Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:90.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Saito, Kosuke; Uno, Masayoshi*
Nuclear Technology, 205(3), p.474 - 485, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study evaluated the effects of plutonium content and self-irradiation on the thermal conductivity of mixed-oxide (MOX) fuel. Samples of UO fuel and various MOX fuels were tested. The MOX fuels had a range of plutonium contents, and some samples were stored for 20 years. The thermal conductivity of these samples was determined from thermal diffusivity measurements taken via laser flash analysis. Although the thermal conductivity decreased with increasing plutonium content, this effect was slight. The effect of self-irradiation was investigated using the stored samples. The reduction in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation depended on the plutonium content, its isotopic composition, and storage time. The reduction in thermal conductivity over 20 years' storage can be predicted from the change of lattice parameter. In addition, the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation was recovered with heat treatment, and recovered almost completely at temperatures over 1200 K. From these evaluation results, we formulated an equation for thermal conductivity that is based on the classical phonon-transport model. This equation can predict the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel thermal conductivity by accounting for the influences of plutonium content and self-irradiation.
fuel and various MOX fuels were tested. The MOX fuels had a range of plutonium contents, and some samples were stored for 20 years. The thermal conductivity of these samples was determined from thermal diffusivity measurements taken via laser flash analysis. Although the thermal conductivity decreased with increasing plutonium content, this effect was slight. The effect of self-irradiation was investigated using the stored samples. The reduction in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation depended on the plutonium content, its isotopic composition, and storage time. The reduction in thermal conductivity over 20 years' storage can be predicted from the change of lattice parameter. In addition, the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation was recovered with heat treatment, and recovered almost completely at temperatures over 1200 K. From these evaluation results, we formulated an equation for thermal conductivity that is based on the classical phonon-transport model. This equation can predict the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel thermal conductivity by accounting for the influences of plutonium content and self-irradiation.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Naito, Masanori*; Kojima, Masayoshi*; Kikura, Hiroshige*; Lister, D. H.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 341, p.112 - 123, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Improvement of plant reliability based on reliability-centered-maintenance (RCM) is going to be undertaken in NPPs. RCM is supported by risk-based maintenance (RBM). The combination of prediction and inspection is one of the key issues to promote RBM. Early prediction of IGSCC occurrence and its propagation should be confirmed throughout the entire plant systems which should be accomplished by inspections at the target locations followed by timely application of suitable countermeasures. From the inspections, accumulated data will be applied to confirm the accuracy of the code, to tune some uncertainties of the key data for prediction, and then, to increase their accuracy. The synergetic effects of prediction and inspection on application of effective and suitable countermeasures are expected. In the paper, the procedures for the combination of prediction and inspection are introduced.
 observation of dislocation evolution in ferritic and austenitic stainless steels under tensile deformation by using neutron diffraction
observation of dislocation evolution in ferritic and austenitic stainless steels under tensile deformation by using neutron diffractionSato, Shigeo*; Kuroda, Asumi*; Sato, Kozue*; Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Harjo, S.; Tomota, Yo*; Saito, Yoichi*; Todoroki, Hidekazu*; Onuki, Yusuke*; Suzuki, Shigeru*
Tetsu To Hagane, 104(4), p.201 - 207, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:44.29(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hoashi, Eiji*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Yagi, Juro*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2014 (PLASMA 2014) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2014/11
In the IFMIF/EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility/ Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity), the validation tests of the EVEDA lithium test loop with the world's highest flow rate of 3000 L/min was succeeded in generating a 100 mm-wide and 25 mm-thick free-surface lithium flow steadily under the IFMIF operation condition of a high-speed of 15 m/s at 250 C in a vacuum of 10
C in a vacuum of 10  Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Ida, Mizuho*; Ito, Yuzuru; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Edao, Yuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 66(1), p.46 - 56, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Hamaguchi, Dai; Endo, Shinya; Sakuraba, Naotoshi; Miyai, Hiromitsu; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Dai, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 450(1-3), p.27 - 31, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Masato*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hori, Toshihiko; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sato, Fumiaki; Fukui, Yuji*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Yamazaki, Masayoshi*; Sagawa, Ryu*; Miyajima, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.605 - 607, 2014/06
This report describes the present status of the klystron power supply systems for the J-PARC linac. The systems for the 181 MeV linac were operated from September to May. A few breakdowns were occurred, and are described in this report. The new systems for the upgrade of the linac from 181MeV to 400 MeV have been installed until now, and the 3 HVDCPSs and the 3 anode modulators of the new systems have been operated. All the systems for 400 MeV linac will be operated in this autumn.
