Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku*; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.14971_1 - 14971_8, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:78.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.30720_1 - 30720_7, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In this Letter, we report model verifications for a key physics for the L-H transition. Radial electric field excitation, using discharges having a two-step transition. Examining time derivative of Poissons equation, it is found that the sum of the loss cone loss current and neoclassical bulk viscosity current agrees the experimentally observed current in the order of magnitude at the first transition. Following second transition and an ambipolar condition in the L-mode cannot be explained by the models.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oda, Chie; Ishidera, Takamitsu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2014-030, 457 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and post-closure performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, based on some examples of developing method of hydro-geological structure model, acquired knowledge are arranged using the tree diagram, and model uncertainty and its influence on the evaluation items were discussed. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the developed approach for "defining conditions" has been reevaluated and improved from practical viewpoints. In addition, the uncertainty evaluation for the effect of use of cementitious material, as well as glass dissolution model, was conducted with analytical evaluation. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, based on survey of precedent procedures, multiple-approach for distribution coefficient of rocks was established, and the adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to sedimentary rock and granitic rock. Besides, an approach for solubility setting was developed including the procedure of selection of solubility limiting solid phase. The adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to key radionuclides.
Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto*; Inagaki, Manabu*; Koo, Shigeru*; Shibata, Masahiro; Itazu, Toru; Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Miyahara, Kaname; Apted, M. J.*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1665, p.39 - 45, 2014/07
In Japan, the likelihood of uplift/erosion on repository performance and waste isolation can be typically greatly reduced or excluded by careful siting, however, the inability to completely exclude the uplift/erosion scenario may require an analysis of the consequences of such a scenario. For this purpose, an assessment approach has been developed to more realistically treat the effect of uplift/erosion for a hypothetical repository located in sedimentary host rock. A key advantage to this approach is the extrapolation of the geohistory of modern analogue sites to develop credible initial inputs for future volunteer sites that may be poorly characterized at the initial stages of site investigation. In addition, the approach provides a systematic basis for bounding the range of possible evolution in thermal-hydrological-mechanical-chemical conditions of a repository experiencing different uplift/ erosion rates.
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(7), p.073017_1 - 073017_14, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:77.22(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the JFT-2M tokamak, limit-cycle oscillation among several variables is observed before L-to-H transition. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the LCO is analyzed in detail. Zonal fows are not seen, and modulation in edge-localized poloidal flow and density gradient is observed. Modulation is also seen in Reynolds stress, caused by that in turbulence intensity and turbulence wavenumber. However, flow acceleration is not able to be explained by the modulation in the Reynolds stress. Rapid inward propagation in density gradient and turbulence packet is also observed. Characteristics of the propagation are veried by means of turbulence spreading theory and diffusion theory.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Hayano, Akira; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Oda, Chie; Kitamura, Akira; Osawa, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-037, 455 Pages, 2013/12
Following FY2011, JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, the tree diagram of methodology of groundwater travel time has been extended for crystalline rock, in addition, tree diagram for sedimentary rock newly has been organized. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the existing approach has been improved in terms of a practical task, and applied and tested for near field focusing on the buffer. In addition, the uncertainty of some important processes and its impact on safety functions are discussed though analysis. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, the approaches for parameter setting have been developed for sorption for rocks and solubility, and applied and tested through parameter setting exercises for key radionuclides.
Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Ito, Sanae*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Ida, Katsumi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 111(3), p.035002_1 - 035002_5, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:94 Percentile:94.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In this Letter, we report analyses of spatiotemporal dynamics of turbulence and structure in the limit cycle oscillation that precedes L-to-H transition. Zonal flows are not observed during LCO, and the oscillation is the periodic generations/decays of barrier with edge localized mean flow. Oscillatory Reynolds stress is found too small to accelerate the LCO flow. Changes of the density gradient and turbulence amplitude are found to propagate into the core in a ballistic manner, suggesting a cause of fast change of core transport after H-mode transition.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Hayano, Akira; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Taniguchi, Naoki; Oda, Chie; Kitamura, Akira; Osawa, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-032, 298 Pages, 2012/09
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and performance assessment in preliminary investigation phase. The topics and the conducted research are follows; (1) Study on selection of host rock: in terms of hydraulic properties, items for assessing rock property, and assessment methodology of groundwater travel time has been organized with interaction from site investigation. (2) Study on development of scenario: the existing approach has been embodied, in addition, the phenomenological understanding regarding dissolution of and nuclide release from vitrified waste, corrosion of the overpack, long-term performance of the buffer are summarized. (3) Study on setting nuclide migration parameters: the approach for parameter setting has been improved for sorption and diffusion coefficient of buffer/rock, and applied and tested for parameter setting of key radionuclides. (4) Study on ensuring quality of knowledge: framework for ensuring quality of knowledge has been studied and examined aimed at the likely disposal facility condition.
Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kanki, Takashi*; Koga, J. K.; Ishihara, Osamu*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(9), p.534 - 536, 2012/09
Kawamura, Makoto; Makino, Hitoshi; Sasao, Eiji; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Umeda, Koji; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Osawa, Hideaki; Ebashi, Takeshi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-027, 85 Pages, 2010/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have developed a formal evaluation method to assess the potential impacts of natural phenomena (earthquakes and faulting; volcanism; uplift, subsidence, denudation and sedimentation; climatic and sea-level changes) on a high level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal system for the purpose of maintenance of evaluation method for potential impacts of natural phenomena within more realistic view. In this report, we developed a framework as a part of the total system performance assessment for two purposes: the first one is quantification of relationship of characteristic of natural phenomena between geological environmental conditions (T-H-M-C-G), and the other one is quantification of relationship of T-H-M-C-G condition between parameters of performance assessment. We tried to apply the framework to all natural phenomena to confirm the effectiveness of the framework. On the other hand, we applied an argument-diagram that was developed one of the methods of the knowledge management to elicit future tasks. As a result, to apply the framework, we could show that information integration could carry out efficiently, and information integration was attained by the common framework by combining information on geohistory and existing information of natural phenomena and geological environmental conditions as modern-analogue. We could show that suitable scenarios might be chosen by information integration. Furthermore, we were able to elicit future tasks to this study by applying the argument-diagram.
Koo, Shigeru*; Inagaki, Manabu
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-006, 41 Pages, 2010/06
In the HLW disposal system, numerical evaluation for radionuclide transport with the time-dependent parameters is necessary to evaluate various scenarios. In H12 report, numerical code MESHNOTE and TIGER were used for the evaluation of some natural phenomena scenarios that had to handle the time-dependent parameters. In the future, the necessity of handling the time-dependent parameters will be expected to increase, and more efficient calculation and improvement of quality control of input/output parameters will be required. Therefore, for the purpose of corresponding this requirement, a radionuclide transport model has been developed on the Goldsmith GoldSim is a general simulation software, that was used for the computation modeling of Yucca Mountain Project. The conceptual model, the mathematical model and the verification of the GoldSim Model are described in this report. In the future, application resources on this report will be able to upgrade for perturbation scenarios analysis model.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Koo, Shigeru*; Ebina, Takanori*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Inagaki, Manabu
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-009, 62 Pages, 2009/07
Reference case of safety assessment analysis at the H12 report was calculated using the numerical code MESHNOTE and MATRICS mainly. On the other hand, recently general simulation software witch has a character of object-oriented is globally used and the numerical code GoldSim is typical software. After the H12 report, probability theory analysis and sensitivity analysis using GoldSim have carried out by statistical method for the purpose of following up safety assessment analysis at the H12 report. On this report, details of the method for the model design using GoldSim are summarized, and to confirm calculation reproducibility, verification between the H12 report and GoldSim results were carried out. And the guide book of calculation method using GoldSim is maintained for other investigators at JAEA who want to calculate reference case on the H12 report. In the future, application resources on this report will be able to upgrade probability theory analysis and other conceptual models.
Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Inagaki, Manabu; Koo, Shigeru*; Shibata, Masahiro; Itazu, Toru; Nakajima, Kunihiko*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Research 2008-117, 36 Pages, 2009/03
It is considered that it is possible to avoid the effect of the uplift and denudation process on geological disposal system by siting and a repository design. However, since the uplift/denudation continues far into the future, it is important to enhance the confidence of the methodology to evaluate such an effect, based on the understanding of geohistorical information and potential impact on the disposal system. This paper presents an evolution pattern of the geological environment and the influence analysis in terms of system performance affected by the uplift and denudation process based on the relevant conceptual models for groundwater scenarios of the disposal system for a hypothetical sedimentary rock. As a result, it is indicated that the conceptual model is capable to identify a specific combination of patterns of system evolution of the geological environment in terms of features on the uplift and denudation process, and also provides technical basis for setting up parameters of nuclide migration model and the subsequent influence analysis. Consequently, it is also indicated that the evaluation methodology applied in this study is valuable to evaluate the uplift/denudation phenomena with specific geological environment, and the results obtained by the analysis could be valuable information for site investigation and/or the prediction of a future change trend for the uplift/denudation.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(1), p.015005_1 - 015005_7, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:45.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Transport analysis during the transient phase of heating (a dynamic transport study) applied to the plasma with internal transport barriers (ITBs) in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and the JT-60U tokamak is described. In the dynamic transport study the time of transition from the L-mode plasma to the ITB plasma is clearly determined by the onset of flattening of the temperature profile in the core region and a spontaneous phase transition from a zero curvature ITB (hyperbolic tangent shaped ITB) or a positive curvature ITB (concaved shaped ITB) to a negative curvature ITB (convex shaped ITB) and its back-transition are observed. The flattening of the core region of the ITB transition and the back-transition between a zero curvature ITB and a convex ITB suggest the strong interaction of turbulent transport in space.
Ida, Katsumi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ito, Kimitaka*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 101(5), p.055003_1 - 055003_4, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:79.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A spontaneous transition phenomena between two meta-stable states of plasmas with internal transport barrier (ITB), that are characterized by different radial profiles of second derivative of ion temperature inside the ITB region where the ion temperature gradient is large, is observed in the steady-state phase of magnetic shear in the negative magnetic shear plasma in JT-60U tokamak. The curvature asymmetry factor evaluated from the radial profile of second derivative of ion temperature profiles changes from 0.08 (symmetric curvature ITB) to -0.43 (asymmetric curvature ITB) during transition phase.
Ida, Katsumi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Matsunaga, Go; Koide, Yoshihiko
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(5), p.053506_1 - 053506_6, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:64.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new technique to measure the first and second derivative of the ion temperature profile has been developed using a charge exchange spectroscopy system with space modulation optics. The space observed is scanned up to  3 cm with a cosine wave modulation frequency up to 30 Hz by shifting the object lens in front of the optical fiber bundle by 0.5 mm with a piezoelement. The first and second derivatives of ion temperature are derived from the modulation component of the ion temperature measured using Fourier analysis.
3 cm with a cosine wave modulation frequency up to 30 Hz by shifting the object lens in front of the optical fiber bundle by 0.5 mm with a piezoelement. The first and second derivatives of ion temperature are derived from the modulation component of the ion temperature measured using Fourier analysis.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kubo, Hirotaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 53(1), p.114 - 129, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)We report on the applications of the ECH to the JT-60U tokamak. The ECH contributes to the advanced tokamak study in JT-60U in such respects as (1)NTM suppression, (2)Study on the internal transport barrier, (3)Impurity exhaust, (4)Tokamak start-up without center solenoid, (5)Current hole study, (6)Confinement and transport study, and (7)Start-up and shut-down assist. These contributions comes from the good local coupling of the ECH to the tokamak plasma.
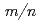 =2/1 rational surface during counter neutral beam injection in the large helical device
=2/1 rational surface during counter neutral beam injection in the large helical deviceIsayama, Akihiko; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Narushima, Yoshiro*; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Ida, Katsumi*; Nagayama, Yoshio*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(1), p.L45 - L55, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:39.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Inagaki, Shigeru*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ida, Katsumi*; Isayama, Akihiko; Tamura, Naoki*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shimozuma, Takashi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kubo, Shin*; Miura, Yukitoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(1), p.133 - 141, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:85.24(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English