Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

McGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kimuro, Shingo; Ishidera, Takamitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(12), p.1586 - 1594, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishidera, Takamitsu; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Yamada, Yoshihide*; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.536 - 546, 2023/05
The distribution coefficient ( ) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The
) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The  values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the
values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the  values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The
values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The  values were determined in the range 8
values were determined in the range 8  pH
pH  12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the
12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the  values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the
values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the  values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
Yanagida, Akinobu*; Ura, Yoko*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kawakita, Ryohei
Nara Bunkazai Kenkyujo Soritsu 70-Shunen Kinen Rombunshu; Bunkazai Ronso 5, p.843 - 856, 2023/03
To investigate chloride salt accumulation inside an iron artifact in soil, non-destructive analysis of three iron artifacts excavated from the Heijo Palace Site was conducted using elemental mapping by X-ray fluorescence analysis, micro-X-ray diffraction analysis, and X-ray computed tomography. Furthermore, the buried environments of the artifacts were presumed based on the previous reports of the environmental investigation at the Heijo Palace site. The results revealed the iron artifact's corrosion behavior was different individually- (1) the iron artifact that was presumed buried under oxidation environments had a goethite/magnetite corrosion layer and contained akageneite inside the corrosion layer. (2) the metal of the other iron artifacts buried under the oxidation environment had eluted absolutely and the artifacts had a rust layer formed by only goethite. (3) the other artifact buried in reduction environments had a rust layer composed of siderite. Accumulation of chloride salts inside an iron artifact was observed only in (1). Because each Cl concentration measured in underground water observation holes at the Heijo Palace Site showed almost the same level concentrations, it was presumed that the accumulation of chloride salts depended on the environmental factor except for Cl
concentration measured in underground water observation holes at the Heijo Palace Site showed almost the same level concentrations, it was presumed that the accumulation of chloride salts depended on the environmental factor except for Cl concentration. Based on these results, there was a possibility that the occurrence of local corrosion attributed to the separation of anodic and cathodic regions through the formation of the goethite/magnetite rust layer caused chloride salts accumulation inside an iron artifact.
concentration. Based on these results, there was a possibility that the occurrence of local corrosion attributed to the separation of anodic and cathodic regions through the formation of the goethite/magnetite rust layer caused chloride salts accumulation inside an iron artifact.
Francisco, P. C. M.; Matsumura, Daiju; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Environmental Science & Technology, 56(5), p.3011 - 3020, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.93(Engineering, Environmental)Ishidera, Takamitsu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 330(1), p.149 - 158, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Endo, Takashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Terashima, Motoki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(1), p.9 - 22, 2021/03
Evaluation method of colloid diffusion and filtration in compacted bentonites was developed using dendrimers. Diffusion and filtration behavior of PAMAM dendrimers with the size of 5.7 7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m
7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m and saturated with 0.005
and saturated with 0.005 0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 200, p.105910_1 - 105910_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.59(Chemistry, Physical)Tachi, Yukio; Sato, Tomofumi*; Takeda, Chizuko*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Fujiwara, Kenso; Iijima, Kazuki
Science of the Total Environment, 724, p.138097_1 - 138097_10, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.42(Environmental Sciences)To understand and predict radiocesium transport behaviors in the environment, sorption and fixation behaviors of radiocesium on river sediments from Ukedo and Odaka rivers around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were investigated systematically focusing on Cs sorption and fixation mechanisms and their relationship with Cs concentrations and sediment properties including clay mineralogy and organic matter.
Sugiura, Yuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Doi, Reisuke; Francisco, P. C. M.; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Matsumura, Daiju; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 324(2), p.615 - 622, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Chemistry, Analytical)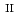 and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitates
and Si under anoxic and reducing conditions; Structural characteristics of ferrous silicate co-precipitatesFrancisco, P. C. M.; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio; Doi, Reisuke; Shiwaku, Hideaki
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 270, p.1 - 20, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:76.71(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio; Akagi, Yosuke*; Ashida, Takashi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.221 - 224, 2018/11
In Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, radionuclides are removed from contaminated water by the decontamination system using zeolite. In this study, sorption properties of U and Np on zeolite were investigated by batch sorption experiments to obtain fundamental information for predicting the radionuclides inventory. High distribution coefficients were observed for U in the simulated sea water diluted 10 times by deionized water. In contrast, low distribution coefficient of U was observed in simulated sea water. Low distribution coefficients were observed for Np independent of simulated sea water concentration. Batch sorption experiments of U carried out as functions of sodium ion and total inorganic carbon concentration suggested that the distribution coefficient of U was strongly affected by the total inorganic carbon concentration. This result suggests that aqueous species of radionuclides and their sorption behavior need to be considered to estimate the inventory of radionuclides in zeolite.
