Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
Ni D
D at high
at high 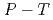 conditions
conditionsShito, Chikara*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Abe, Jun*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
American Mineralogist, 108(4), p.659 - 666, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:64.83(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The phase relation and crystal structure of Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D ) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under
) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under 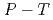 conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal (
conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal ( ) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe
) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe Ni
Ni D
D unlike fcc FeH
unlike fcc FeH (D
(D ). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium
). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium 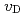 was determined as 2.45(4)
was determined as 2.45(4) 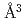 and 3.31(6)
and 3.31(6) 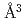 for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD
for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD . The
. The 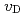 value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that
value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that 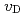 is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Yano, Yasuhide; Hashidate, Ryuta; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Kato, Shoichi; Onizawa, Takashi; Ito, Chikara; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-015, 64 Pages, 2022/01
From a view point of practical application of fast breeder reactor cycles, which takes advantage of safety and economic efficiency and makes a contribution of volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste, it is necessary to develop fuel cladding materials for fast reactors (FRs) in order to achieve high-burnup. Oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel have been studied for use as potential fuel cladding materials in FRs owing to their excellent resistance to swelling and their high-temperature strength in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It is very important to establish the materials strength standard in order to apply ODS steels as a fuel cladding. Therefore, it is necessary to acquire the mechanical properties such as tensile, creep rupture strength tests and so on. In this study, tensile and creep rupture strengths of 9Cr-ODS steel claddings were evaluated using by acquired these data. Because of the phase transformation temperature of 9Cr-ODS steel, temperature range for the evaluation was divided into two ones at AC1 transformation temperature of 850 C.
C.
Iizuka, Riko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Shito, Chikara*; Fukuyama, Ko*; Mori, Yuichiro*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12632_1 - 12632_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The Earth's core consist of Fe-Ni alloy with some light elements (H, C, O, Si, S etc.). Hydrogen (H) is the most abundant element in the universe and one of the promising candidates. In this study, we have investigated the effects of sulfur(S) on hydrogenation of iron-hydrous silicate system containing saturated water in the ideal composition of the primitive Earth. We observed a series of phase transitions of Fe, dehydration of the hydrous mineral, and formation of olivine and enstatite with increasing temperature. The FeS formed as the coexisting phase of Fe under high-pressure and temperature condition, but its unit cell volume did not increase, suggesting that FeS is hardly hydrogenated. Recovered samples exhibited that H and S can be incorporated into solid Fe, which lowers the melting temperature as Fe(H )-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
)-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
Sano, Asami; Kakizawa, Sho*; Shito, Chikara*; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
High Pressure Research, 41(1), p.65 - 74, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We applied Kawai-type multi-anvil assemblies (MA6-8) for time-of-flight neutron-diffraction experiments to achieve high pressures and high temperatures simultaneously. To achieve sufficient signal intensities, the angular access to the sample was enlarged using slits and tapers on the first-stage anvils. Using SiC-binder sintered diamond for the second-stage anvils that transmits neutrons, sufficient signal intensities were achieved at a high-pressure of  23.1 GPa. A high-temperature experiment was also conducted at 16.2 GPa and 973 K, validating the use of tungsten carbide for the second-stage anvils. The present study reveals the capability of the MA6-8 cells in neutron-diffraction experiments to attain pressures and temperatures beyond the limits of the conventional MA6-6 cells used in the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET at the MLF, J-PARC.
23.1 GPa. A high-temperature experiment was also conducted at 16.2 GPa and 973 K, validating the use of tungsten carbide for the second-stage anvils. The present study reveals the capability of the MA6-8 cells in neutron-diffraction experiments to attain pressures and temperatures beyond the limits of the conventional MA6-6 cells used in the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET at the MLF, J-PARC.
Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takuya; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Laser Applications, 33(1), p.012001_1 - 012001_16, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si at 14.7 GPa and 800 K
at 14.7 GPa and 800 KMori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Shito, Chikara*; Iizuka, Riko*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(6), p.309 - 313, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Mineralogy)The Earth's core is believed to contain some light elements because it is 10% less dense than pure Fe under the corresponding pressure and temperature conditions. Hydrogen, a promising candidate among light elements, has phase relations and physical properties that have been investigated mainly for the Fe-H system. This study specifically examined an Fe-Si-H system using in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to investigate the site occupancy of deuterium of hcp-Fez Si
Si hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe
hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe Si
Si hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe
hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe Si
Si ) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
Ito, Chikara; Maeda, Shigetaka; Inoue, Toshihiko; Tomita, Hideki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*
Radiation Protection, 40(6), p.491 - 495, 2020/11
A highly accurate and precise technique for measurement of the  Nb(n,n')
Nb(n,n') Nb reaction rate was established for the material surveillance tests, etc. in fast reactors. The self-absorption effect on the measurement of the characteristic X-rays emitted by
Nb reaction rate was established for the material surveillance tests, etc. in fast reactors. The self-absorption effect on the measurement of the characteristic X-rays emitted by  Nb was decreased by the solution and evaporation to dryness of niobium dosimeter. A highly precise count of the number of
Nb was decreased by the solution and evaporation to dryness of niobium dosimeter. A highly precise count of the number of  Nb atoms was obtained by measuring the niobium solution concentration using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. X-rays of
Nb atoms was obtained by measuring the niobium solution concentration using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. X-rays of  Nb were measured accurately by means of comparing the X-ray intensity of irradiated niobium solution with that of the solution in which stable
Nb were measured accurately by means of comparing the X-ray intensity of irradiated niobium solution with that of the solution in which stable  Nb was added. The difference between both intensities indicates the effect of
Nb was added. The difference between both intensities indicates the effect of 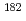 Ta, which is generated from an impurity tantalum, and the intensity of X-rays from
Ta, which is generated from an impurity tantalum, and the intensity of X-rays from  Nb was evaluated. Measurement error of the
Nb was evaluated. Measurement error of the  Nb(n,n')
Nb(n,n') Nb reaction rate was reduced to be less than 4%, which was equivalent to the other reaction rate errors of dosimeters used for Joyo dosimetry. In addition, an advanced technique using Resonance Ionization Mass Spectrometry was proposed for the precise measurement of
Nb reaction rate was reduced to be less than 4%, which was equivalent to the other reaction rate errors of dosimeters used for Joyo dosimetry. In addition, an advanced technique using Resonance Ionization Mass Spectrometry was proposed for the precise measurement of  Nb yield, and
Nb yield, and  Nb will be resonance-ionized selectively by discriminating the hyperfine splitting of the atomic energy levels between
Nb will be resonance-ionized selectively by discriminating the hyperfine splitting of the atomic energy levels between  Nb and
Nb and  Nb at high resolution.
Nb at high resolution.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Tanno, Takashi; Oka, Hiroshi; Yano, Yasuhide; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Kaito, Takeji; Hashidate, Ryuta; Kato, Shoichi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Ito, Chikara; et al.
2018 GIF Symposium Proceedings (Internet), p.305 - 314, 2020/05
Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) steel has been developed worldwide as a high-strength and radiation-tolerant steel used for advanced nuclear system. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing ODS steel as the primary candidate material of Sodium cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) high burn-up fuel cladding tube. Application of high burn-up fuel to SFR core can contribute to improvement of economical performance of SFR in conjunction with volume and hazardousness reduction of radioactive waste. This paper described the current status and future prospects of ODS tempered martensitic steel development in JAEA for SFR fuel application.
