, p.163795_1 - 163795_8, 2020/06
To date, alpha and high beta particle emitters have been detected in the reactor buildings of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). Since the beta radiation levels in the FDNPS buildings are extremely high, a commercial beta survey meter, such as a Geiger-Muller (GM) counter, would no longer have the ability to measure the beta contamination levels. In order to solve this issue, we utilized ultra-thin plastic scintillators to increase the detection rate of alpha and beta contamination. In this study, ultra-thin plastic scintillators with varied thicknesses of 7, 22, 24, 31, 39, and 55 um were prepared. To test their sensitivity, each scintillator was optically coupled to a glass plate and a 2-in square position-sensitive photomultiplier tube, and exposed to either an alpha, beta, or gamma source. Results from alpha spectrometry show that only the 55 um-thick plastic scintillator fully absorbed the alpha particles (5.5 MeV) with a 16.7% Full Width at Half Maximum. For alpha imaging under a high beta background, the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator was found to be the best choice, with an alpha to beta ratio of 652. This plastic scintillator also had the lowest sensitivity to beta particles, measuring only 41.74 cps when exposed to a 1 MBq  Sr/
Sr/ Y source in contact. It would therefore be possible to use the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator, to directly measure the surface contamination levels at the FDNPS site in real-time, where previous methods have fallen short. Thus, the developed detector would be a useful tool for the detection of alpha and beta contamination in the FDNPS.
Y source in contact. It would therefore be possible to use the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator, to directly measure the surface contamination levels at the FDNPS site in real-time, where previous methods have fallen short. Thus, the developed detector would be a useful tool for the detection of alpha and beta contamination in the FDNPS.
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(2), p.172 - 181, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We developed a remote continuous air monitoring (RCAM) system. The RCAM system consisted of a personal air monitor and a robot. The personal air monitor (poCAMon, SARAD, Germany) had a 400 mm ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the
ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the  Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of
Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of 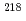 Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and
Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and  Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Measurements, 112, p.1 - 5, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:85.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)To detect plutonium isotopes ( Pu,
Pu,  Pu, and
Pu, and  Pu) in a field of high beta and
Pu) in a field of high beta and  background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and
background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and  -ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and
-ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and  background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and
background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and  rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to
rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to  rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and
rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and  background.
background.
Seki, Kotaro; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akimoto, Yuji*; Tokunaga, Takahito; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Haraga, Tomoko; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2016-013, 37 Pages, 2016/07
In this study, based on the simple and rapid analytical method established from the wastes from research facilities, we created analytical schemes which is applicable to rubble and plants collected at Fukushima Daiichi, then transported to Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. We examined the applicability, and confirmed quantifiability of radioactivity concentration with high recovery rate without being affected by fission products such as  Sr and
Sr and  Cs.
Cs.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Sakurai, Shinji; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Yagyu, Junichi; Hoshi, Ryo*; Kawamata, Yoichi; Kurihara, Kenichi; JT-60SA Team; Nishikawa, T.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.985 - 988, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Omori, Hiroyuki; Nebashi, Koji; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-029, 31 Pages, 2015/03
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required for the radioactive waste generated from research facilities in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to dispose of in a near-surface repository. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid waste generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid waste generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In this report, we reported the analytical data determined in fiscal 2014 ( Cs and
Cs and  Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
Mo) and summarized them with the radioactivity concentrations obtained in the past as basic data to consider the evaluation method of radioactivity concentrations in the stored waste taken from JPDR.
 -ray emitting radioactive nuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
-ray emitting radioactive nuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentSaito, Kimiaki; Tanihata, Isao*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Saito, Takashi*; Shimoura, Susumu*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Onda, Yuichi*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Ikeuchi, Yoshihiro*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.308 - 319, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:224 Percentile:98.8(Environmental Sciences)Yasuda, Mari; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-011, 59 Pages, 2014/08
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data about the radioactivity concentrations which accumulated by the analysis.
 adsorption
adsorption  lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water molecules
lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water moleculesIshizaki, Manabu*; Akiba, Sae*; Otani, Asako*; Hoshi, Yuji*; Ono, Kenta*; Matsuba, Mayu*; Togashi, Takanari*; Kanaizuka, Katsuhiko*; Sakamoto, Masatomi*; Takahashi, Akira*; et al.