 Mn
Mn )O
)O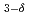
Shinoda, Ryoichi*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Sakurai, Yoshiharu*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Hirao, Norie; Baba, Yuji; Iwase, Akihiro*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 113(17), p.17E307_1 - 17E307_3, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.98(Physics, Applied)We revealed that the Ba(Co Mn
Mn )O
)O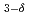 (BCMO) ceramic samples exhibited ferromagnetic-dielectric behavior below the magnetic transition temperature of about 35 K. The origin of their magnetic ordering was expected to super-exchange coupling of Co
(BCMO) ceramic samples exhibited ferromagnetic-dielectric behavior below the magnetic transition temperature of about 35 K. The origin of their magnetic ordering was expected to super-exchange coupling of Co (
(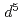 )-O
)-O -Mn
-Mn (
(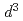 ) with bonding angle of 180
) with bonding angle of 180 . and/or Mn
. and/or Mn (
(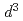 )-O
)-O -Mn
-Mn (
(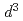 ) with bonding angle of 90
) with bonding angle of 90 . The magnetic spin momentum estimated by the magnetic Compton profiles (MCP) of the samples had similar temperature dependence as that determined by the SQUID measurement, which meant that the observed magnetic moments could be ascribed to the spin moment. The shapes of the MCPs of the samples were completely same regardless of the temperature measured. This result indicates that there are no changes of the momentum space distribution of spin density between ferromagnetic and paramagnetic states. So, this magnetic transition is simply caused by a thermal fluctuation of the spin.
. The magnetic spin momentum estimated by the magnetic Compton profiles (MCP) of the samples had similar temperature dependence as that determined by the SQUID measurement, which meant that the observed magnetic moments could be ascribed to the spin moment. The shapes of the MCPs of the samples were completely same regardless of the temperature measured. This result indicates that there are no changes of the momentum space distribution of spin density between ferromagnetic and paramagnetic states. So, this magnetic transition is simply caused by a thermal fluctuation of the spin.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kim, B. J.; Nozawa, Takashi; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Hirano, Michiko*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Kasada, Ryuta*; Yokomine, Takehiko*; Yoshida, Takahide*; Nogami, Shuhei*; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2013/03
 and TbFe
and TbFe
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Abe, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Mitsuaki*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.109 - 112, 2013/03
We performed local structure analysis of SmFe and TbFe
and TbFe in the crystallization process from amorphous by using synchrotron X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method. The giant mangetostrictive materials of these compounds can be controlled its property by ion irradiation. In amorphous TbFe
in the crystallization process from amorphous by using synchrotron X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method. The giant mangetostrictive materials of these compounds can be controlled its property by ion irradiation. In amorphous TbFe and SmFe
and SmFe , the mosaic block size was small and the short-range order structure owing to Fe-Fe network maintained. In crystalline SmFe
, the mosaic block size was small and the short-range order structure owing to Fe-Fe network maintained. In crystalline SmFe , a rigid long-range order structure of Fe-Fe and Sm-Sm network coexisted and it had a large mosaic block size. On the other hand, in crystalline TbFe
, a rigid long-range order structure of Fe-Fe and Sm-Sm network coexisted and it had a large mosaic block size. On the other hand, in crystalline TbFe , Fe-Fe network degraded by Tb-Tb network owing to its lattice tolerance.