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Keisuke; Wakaida, Ikuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
A high-radiation resistant optical fiber has been developed in order to investigate the interiors of the reactor pressure vessels and the primary containment vessels at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The tentative dose rate in the reactor pressure vessels is assumed to be up to 1 kGy/h. We developed a radiation resistant optical fiber consisting of a 1000 ppm hydroxyl doped pure silica core and 4 % fluorine doped pure silica cladding. We attempted to apply the optical fiber to remote imaging technique by means of fiberscope. The number of core image fibers was increased from 2000 to 22000 for practical use. The transmissive rate of infrared images was not affected after irradiation of 1 MGy. No change in the spatial resolution of the view scope by means of image fiber was noted between pre- and post-irradiation. We confirmed the applicability of the probing system, which consists of a view scope using radiation-resistant optical fibers.
Sato, Satoshi*; Konno, Chikara; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Shionaga, Ryosuke*; Nose, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Yuji*; Hashimoto, Hirohide*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(4), p.410 - 417, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to enhance the neutron shielding performance, we developed concrete with boron of more than 10 wt%. We performed a neutron shielding experiment using the mockup of the newly developed boron-loaded concrete and DT neutrons at FNS in JAEA, and measured the reaction rates of the  Nb(n,2n)
Nb(n,2n)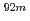 Nb and
Nb and  Au(n,
Au(n, )
)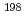 Au reactions in the mockup. The calculations were conducted by using MCNP-5.14 and FENDL-2.1. The calculation results agreed well with the measured ones, and we confirmed that the accuracy was very good on the atomic composition data of the boron-loaded concrete and their nuclear data. In addition, we calculated effective dose rates and reaction rates of the
Au reactions in the mockup. The calculations were conducted by using MCNP-5.14 and FENDL-2.1. The calculation results agreed well with the measured ones, and we confirmed that the accuracy was very good on the atomic composition data of the boron-loaded concrete and their nuclear data. In addition, we calculated effective dose rates and reaction rates of the  Co(n,
Co(n, )
) Co and
Co and  Eu(n,
Eu(n, )
) Eu reactions in the boron-loaded concrete and other concretes. It is concluded that the boron-loaded concrete has much better shielding performance for DT neutrons than other concretes.
Eu reactions in the boron-loaded concrete and other concretes. It is concluded that the boron-loaded concrete has much better shielding performance for DT neutrons than other concretes.
Yamamoto, Takahiro; Ito, Chikara; Maeda, Shigetaka; Ito, Hideaki; Sekine, Takashi
JAEA-Technology 2017-036, 41 Pages, 2018/02
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, the damaged upper core structure (UCS) was retrieved into the cask in May 2014 The dose rate on UCS surface was quite high due to the activation for over 30 years operation. In order to attain the optimum safety design, manufacture and operation of equipment for UCS replacement, the method to evaluate UCS surface dose rate was developed on the basis of C/E obtained by the in-vessel dose rate measurement in Joyo. In order to verify the evaluation method, the axial gamma-ray distribution measurement on the surface of the cask, which contained UCS, was conducted using a plastic scintillating optical fiber (PSF) detector. This paper describes the comparison results between calculation and measurement as follows. (1) The measured axial gamma-ray distribution on the cask surface had a peak on proper location with considering the cask shielding structure and agree well with the calculated distribution. (2) The C/E of axial gamma-ray distribution on the cask surface was ranged from 1.1 to 1.7. It was confirmed that the calculation for UCS replacement equipment design had a margin conservatively. Then, the results showed that the developed evaluation method for UCS replacement equipment design was sufficiently reliable.
Obana, Tetsuhiro*; Murakami, Haruyuki; Takahata, Kazuya*; Hamaguchi, Shinji*; Chikaraishi, Hirotaka*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; Kizu, Kaname; Natsume, Kyohei; Yoshida, Kiyoshi
Physica C, 518, p.96 - 100, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.97(Physics, Applied)Iwata, Yoshihiro; Sekiya, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.64 - 69, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)An ultrasensitive resonance ionization mass spectrometer that can be applied to evaluate krypton (Kr) contamination in xenon (Xe) dark matter detectors has been developed for measuring Kr at the parts-per-trillion (ppt) or sub-ppt level in Xe. The gas sample is introduced without any condensation into a time-of-flight mass spectrometer through a pulsed supersonic valve. Using a nanosecond pulsed laser at 212.6 nm, 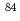 Kr atoms in the sample are resonantly ionized along with other Kr isotopes.
