Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Takano, Masao*; Sano, Naomi; Tani, Yukinori*; Ochiai, Shinya*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Niwa, Masakazu; Kawakami, Shinichi*
Sedimentology, 66(6), p.2490 - 2510, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:49.6(Geology)Micro-X-ray fluorescence (XRF) scanning spectroscopy of marine and lake sedimentary sequences can provide detailed paleoenvironmental records available through element intensities proxy data. However, problems for effects of interstitial pore water on the micro-XRF intensities have been pointed out so far because of direct measurement on the split wet sediment surfaces. In this study, new methods for the XRF corrections were developed by being considered with the micro-X-ray scanning spectroscopy.
Takano, Kazuya; Sakamoto, Yoshihiko; Morohoshi, Kyoichi*; Okazaki, Hitoshi*; Gima, Hiromichi*; Teramae, Takuma*; Ikarimoto, Iwao*; Botte, F.*; Dirat, J.-F.*; Dechelette, F.*
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
ASTRID has the objective to integrate innovative options in order to prepare the 4th generation reactors. In ASTRID, large number of tubes are installed above each fuel subassembly to monitor the core. These instrumentations such as thermocouples (TC) and Failed Fuel Detection and Location (FFDL) systems are integrated into Above Core Structure (ACS) with various sizes tubes. In the present study, the routing study for TC tubes and FFDL tubes was performed with 3D modeling and mock-up experiment of the ACS designed for ASTRID with 1500 MW thermal power in order to clarify the integration process and secure the design hypotheses. Although some problems on fabricability were found in the mock-up experiment, the possible solutions were proposed. The present study gives manufacturing feedback to design team and will contribute to increase the knowledge for ACS design and fabricability.
Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Ikeda, Hisashi*; Shibata, Kenji*; Kokubu, Yoko; Murakami, Takuma*; Tani, Yukinori*; Takano, Masao*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Tanaka, Atsushi*; Naito, Sayuri*; et al.
Global and Planetary Change, 164, p.11 - 26, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.77(Geography, Physical)Paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate changes in Siberia were reconstructed by continuous, high-resolution records of chemical compositions from a sediment core retrieved from the Buguldeika Saddle, Lake Baikal, dating back to the last 33 cal. ka BP. The Holocene climate followed by a shift at ca. 6.5 cal. ka BP toward warm and dry, suggesting that the climate system transition from the glacial to interglacial state occurred. In the last glacial period, the deposition of carbonate mud from the Primorsky Range was associated with Heinrich events (H3 and H1) and the Selenga River inflow was caused by meltwater of mountain glaciers in the Khamar-Daban Range. The anoxic bottom-water during Allerod-Younger Dryas was probably a result of weakened ventilation associated with reduced Selenga River inflow and microbial decomposition of organic matters from the Primorsky Range. The rapid decline in precipitation during the early Holocene may have been a response to the 8.2 ka cooling event.
Sasa, Narimasa; Kano, Takuma*; Machida, Masahiko; L'vov, V. S.*; Rudenko, O.*; Tsubota, Makoto*
Physical Review B, 84(5), p.054525_1 - 054525_6, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:84.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In a 2048 simulation of quantum turbulence within the Gross-Pitaevskii equation, it is demonstrated that the large-scale motions have a classical Kolmogorov-1941 energy spectrum
simulation of quantum turbulence within the Gross-Pitaevskii equation, it is demonstrated that the large-scale motions have a classical Kolmogorov-1941 energy spectrum 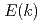
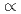

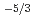 , followed by an energy accumulation with
, followed by an energy accumulation with 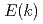
 const at
const at  about the reciprocal mean intervortex distance. This behavior was predicted by the L'vov-Nazarenko-Rudenko bottleneck model of gradual eddy-wave crossover, further developed in the paper.
