Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cr
CrKleis, H.*; Seidlitz, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Kaya, L.*; Reiter, P.*; Arnswald, K.*; Dewald, A.*; Droste, M.*; Fransen, C.*; M ller, O.*; et al.
ller, O.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(3), p.034310_1 - 034310_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.88(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Rohrhofer, C.*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Gattringer, C.*; Glozman, L. Ya.*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Lang, C. B.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.227_1 - 227_7, 2020/08
Properties of QCD matter change significantly around the chiral crossover temperature, and the effects on 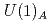 and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial
and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial 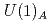 symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent
symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent 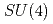 and
and 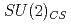 symmetries is discussed.
symmetries is discussed.
 Ba and high-spin structure of
Ba and high-spin structure of  Ba
BaKaya, L.*; Vogt, A.*; Reiter, P.*; Siciliano, M.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Wang, H.-K.*; Gargano, A.*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(2), p.024323_1 - 024323_18, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:77.09(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 single unit-cell FeSe superconductor
single unit-cell FeSe superconductorFukaya, Yuki; Zhou, G.*; Zheng, F.*; Zhang, P.*; Wang, L.*; Xue, Q.-K.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 31(5), p.055701_1 - 055701_6, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.39(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
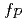 shell; Lifetime measurements in
shell; Lifetime measurements in  Zn
ZnQueiser, M.*; Vogt, A.*; Seidlitz, M.*; Reiter, P.*; Togashi, Tomoaki*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Homma, Michio*; Petkov, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044313_1 - 044313_13, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.41(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 decay of unbound neutron-hole states in
decay of unbound neutron-hole states in  Sn
SnVaquero, V.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Wimmer, K.*; Gargano, A.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Chen, S.*; N cher, E.*; Sahin, E.*; Shiga, Yoshiaki*; et al.
cher, E.*; Sahin, E.*; Shiga, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(20), p.202502_1 - 202502_5, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)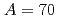 isobars from the
isobars from the 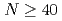 island of inversion
island of inversionMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, T.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 765, p.328 - 333, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:91.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)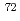 Ni
NiMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; Lorusso, G.*; Patel, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(3), p.034328_1 - 034328_14, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:85.25(Physics, Nuclear)Simanullang, I. L.*; Honda, Yuki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Takada, Shoji
JAEA-Technology 2015-032, 26 Pages, 2016/01
Decay heat of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor had been evaluated by the Shure Equation and/or ORIGEN code based on the LWR's data. However, to evaluate more accurately, a suitable method must be considered because of the differences neutron spectrums from the LWRs. Therefore, the decay heat and the generated nuclides for the neutron spectrums of the core with different graphite moderator amount were calculated by the ORIGEN2 code. As a result, it is clear that the calculated decay heats are similar value with LWRs for about one year after the reactor shutdown, and that the significant differences are observed on the longer period affected by the generated nuclides such as  Y,
Y,  Cs,
Cs,  Pr,
Pr, 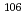 Rh,
Rh,  Am etc. It is also clear that the dose is affected by
Am etc. It is also clear that the dose is affected by  Pu on the initial stage after the reactor shutdown.
Pu on the initial stage after the reactor shutdown.
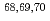 Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chain
Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chainBenzoni, G.*; Morales, A. I.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; Gargano, A.*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 751, p.107 - 112, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics) =40;
=40;  Cu
CuSahin, E.*; Doncel, M.*; Sieja, K.*; De Angelis, G.*; Gadea, A.*; Quintana, B.*; G rgen, A.*; Modamio, V.*; Mengoni, D.*; Valiente-Dob
rgen, A.*; Modamio, V.*; Mengoni, D.*; Valiente-Dob n, J. J.*; et al.
n, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(3), p.034302_1 - 034302_9, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:84.43(Physics, Nuclear)Obara, Satoshi; Takaya, Shigeru; Wakai, Takashi; Asayama, Tai; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saito, Toru; Martin, L.*
Kensa Gijutsu, 16(3), p.24 - 30, 2011/03
For the commercialization of fast breeder reactors (FBR), it is essential to enhance the economic competitiveness by reduction of total cost by elongation of plant service period. In this point of view, it is important to establish the assessment method of integrity of aged weld joint and repair welding for the components of future long life FBR. In the present study, evolution of microstructure is evaluated for the 304SS-304SS weld joint which was used for 88,000h at 526-545 C in the French proto-type fast reactor Phenix (as secondary pipes), and for the repair weld joint made from the 304SS of Phenix and new 316LSS plate. In addition, residual stress of the joints were measured by means of RESA and RESA-II. As the results, the microstructure and the residual stress of the joints had changed in the high temperature-long service environment and by the repair welding, and those of the repair weld joint were correlated with its hardness.