Kr atoms in the sample are resonantly ionized along with other Kr isotopes. 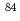 Kr ions are then mass separated and detected by the mass spectrometer in order to measure the Kr impurity concentration. With our current setup, approximately 0.4 ppt of Kr impurities contained in pure argon (Ar) gas are detectable with a measurement time of 1,000 s. Although Kr detection sensitivity in Xe is expected to be approximately half of that in Ar, our spectrometer can evaluate Kr contamination in Xe to the sub-ppt level.
Kr ions are then mass separated and detected by the mass spectrometer in order to measure the Kr impurity concentration. With our current setup, approximately 0.4 ppt of Kr impurities contained in pure argon (Ar) gas are detectable with a measurement time of 1,000 s. Although Kr detection sensitivity in Xe is expected to be approximately half of that in Ar, our spectrometer can evaluate Kr contamination in Xe to the sub-ppt level.
Murakami, Haruyuki; Kizu, Kaname; Ichige, Toshikatsu; Furukawa, Masato; Natsume, Kyohei; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kamiya, Koji; Koide, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Obana, Tetsuhiro*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.4201305_1 - 4201305_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:34.26(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)JT-60U magnet system will be upgraded to the superconducting coils in the JT-60SA programme of the Broader Approach activities. Terminal joint of Central Solenoid (CS) is wrap type Nb Sn-NbTi joint used for connecting CS (Nb
Sn-NbTi joint used for connecting CS (Nb Sn) and current feeder (NbTi). The terminal joints are placed at the top and the bottom of the CS systems. CS modules located at middle position of CS system need the lead extension from the modules to the terminal joint. The joint resistance measurement of terminal joint was performed in the test facility of National Institute for Fusion Science. The joint resistance was evaluated by the operating current and the voltage between both ends of the terminal joint part. Test results met the requirement of JT-60SA magnet system. The structural analysis of the lead extension and its support structure was conducted to confirm the support design. In this paper, the results of resistance test of joint and the structural analysis results of lead extension are reported.
Sn) and current feeder (NbTi). The terminal joints are placed at the top and the bottom of the CS systems. CS modules located at middle position of CS system need the lead extension from the modules to the terminal joint. The joint resistance measurement of terminal joint was performed in the test facility of National Institute for Fusion Science. The joint resistance was evaluated by the operating current and the voltage between both ends of the terminal joint part. Test results met the requirement of JT-60SA magnet system. The structural analysis of the lead extension and its support structure was conducted to confirm the support design. In this paper, the results of resistance test of joint and the structural analysis results of lead extension are reported.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Takegami, Hiroaki; Ito, Chikara; Suzuki, Keiichi*; Onuma, Hiroshi*; Hino, Ryutaro; Okumura, Tadahiko*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 78, p.166 - 175, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)In our study, we focused on a nondestructive inspection method by which cosmic-ray muons could be used to observe the internal reactor from outside the RPV and the CV. We conducted an observation test on the HTTR to evaluate the applicability of the method to the internal visualization of a reactor. We also analytically evaluated the resolution of existing muon telescopes to assess their suitability for the HTTR observation, and were able to detect the major structures of the HTTR based on the distribution of the surface densities calculated from the coincidences measured by the telescopes. Our findings suggested that existing muon telescopes could be used for muon observation of the internal reactor from outside the RPV and CV.