about the reciprocal mean intervortex distance. This behavior was predicted by the L'vov-Nazarenko-Rudenko bottleneck model of gradual eddy-wave crossover, further developed in the paper.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:175 Percentile:98.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 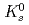 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
 dinger equation on
dinger equation on 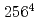 grids
gridsImamura, Toshiyuki*; Kano, Takuma*; Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko*; Machida, Masahiko
International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications, 24(3), p.319 - 334, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture)In order to explore quantum dynamics of coupled Josephson junctions, we develop a program solving directly the time-dependent Schr dinger equation by diagonalizing the Hamiltonian matrix and obtaining its ground and multiple low-lying excitation states. The Schr
dinger equation by diagonalizing the Hamiltonian matrix and obtaining its ground and multiple low-lying excitation states. The Schr dinger equation is defined on
dinger equation is defined on 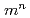 grids, in which
grids, in which  is the number of grid points discretized on a characteristic phase space of each junction and
is the number of grid points discretized on a characteristic phase space of each junction and  is the number of coupled junctions. In this paper, the calculated maximum system is that
is the number of coupled junctions. In this paper, the calculated maximum system is that 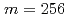 and
and 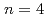 , i.e. the number of degrees of freedom reaches
, i.e. the number of degrees of freedom reaches 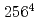 (=4,294,967,296). We examine possible effective numerical schemes and make a parallel tuning to optimize the communication on the Earth Simulator. We sustain floating-point operation performance exceeding 20% of the peak on 512 nodes (4,096 PEs). From systematic calculations, we find a new concept that "quantum-assisted synchronization" occurs with downsizing the junction plane. This is a discovery adding a quantum flavor to the classical concept "synchronization".
(=4,294,967,296). We examine possible effective numerical schemes and make a parallel tuning to optimize the communication on the Earth Simulator. We sustain floating-point operation performance exceeding 20% of the peak on 512 nodes (4,096 PEs). From systematic calculations, we find a new concept that "quantum-assisted synchronization" occurs with downsizing the junction plane. This is a discovery adding a quantum flavor to the classical concept "synchronization".
Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Kano, Takuma; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 69(12), p.3395 - 3397, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We numerically investigate a dependence of pairing interaction strength on quantum coherence and related tunneling dynamics in order to clarify whether the strong pairing interaction suppresses quantum coherent characters. The simulation is performed by using the attractive Hubbard model with double well potential. The simulation result reveals that the tunneling dynamics between the separated wells is dramatically suppressed with increasing the pairing interaction. This fact implies that the pair coherence is easily lost under randomness when the pairing interaction becomes very strong. We claim that such an issue is related to the loss of the pair coherence in under-doped High-
 superconductors. In addition, we note that the tunneling dynamics can be directly confirmed by using the crossover from BCS to BEC in atomic Fermi gases.
superconductors. In addition, we note that the tunneling dynamics can be directly confirmed by using the crossover from BCS to BEC in atomic Fermi gases.
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kano, Takuma
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2007 - March 2008, p.217 - 221, 2008/09
no abstracts in English
 five-dimensional Vlasov simulation
five-dimensional Vlasov simulationIdomura, Yasuhiro; Ida, Masato; Kano, Takuma; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji
Computer Physics Communications, 179(6), p.391 - 403, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:82 Percentile:95.34(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)A new conservative global gyrokinetic toroidal full- five-dimensional Vlasov simulation (GT5D) is developed using a novel non-dissipative conservative finite difference scheme. The scheme guarantees numerical stability by satisfying relevant first principles in the modern gyrokinetic theory, and enables robust and accurate simulations of tokamak micro-turbulence. GT5D is verified through comparisons of zonal flow damping tests, linear analyses of ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) modes, and nonlinear ITG turbulence simulations against a global gyrokinetic toroidal
five-dimensional Vlasov simulation (GT5D) is developed using a novel non-dissipative conservative finite difference scheme. The scheme guarantees numerical stability by satisfying relevant first principles in the modern gyrokinetic theory, and enables robust and accurate simulations of tokamak micro-turbulence. GT5D is verified through comparisons of zonal flow damping tests, linear analyses of ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) modes, and nonlinear ITG turbulence simulations against a global gyrokinetic toroidal  particle code. In the comparison, global solutions of the ITG turbulence are identified quantitatively by using two gyrokinetic codes based on particle and mesh approaches.
particle code. In the comparison, global solutions of the ITG turbulence are identified quantitatively by using two gyrokinetic codes based on particle and mesh approaches.
Oishi, Takuma*; Sasaki, Atsushi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ishiuchi, Shogo*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Nakano, Takashi*; Nakazato, Yoichi*
Neuropathology, 28(4), p.408 - 416, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:44.29(Clinical Neurology) thin film detector for neutrons
thin film detector for neutronsIshida, Takekazu*; Nishikawa, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Yoshifumi*; Okayasu, Satoru; Katagiri, Masaki*; Sato, Kazuo*; Yotsuya, Tsutomu*; Shimakage, Hisashi*; Miki, Shigehito*; Wang, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 151(3-4), p.1074 - 1079, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:78.05(Physics, Applied)The superconducting neutron detector using high-quality  B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB thin films at higher operating temperatures has been proposed, where a resistance change induced by the nuclear reaction of neutron and
thin films at higher operating temperatures has been proposed, where a resistance change induced by the nuclear reaction of neutron and  B in MgB
B in MgB is used to detect a neutron. Cold neutrons from a nuclear research reactor irradiated the MgB
is used to detect a neutron. Cold neutrons from a nuclear research reactor irradiated the MgB detector, and the output voltage was clearly observed through a low-noise amplifier by using a digital oscilloscope. The out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics was investigated by means of the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equations by using the Earth Simulator.