Ishidera, Takamitsu
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(1), p.99 - 101, 2016/06
In this presentation, the author introduced an overview of the research and development on repository design and engineering technology and safety assessment on the geological disposal of radioactive waste as well as the examples of evaluation methods used in these R&Ds and recent studies.
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kurosawa, Seiichi*; Hayashi, Masanori*; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Beppu, Hikari*
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.161 - 172, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.04(Chemistry, Physical)The sorption and diffusion behavior of Cs in illite-added compacted montmorillonite was investigated by through-diffusion experiment. The obtained distribution coefficient of Cs for the illite-added compacted montmorillonite was several times larger than that for the montmorillonite without illite, while no increase of effective diffusion coefficient was observed for the illite-added compacted montmorillonite. The dominant sorption site of Cs on illite is considered to be the frayed edge site (FES) considering the Cs concentration in this experiment. Therefore, the surface diffusion of Cs sorbing on the FES on illite surface was considered to be negligible in compacted montmorillonite.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oda, Chie; Ishidera, Takamitsu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2014-030, 457 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and post-closure performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, based on some examples of developing method of hydro-geological structure model, acquired knowledge are arranged using the tree diagram, and model uncertainty and its influence on the evaluation items were discussed. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the developed approach for "defining conditions" has been reevaluated and improved from practical viewpoints. In addition, the uncertainty evaluation for the effect of use of cementitious material, as well as glass dissolution model, was conducted with analytical evaluation. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, based on survey of precedent procedures, multiple-approach for distribution coefficient of rocks was established, and the adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to sedimentary rock and granitic rock. Besides, an approach for solubility setting was developed including the procedure of selection of solubility limiting solid phase. The adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to key radionuclides.
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Xia, X.*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kikuchi, Yoshio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(8), p.763 - 772, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)For safety assessment of high-level radioactive waste disposal, it is important to identify the forms of corrosion products migrating from overpack material into compacted bentonite. In this study, the carbon steel, which was previously corroded electrochemically under aerobic condition, was in contact with compacted Kunigel V1 and Kunipia F under reducing condition for 3-4 years at room temperature. The corrosion products migrating from carbon steel into compacted bentonites were investigated by the selective dissolution analysis, which can estimate the crystallinity of Fe-bearing compounds. The valence of iron in corrosion products was investigated spectrophotometrically. Furthermore, the alteration of smectite contained in compacted bentonite to Fe-smectite was analyzed by X-ray diffractometry (XRD). The results of selective dissolution and valence analysis suggested that the corrosion products in compacted bentonite were amorphous, non-crystalline or poorly ordered Fe(OH) and Fe(OH)
and Fe(OH) . In the XRD profiles, no diffraction peak suggesting the existence of Fe-smectite in the compacted bentonite was found. Therefore, the corrosion products in compacted bentonite were considered to have no effect on the alteration of smectite contained in Kunigel V1 and Kunipia F to Fe-smectite.
. In the XRD profiles, no diffraction peak suggesting the existence of Fe-smectite in the compacted bentonite was found. Therefore, the corrosion products in compacted bentonite were considered to have no effect on the alteration of smectite contained in Kunigel V1 and Kunipia F to Fe-smectite.