C in the French proto-type fast reactor Phenix (as secondary pipes), and for the repair weld joint made from the 304SS of Phenix and new 316LSS plate. In addition, residual stress of the joints were measured by means of RESA and RESA-II. As the results, the microstructure and the residual stress of the joints had changed in the high temperature-long service environment and by the repair welding, and those of the repair weld joint were correlated with its hardness.
Obara, Satoshi; Takaya, Shigeru; Wakai, Takashi; Asayama, Tai; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saito, Toru*; Martin, L.*
Hozengaku, 9(1), p.32 - 38, 2010/04
For the commercialization of fast breeder reactors (FBR), it is essential to enhance the economic competitiveness by reduction of total cost by elongation of plant service period. In this point of view, it is important to establish the assessment method of integrity of aged weld joint and repair welding for the components of future long life FBR. In the present study, evolution of microstructure is evaluated for the 304SS-304SS weld joint which was used for 88,000h at 526-545 C in the French proto-type fast reactor Phenix (secondary pipes), and for the repair weld joint made from the 304SS of Phenix and new 316LSS plate. In addition, residual stress of the joints were measured by means of RESA and RESA-II. As the results, the microstructure and the residual stress of the joints had changed in the high temperature-long service environment and by the repair welding, and those of the repair weld joint were correlated with its hardness.
C in the French proto-type fast reactor Phenix (secondary pipes), and for the repair weld joint made from the 304SS of Phenix and new 316LSS plate. In addition, residual stress of the joints were measured by means of RESA and RESA-II. As the results, the microstructure and the residual stress of the joints had changed in the high temperature-long service environment and by the repair welding, and those of the repair weld joint were correlated with its hardness.
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Amano, Hikaru; Ito, Toshimichi; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Suzuki, Takashi; Togawa, Orihiko; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Lishavskaya, T. S.*; Novichkov, V. P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 91(3), p.128 - 145, 2006/00
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:42.21(Environmental Sciences)Distributions of radionuclides ( Sr,
Sr,  Cs and
Cs and  Pu) in seabed sediment in the Japan Sea were observed during 1998-2002. Observed inventories of anthropogenic radionuclides in sediment ranged 0.1-86 Bq m
Pu) in seabed sediment in the Japan Sea were observed during 1998-2002. Observed inventories of anthropogenic radionuclides in sediment ranged 0.1-86 Bq m for
for  Sr, 23-379 Bq m
Sr, 23-379 Bq m for
for  Cs and 0.1-86 Bq m
Cs and 0.1-86 Bq m for
for  Pu. In the deep part (
Pu. In the deep part ( 2 km depth) of the western Japan Basin,
2 km depth) of the western Japan Basin,  Pu/
Pu/ Cs inventory ratios were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin although inventories of radionuclides were not different between basins. The higher
Cs inventory ratios were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin although inventories of radionuclides were not different between basins. The higher  Pu/
Pu/ Cs ratios in the western Japan Basin were derived by the production of Pu-enriched particle in the surface layer and effective sinking of particulate materials in this region. In the marginal Yamato Basin and the Ulleung Basin, both inventories and
Cs ratios in the western Japan Basin were derived by the production of Pu-enriched particle in the surface layer and effective sinking of particulate materials in this region. In the marginal Yamato Basin and the Ulleung Basin, both inventories and  Pu/
Pu/ Cs ratios in sediment were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin. In the eastern/southern Japan Sea, it was suggested that the supply of particulate radionuclides by the TWC enhanced accumulation of radionuclides in this region.
Cs ratios in sediment were larger than those in the central Yamato Basin. In the eastern/southern Japan Sea, it was suggested that the supply of particulate radionuclides by the TWC enhanced accumulation of radionuclides in this region.
Ito, Toshimichi; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi; Togawa, Orihiko; Kobayashi, Takuya; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Amano, Hikaru; Senju, Tomoharu*; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(1), p.90 - 100, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:67.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)During 1996-2002, a wide-area research project on anthropogenic radionuclides was done in the Japanese and Russian EEZ of the Japan Sea to investigate their migration. As the results of expeditions in 2001 and 2002, (1) the concentrations and distributions of radionuclides are similar to the results of previous, (2) inventories of these radionuclides indicate accumulation in the Japan Sea seawater compared to the amounts supplied by global fallout, (3)  Sr and
Sr and  Cs concentrations in intermediate layer show temporal variations, and 4) the variations may reflect the water mass movement in upper part of the Japan Sea.