Obana, Tetsuhiro*; Takahata, Kazuya*; Hamaguchi, Shinji*; Chikaraishi, Hirotaka*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; Kizu, Kaname; Murakami, Haruyuki; Natsume, Kyohei; Yoshida, Kiyoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 90, p.55 - 61, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the cold test of the JT-60SA CS model coil made by Nb Sn CIC conductor, magnetic fields were measured using Hall sensors. While holding coil current of 20 kA, the magnetic fields were varying slightly with several long time constants. The range of the time constant was from 17 sec to 571 sec, which was much longer than the time constant derived from the measurement using the short straight sample. To validate the measurements, the magnetic fields of the model coil were calculated using the calculation model representing the positions of Nb
Sn CIC conductor, magnetic fields were measured using Hall sensors. While holding coil current of 20 kA, the magnetic fields were varying slightly with several long time constants. The range of the time constant was from 17 sec to 571 sec, which was much longer than the time constant derived from the measurement using the short straight sample. To validate the measurements, the magnetic fields of the model coil were calculated using the calculation model representing the positions of Nb Sn strands inside the CIC conductor. The calculations were in good agreement with the measurements. Consequently, the validity of magnetic field measurements was confirmed.
Sn strands inside the CIC conductor. The calculations were in good agreement with the measurements. Consequently, the validity of magnetic field measurements was confirmed.
Oguri, Shugo*; Kuroda, Yasuhiro*; Kato, Yo*; Nakata, Ryoko*; Inoue, Yoshizumi*; Ito, Chikara; Minowa, Makoto*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 757, p.33 - 39, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:95.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)We developed a segmented reactor antineutrino detector made of plastic scintillators for the nuclear safeguard application and demonstrate almost unmanned field operation at a commercial power plant reactor. We observed the difference of the reactor antineutrino flux with the reactor ON and OFF above the ground outside the reactor building.
Saeki, Morihisa; Iwanade, Akio; Ito, Chikara; Wakaida, Ikuo; Thornton, B.*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Oba, Hironori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.930 - 938, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:98.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)To inspect post-accident nuclear core reactor of the TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, a transportable fiber-coupled LIBS instrument was developed. The developed LIBS instrument was designed to analyze the underwater sample in high-radiation field by single-pulse breakdown with gas flow or double-pulse breakdown. To check the feasibility of the assembled fiber-coupled LIBS instrument to the inspection inside Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, we investigated (1) influence of radiation dose on optical transmittance of the laser delivery fiber, (2) survey of the LIBS techniques to analyze the underwater sample and (3) candidates of emission lines for analysis of the debris. By employing the selected emission lines, we demonstrated that the developed LIBS instrument can analyze the simulated debris underwater by the single-pulse breakdown with the gas flow with high signal to noise ratio.
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Nishimura, Akihiko; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo; Sugiyama, Akira; Chiyatani, Keiji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.944 - 950, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:90.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, it is necessary to survey the locations and conditions of fuel debris inside reactor pressure vessels or primary containment vessels under water and radiation environment in preparation for removing fuel debris. An optical fiber is well known for features such as signal transmission, light weight, superior insulation performance, water resistance and electromagnetic noise resistance. These features allow the optical fiber to simplify the instrumentation systems for in-vessel inspection, as long as provide that the optical fiber can be used under high radiation dose environment. The radiation resistance of an optical fiber was improved by increasing the amount of hydroxyl up to 1000 ppm in pure silica fiber. The improved optical fibers were irradiated with  -ray up to 1
-ray up to 1  10
10 Gy using a
Gy using a  Co source. They indicated a large peak around 600 nm and a peak tail from ultraviolet region, but no large absorption in infrared region except a hydroxyl absorption peak of 945 nm. We have confirmed that the optical fiber containing 1000 ppm hydroxyl has enough radiation resistance for radiation induced transmission losses and the infrared imaging is effective for observation under high radiation doses.
Co source. They indicated a large peak around 600 nm and a peak tail from ultraviolet region, but no large absorption in infrared region except a hydroxyl absorption peak of 945 nm. We have confirmed that the optical fiber containing 1000 ppm hydroxyl has enough radiation resistance for radiation induced transmission losses and the infrared imaging is effective for observation under high radiation doses.