, Fe-Fe network degraded by Tb-Tb network owing to its lattice tolerance.
Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji*; Hamaguchi, Dai; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Ono, Katsuto; Matsui, Hiroki; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Dai, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 431(1-3), p.44 - 51, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.8(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To evaluate the lifetime of the beam window of an accelerator-driven transmutation system (ADS), post irradiation examination (PIE) of the STIP (SINQ target irradiation program, SINQ; Swiss spallation neutron source) specimens was carried out. The specimens tested in this study were made from the austenitic steel JPCA (Japan primary candidate alloy). The specimens were irradiated at SINQ Target 4 (STIP-II) with high-energy protons and spallation neutrons. The irradiation conditions were as follows: the proton energy was 580 MeV, irradiation temperatures ranged from 100 to 430 C, and displacement damage levels ranged from 7.1 to 19.5 dpa. Tensile tests were performed in air at room temperature (R.T.), 250
C, and displacement damage levels ranged from 7.1 to 19.5 dpa. Tensile tests were performed in air at room temperature (R.T.), 250 C and 350
C and 350 C. Fracture surface observation after the tests was done by SEM (Scanning electron microscope). Results of the tensile tests performed at R.T. showed the extra hardening of JPCA at higher dose compared to the fission neutron irradiated data. At the higher temperatures, 250
C. Fracture surface observation after the tests was done by SEM (Scanning electron microscope). Results of the tensile tests performed at R.T. showed the extra hardening of JPCA at higher dose compared to the fission neutron irradiated data. At the higher temperatures, 250 C and 350
C and 350 C, the extra hardening was not observed. Degradation of ductility bottomed around 10 dpa, and specimens kept their ductility until 19.5 dpa. All specimens fractured in ductile manner. The result from a microstructure observation on a specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420
C, the extra hardening was not observed. Degradation of ductility bottomed around 10 dpa, and specimens kept their ductility until 19.5 dpa. All specimens fractured in ductile manner. The result from a microstructure observation on a specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420 C indicates that some agglomeration of bubbles on grain boundaries was observed in the specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420
C indicates that some agglomeration of bubbles on grain boundaries was observed in the specimen irradiated to 19.3 dpa at 420 C. However the tensile specimen irradiated up to 18.4 dpa at 425
C. However the tensile specimen irradiated up to 18.4 dpa at 425 C still exhibited little loss of ductility. Since He/dpa was very high on SINQ target irradiations, the formation of highly dense small bubbles in the matrix consequently avoided the accumulation of He on grain boundaries, which might have resulted in avoiding grain boundary embrittlement.
C still exhibited little loss of ductility. Since He/dpa was very high on SINQ target irradiations, the formation of highly dense small bubbles in the matrix consequently avoided the accumulation of He on grain boundaries, which might have resulted in avoiding grain boundary embrittlement.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Fukada, Satoshi*; Yagi, Juro*; Ida, Mizuho; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(12), p.691 - 705, 2012/12
no abstracts in English
Seito, Hajime; Matsui, Shinjiro*; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Ishikawa, Masayoshi*; Haruyama, Yasuyuki; Kaneko, Hirohisa; Kimura, Jun*; Kojima, Takuji
Zairyo Gijutsu, 30(1), p.10 - 16, 2012/01
The dosimetry of a 110 keV electron beam (EB) irradiation field is studied using a calorimeter, film dosimeter, and Monte Carlo simulation. This is important base for dose control in practical processing to guarantee the process reproducibility and product reliability. The simulation results are validated on the measurement of the energy fluence obtained by the calorimeter at one position in the air plane at different distances from a beam exit window. The spatial dose distribution obtained from the simulation is compared to that obtained by the film dosimeter. They show good agreement within  5.0%. The precision of
5.0%. The precision of  5.0% is sufficient to control the surface modification of polymers and the development of semiconductor devices in practical radiation processing. These results suggest that film dosimetry results at just one position in the air plane are sufficient to determine the irradiation characteristics of the low energy EB, and to provide a base of quality control measures in practical radiation processing.