Cs concentrations in intermediate layer show temporal variations, and 4) the variations may reflect the water mass movement in upper part of the Japan Sea.
Ito, Toshimichi; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi; Togawa, Orihiko; Kobayashi, Takuya; Senju, Tomoharu*; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Lishavskaya, T. S.*; Karasev, E. V.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.396 - 401, 2003/10
no abstracts in English
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Suzuki, Takashi; Kobayashi, Takuya; Ito, Toshimichi; Togawa, Orihiko; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Dunaev, A. L.*; Karasev, E. V.*; Novichkov, V. P.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.390 - 395, 2003/10
Seabed sediments were collected at 22 stations in the Japan Sea, and anthropogenic radionuclides were measured in order to understand distributions and accumulation processes of these materials. Averaged concentrations of  Cs in sediment in the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin were 1.0 Bq/kg and 1.0 Bq/kg, respectively. Although there was no significant difference in mean
Cs in sediment in the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin were 1.0 Bq/kg and 1.0 Bq/kg, respectively. Although there was no significant difference in mean  Cs concentration between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin, distributions of radionuclides in these 2 basins showed different features. In the Japan Basin, the spatial variation of concentration of radionuclides was smaller than that at the Yamato Basin. At most stations in the Yamato Basin, significant concentrations of radionuclides were not detected, but remarkable large activities were observed at several stations in the Yamato Basin. For all radionuclides, the highest concentration was observed in the southeastern margin of the Yamato Basin. These results would suggest that there were different accumulation processes of radionuclides between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin.
Cs concentration between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin, distributions of radionuclides in these 2 basins showed different features. In the Japan Basin, the spatial variation of concentration of radionuclides was smaller than that at the Yamato Basin. At most stations in the Yamato Basin, significant concentrations of radionuclides were not detected, but remarkable large activities were observed at several stations in the Yamato Basin. For all radionuclides, the highest concentration was observed in the southeastern margin of the Yamato Basin. These results would suggest that there were different accumulation processes of radionuclides between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin.
Ito, Toshimichi; Aramaki, Takafumi; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi; Togawa, Orihiko; Kobayashi, Takuya; Senju, Tomoharu*; Chaykovskaya, E. L.*; Karasev, E. V.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 68(3), p.249 - 267, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:62.84(Environmental Sciences)The anthropogenic radionuclides,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs and
Cs and  Pu, in the seawater column of the Japan Sea were measured during 1997-2000. The vertical profiles of radionuclide concentrations showed their typical features; exponential decrease with depth for the
Pu, in the seawater column of the Japan Sea were measured during 1997-2000. The vertical profiles of radionuclide concentrations showed their typical features; exponential decrease with depth for the  Sr and
Sr and  Cs and surface minimum - subsurface maximum for the
Cs and surface minimum - subsurface maximum for the  Pu, and there are no substantial differences between the present study and the previous ones. The area-averaged concentrations and the inventories of radionuclides in the Japan Sea are higher than those in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. In the spatial distributions, high inventory area extends and intrudes from the Japan Basin into the Yamato Basin. It is suggested that radionuclides sink by the vertical transport occurring mainly in the Japan Basin then advect into the Yamato Basin after detouring around the Yamato Rise, and finally, they are accumulated in the deep seawater of the Japan Sea.
Pu, and there are no substantial differences between the present study and the previous ones. The area-averaged concentrations and the inventories of radionuclides in the Japan Sea are higher than those in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. In the spatial distributions, high inventory area extends and intrudes from the Japan Basin into the Yamato Basin. It is suggested that radionuclides sink by the vertical transport occurring mainly in the Japan Basin then advect into the Yamato Basin after detouring around the Yamato Rise, and finally, they are accumulated in the deep seawater of the Japan Sea.
Kato, Takashi; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Ando, Toshinari; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nakajima, Hideo; Sugimoto, Makoto; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 56-57, p.59 - 70, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi*; Thome, R.*; Salpietro, E.*; Egorov, S. A.*; Martovetsky, N.*; Ricci, M.*; Zanino, R.*; Zahn, G.*; Martinez, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 41(5), p.645 - 651, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:83.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English