 and I
and I in compacted bentonite
in compacted bentoniteIshidera, Takamitsu; Miyamoto, Shinya*; Sato, Haruo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(7), p.610 - 616, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, the effective diffusion coefficients (
 ) for CO
) for CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I ions in compacted bentonite (Kunigel V1) were determined as a function of NaNO
ions in compacted bentonite (Kunigel V1) were determined as a function of NaNO concentrations from 0.01 to 5 mol/dm
concentrations from 0.01 to 5 mol/dm . The
. The 
 values increased from 10
values increased from 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s with increasing NaNO
/s with increasing NaNO concentration. The rock capacity factor
concentration. The rock capacity factor  , indicative of the effective porosity, were also increased with increasing NaNO
, indicative of the effective porosity, were also increased with increasing NaNO concentration. The maximum
concentration. The maximum  values of 0.21 for Cl
values of 0.21 for Cl ion and of 0.25 for I
ion and of 0.25 for I ion at 5 mol/dm
ion at 5 mol/dm NaNO
NaNO concentration were lower than the net porosity of compacted bentonite (0.40). Therefore, the increases in the
concentration were lower than the net porosity of compacted bentonite (0.40). Therefore, the increases in the 
 values were interpreted by the decrease of anion exclusion effect. The
values were interpreted by the decrease of anion exclusion effect. The 
 values for Cl
values for Cl and I
and I ions normalized by the diffusivities for diffusants in the bulk water were found to increase in proportion to the
ions normalized by the diffusivities for diffusants in the bulk water were found to increase in proportion to the  values on the log-log diagram. The maximum
values on the log-log diagram. The maximum  value for CO
value for CO
 ion was higher than the net porosity. The high concentration of CO
ion was higher than the net porosity. The high concentration of CO
 ion was also found in the concentration profile in compacted bentonite. This retention of CO
ion was also found in the concentration profile in compacted bentonite. This retention of CO
 ion was possibly accounted for by isotopic exchange of
ion was possibly accounted for by isotopic exchange of  C with inactive carbon of calcite in Kunigel V1.
C with inactive carbon of calcite in Kunigel V1.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Shibata, Masahiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Iijima, Kazuki; Sato, Haruo; Kitamura, Akira; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kurosawa, Susumu; Xia, X.; et al.
Hoshasei Haikibutsu Anzen Kenkyu Nenji Keikaku (Heisei-13-Nendo Heisei-17-Nendo) Kenkyu Seika Hokokushu, p.153 - 170, 2006/03
Heisei-17-Nendo) Kenkyu Seika Hokokushu, p.153 - 170, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
 on Diffusion of CO
on Diffusion of CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I Ions in Tuff
Ions in TuffIshidera, Takamitsu; Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 2005-018, 49 Pages, 2005/09
The migration data of C,
C, Cl and
Cl and I nuclides are required for safety assessment of TRU waste disposal. The specific phenomena for TRU waste disposal such as the influence of NaNO
I nuclides are required for safety assessment of TRU waste disposal. The specific phenomena for TRU waste disposal such as the influence of NaNO concentration and the hyper alkaline groundwater due to degradation of cementitious materials should be considered for reliable safety assessment. In this study, the effective diffusion coefficient (De) for CO
concentration and the hyper alkaline groundwater due to degradation of cementitious materials should be considered for reliable safety assessment. In this study, the effective diffusion coefficient (De) for CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I ions in tuff were determined with various NaNO
ions in tuff were determined with various NaNO concentrations under hyper alkaline condition. The obtained De values for CO
concentrations under hyper alkaline condition. The obtained De values for CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I ions were on the order of 10
ions were on the order of 10 -10
-10 m
m /s and decreased with increasing NaNO3 concentration. The De values for HDO and HTO were also decreased with increasing NaNO
/s and decreased with increasing NaNO3 concentration. The De values for HDO and HTO were also decreased with increasing NaNO concentration. Because the degradation of tuff samples was not observed by X-Ray diffractometry, SEM and EPMA, the decreases in the De values were considered to be due to the decreases in the diffusivities in free water. The apparent diffusion coefficient (Da) values for Cl
concentration. Because the degradation of tuff samples was not observed by X-Ray diffractometry, SEM and EPMA, the decreases in the De values were considered to be due to the decreases in the diffusivities in free water. The apparent diffusion coefficient (Da) values for Cl ion with 5mol/dm
ion with 5mol/dm NaNO
NaNO concentration and for CO
concentration and for CO
 ion were lower than those of the other conditions. These low Da values suggested retardation in tuff samples.
ion were lower than those of the other conditions. These low Da values suggested retardation in tuff samples.