5.0% is sufficient to control the surface modification of polymers and the development of semiconductor devices in practical radiation processing. These results suggest that film dosimetry results at just one position in the air plane are sufficient to determine the irradiation characteristics of the low energy EB, and to provide a base of quality control measures in practical radiation processing.
Sakurai, Hiroshi*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Agui, Akane
Magune, 6(5), p.270 - 276, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
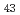 Co
Co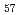 film by magnetic Compton scattering
film by magnetic Compton scatteringAgui, Akane; Matsumoto, Sayaka*; Sakurai, Hiroshi*; Tsuji, Naruki*; Homma, Satoshi*; Sakurai, Yoshiharu*; Ito, Masayoshi*
Applied Physics Express, 4(8), p.083002_1 - 083002_3, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:51.56(Physics, Applied)We have succeeded in measuring microscopic magnetic hysteresis loop of amorphous Tb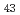 Co
Co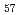 film. Spin selective magnetic hysteresis (SSMH) loop was measured by magnetic Compton scattering at synchrotron radiation facility SPring-8 and obtaining orbital selective magnetic hysteresis (OSMH) loop was firstly obtained by combining with result of macroscopic magnetic hysteresis loop.
film. Spin selective magnetic hysteresis (SSMH) loop was measured by magnetic Compton scattering at synchrotron radiation facility SPring-8 and obtaining orbital selective magnetic hysteresis (OSMH) loop was firstly obtained by combining with result of macroscopic magnetic hysteresis loop.
Kawamura, Masato*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Fang, Z.*; Fukui, Yuji*; Naito, Fujio*; Yamazaki, Masayoshi*; Tsubota, Naoaki; Futatsukawa, Kenta; Sato, Fumiaki; et al.
Proceedings of 8th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), 3 Pages, 2011/08
We will report about status of linac 400 MeV upgrade program and northeast Japan earthquake restoration. On March 11, the linac suffered serious damage as consequence of the earthquake, and was shuttled down for long term. Linac RF group restores the facilities and is accomplishing 400 MeV upgrade at the same time.
Kosugi, Shinya*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Ito, Masayoshi*; Sakurai, Yoshiharu*; Aiko, Kazuma*; Shimizu, Hirotaka*; Tahara, Yuki*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Journal of Applied Physics, 109(7), p.07B737_1 - 07B737_3, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.23(Physics, Applied)The magnetic Compton profiles of FeRh intermetallic compound were measured to study the ferromagnetism induced by 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The magnetic effect at 50 K increases with increasing the ion-fluence. The analysis of the experimental result revealed that the values of spin moment induced by the irradiation were close to the values of magnetization obtained by a superconducting quantum interference device magnetometer, suggesting that the ion irradiation mainly induces the spin magnetic moment.
Kawamura, Masato*; Fukui, Yuji*; Naito, Fujio*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Yamazaki, Masayoshi*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Kazuo
Proceedings of 25th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2010) (CD-ROM), p.887 - 889, 2010/09
This paper describes the present status, technical specifications, operating experience, and upgrade plane for the power supply system (PS system) for the klystrons in the J-PARC. The PS systems include both the high voltage DC power supplies (DCPSs), which drives one or four modulating-anode klystron each, and the anode-modulators, one per klystron. Currently, the energy output of the J-PARC linac is 181 MeV, which includes the energy necessary to run twenty 324 MHz klystrons. In 2012, the linac will add twenty-five 972 MHz klystrons and upgrade the energy output to 400 MeV.
Kita, Kenichiro; Narisawa, Masaki*; Nakahira, Atsushi*; Mabuchi, Hiroshi*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Advances in Polymer Derived Ceramics and Composites; Ceramic Transactions, Vol.213, p.45 - 50, 2010/06