Dalton Transactions, 42(45), p.16049 - 16055, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:178 Percentile:99.58(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have revealed the fundamental mechanism of specific Cs adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs
adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe
adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe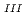
 [Fe
[Fe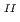 (CN)
(CN) ]3
]3 xH
xH O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH
O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH )0.70Fe
)0.70Fe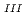 1.10[Fe
1.10[Fe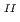 (CN)
(CN) ]
] 1.7H
1.7H O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs
O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe
adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe and 3[Fe
and 3[Fe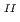 (CN)
(CN) ]
]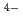 , showed much more efficient Cs
, showed much more efficient Cs adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
Sakamoto, Kensaku; Hoshi, Yoshiyuki*
JAEA-Testing 2013-002, 80 Pages, 2013/11
On research and development of various fields of nuclear energy, visualization of calculated data is especially useful to understand the result of simulation in an intuitive way. Many researchers who run simulations on the supercomputer in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) are used to transfer calculated data files from the supercomputer to their local PCs for visualization. In recent years, as the size of calculated data has gotten larger with improvement of supercomputer performance, reduction of visualization processing time as well as efficient use of JAEA network is being required. As a solution, we introduced a remote visualization system which has abilities to utilize parallel processors on the supercomputer and to reduce the usage of network resources by transferring data of intermediate visualization process. This paper reports a study on the performance of image processing with the remote visualization system. The visualization processing time is measured and the influence of network speed is evaluated by varying the drawing mode, the size of visualization data and the number of processors. Based on this study, a guideline for using the remote visualization system is provided to show how the system can be used effectively. An upgrade policy of the next system is also shown.
Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Watanabe, Koichi; Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Higuchi, Hidekazu
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-008, 16 Pages, 2013/11
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data about the radioactivity concentrations which accumulated by the analysis.
Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kamiya, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Kubo, Hirotaka; Masaki, Kei; Saeki, Hisashi; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.705 - 710, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Kameo, Yutaka; Sakai, Akihiro; Hoshi, Akiko; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Technology 2012-045, 37 Pages, 2013/02
It is necessary to establish practical evaluation methods to determine radioactivity concentrations of the important nuclides for safety assessment on disposal of radioactive wastes in order to dispose of low-level radioactive wastes generated from various nuclear facilities in JAEA. In this report, the practical evaluation methods such as the scaling factor method for JPDR facilities have been studied for disposal of the low-level radioactive wastes generated from nuclear reactor facilities in JAEA.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Hoshi, Yoshiyuki*; Sakamoto, Kensaku; Nakajima, Norihiro
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Computational Methods (ICCM 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/11
We research and develop a three-dimensional vibration simulator for an entire nuclear plant aiming at technical advances for more rational safety assessment of nuclear plant under an earthquake. The simulator includes "an entire structural simulation of ground-building-equipments (beam model)" and "an assembly structural simulation of parts to equipments (solid model)". As one approach to examine the quality of solid model which consists of thousands of parts, we have established a trial tool to perform the assembly structural simulation for a small number of parts by zooming in on a part of equipments in the entire structural simulation, and to compare results. To verify the tool, we applied the tool to static and dynamic simulations for a cantilever with various cross sections, and a static simulation of a small number of parts of nuclear plant, and confirmed results for solid model well coincide with those for beam model.
Hoshi, Akiko; Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Yasuda, Mari; Watanabe, Koichi; Sakai, Akihiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Kogure, Hiroto; Higuchi, Hidekazu; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-011, 31 Pages, 2011/10
Simple and rapid methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations are required to be established for the near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research facilities at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to establish the methods to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of miscellaneous solid wastes generated from research and testing reactors, we collected and analyzed samples from miscellaneous solid wastes generated by the decommissioning of JPDR (Japan Power Demonstration Reactor). In the present paper, we summarized data (262 data) about the radioactivity concentrations of the 7 important nuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs) which accumulated by the analysis.
Cs) which accumulated by the analysis.