 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I ions in Compacted Bentonite
ions in Compacted BentoniteIshidera, Takamitsu; Miyamoto, Shinya*; Sato, Haruo
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.264 - 269, 2005/05
For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, the effective diffusion coefficients (De) for CO
 , Cl
, Cl and I
and I ions in compacted bentonite (Kunigel V1) were determined as a function of silica sand contents under hyper alkaline condition. The obtained De values for three diffusants were on the order of 10
ions in compacted bentonite (Kunigel V1) were determined as a function of silica sand contents under hyper alkaline condition. The obtained De values for three diffusants were on the order of 10 - 10
- 10 m
m /s and increased with increasing silica sand content. The effective porosity for diffusion of Cl
/s and increased with increasing silica sand content. The effective porosity for diffusion of Cl and I
and I ions, estimated from the rock capacity factor values, were also increased with increasing silica sand content. This close relationship indicated that the increases in the De values were due to the increase in effective porosity with increasing silica sand content. In the case of CO
ions, estimated from the rock capacity factor values, were also increased with increasing silica sand content. This close relationship indicated that the increases in the De values were due to the increase in effective porosity with increasing silica sand content. In the case of CO
 ion, the rock capacity factor values were higher than those for Cl
ion, the rock capacity factor values were higher than those for Cl and I
and I ions. The Da values for CO
ions. The Da values for CO
 ion were approximately one order of magnitude lower than those for Cl
ion were approximately one order of magnitude lower than those for Cl and I
and I ions. The differences in these behaviors suggested a possibility of isotopic exchange of
ions. The differences in these behaviors suggested a possibility of isotopic exchange of  C with the carbon of calcite contained in Kunigel V1.
C with the carbon of calcite contained in Kunigel V1.
Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Xia, X.; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Iijima, Kazuki
JNC TY8400 2004-005, 59 Pages, 2004/05
For the safety assessment of high level waste disposal, it is necessary to investigate the radionuclide migration in the presence of corrosion products of carbon steel under reducing condition. In this study, the reliable apparent diffusion coefficients of neptunium (Np) in bentonite were obtained by in-diffusion method and migration of the corrosion products was investigated. Furthermore, effects of the corrosion of carbon steel on Np diffusion were discussed. The corrosion of carbon steel under reducing condition provided Fe ions, which were considered to migrate in the interlayer spaces of montmorillonite sheets of bentonite exchanging with two Na
ions, which were considered to migrate in the interlayer spaces of montmorillonite sheets of bentonite exchanging with two Na ions. The corrosion rate of carbon steel was controlled by the diffusivity of Fe
ions. The corrosion rate of carbon steel was controlled by the diffusivity of Fe ions into bentonite when they were accumulated at the surface of carbon steel. The corrosion rate increased with increasing dry density of bentonite because of the increase of the diffusivity of Fe
ions into bentonite when they were accumulated at the surface of carbon steel. The corrosion rate increased with increasing dry density of bentonite because of the increase of the diffusivity of Fe ions. The corrosion rate was estimated to be ~0.1 micro m/y, which was remarkable lower than the setting value, 20 micro m/y, in the second progress report. The Np profiles in the bentonite consisted of two overlapping slopes, a fast and a slow fractions, for both the experiments with and without carbon steel. The apparent diffusion coefficients of the fast and the slow fraction of Np were 10
ions. The corrosion rate was estimated to be ~0.1 micro m/y, which was remarkable lower than the setting value, 20 micro m/y, in the second progress report. The Np profiles in the bentonite consisted of two overlapping slopes, a fast and a slow fractions, for both the experiments with and without carbon steel. The apparent diffusion coefficients of the fast and the slow fraction of Np were 10 ~10
~10 m
m /s and 10
/s and 10 ~10
~10 m
m /s, which were considered to be the diffusion of Np(V) and Np(IV), respectively. The corrosion of carbon steel provided strong reducing condition to keep most Np in the low oxidation state, Np(IV), which has lower solubility and mobility than Np(V). Therefore, it could be expected that the corrosion of carbon steel will restrain effectively migration of Np into the bentonite.
/s, which were considered to be the diffusion of Np(V) and Np(IV), respectively. The corrosion of carbon steel provided strong reducing condition to keep most Np in the low oxidation state, Np(IV), which has lower solubility and mobility than Np(V). Therefore, it could be expected that the corrosion of carbon steel will restrain effectively migration of Np into the bentonite.