detector, and the output voltage was clearly observed through a low-noise amplifier by using a digital oscilloscope. The out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics was investigated by means of the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equations by using the Earth Simulator.
 neutron detectors
neutron detectorsMachida, Masahiko; Kano, Takuma*; Koyama, Tomio*; Kato, Masaru*; Ishida, Takekazu*
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 151(1), p.58 - 63, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:46.07(Physics, Applied)We perform large-scale numerical simulations on the non-equilibrium superconducting dynamics after a neutron capture at the superconducting transition edge in MgB by solving the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation coupled with the Maxwell and the heat diffusion equations. The simulations are carried out under the current-biased condition in order to explain experimental results made in the JAEA reactor JRR-3, and the time scale of the obtained voltage signal is found tobe almost consistent with the experiments. Moreover, the time evolution of the voltage signal is connected with that of the spatial profile of the superconducting order parameter.
by solving the time-dependent Ginzburg-Landau equation coupled with the Maxwell and the heat diffusion equations. The simulations are carried out under the current-biased condition in order to explain experimental results made in the JAEA reactor JRR-3, and the time scale of the obtained voltage signal is found tobe almost consistent with the experiments. Moreover, the time evolution of the voltage signal is connected with that of the spatial profile of the superconducting order parameter.
Machida, Masahiko; Kano, Takuma*; Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.689 - 694, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:59.93(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Kano, Takuma; Merzari, E.*; Ninokata, Hisashi*
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2006 - March 2007, p.223 - 228, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Hisashi; Yura, Kei; Kano, Takuma; Matsumoto, Atsushi
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2006 - March 2007, p.257 - 263, 2007/09
The Earth Simulator has the highest power ever achieved to perform molecular dynamics simulation of large-scale supra-molecular systems. We are developing a molecular dynamics simulation system, called SCUBA, which is designed to run a system composed of more than a million particles efficiently on parallel computers. This fisical year, the arrays used in the program of SCUBA were intensively optimized to reduce the amount of memory use. This optimization enabled SCUBA to perform molecular dynamics simulations of large-scale supra-molecular systems comprised of more than a million atoms on the Earth Simulator. Moreover, the Martyna-Klein-Tuckerman algorithm was extended to utilize the multiple time step method, which increases the time step length significantly. Then, in order to elucidate the dynamics of the 70S ribosome, molecular dynamics simulation of the 70S ribosome including its explicit solvent, a system which is composed of about two million atoms, has been performed using SCUBA. A model of a nascent polypeptide was included in the system to investigate how the nascent polypeptide passes through the exit tunnel within the large subunit of the 70S ribosome. The ratchet-like motion of the 70S ribosome, which is thought to be important for the genetic translation, was successfully observed.
Shimizu, Futoshi; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Kimizuka, Hajime*; Kano, Takuma; Li, J.*; Kaburaki, Hideo
Journal of the Earth Simulator, 7, p.17 - 21, 2007/06
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Kano, Takuma; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Earth Simulator, 7, p.23 - 35, 2007/06
In order to explore a possibility of superfluidity in confined strongly-correlated fermion systems, e.g., nano-scale cuprate High-Tc superconductors and atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice, we implement an exact diagonalization code for their mathematical model, i.e., a trapped Hubbard model on the Earth Simulator. We compare two diagonalization algorithms, the traditional Lanczos method and a new algorithm, the preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) method, and find that when using the PCG the total CPU time can be reduced to 1/3  1/5 compared to the former one since the convergence can be dramatically improved by choosing a good preconditioner and the communication overhead is much more efficiently concealed in the PCG method. Consequently, such a performance improvement enables us to do systematic studies for several parameters. Numerical simulation results reveal that an unconventional type of pairing specific to the confined system, which can cause superfluidity, develops under a strong repulsive interaction.
1/5 compared to the former one since the convergence can be dramatically improved by choosing a good preconditioner and the communication overhead is much more efficiently concealed in the PCG method. Consequently, such a performance improvement enables us to do systematic studies for several parameters. Numerical simulation results reveal that an unconventional type of pairing specific to the confined system, which can cause superfluidity, develops under a strong repulsive interaction.
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Kano, Takuma; Akimoto, Hajime
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2005 - March 2006, p.261 - 265, 2007/01
no abstracts in English