Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ,
,  ') reaction of
') reaction of  U on the target thickness
U on the target thicknessNegm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Zen, H.*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Hori, Toshitada*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(6), p.811 - 820, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)The dependence of the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) yield on the target thickness was studied. To this end, an NRF experiment was performed on  U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)
U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)  -ray beam at the High Intensity
-ray beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source facility at Duke University.
-ray Source facility at Duke University.
 (Ce) detectors near 2 MeV
(Ce) detectors near 2 MeVOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Bakr, M.*; Zen, H.*; Hori, Toshitada*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 729, p.102 - 107, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The performance of LaBr (Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident
(Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident  -rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B
-rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B C target to excite the
C target to excite the  B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr
B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr (Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
(Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
 U measured with high-resolution LaBr
U measured with high-resolution LaBr (Ce) scintillation detectors
(Ce) scintillation detectorsOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Zen, H.*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(10), p.106401_1 - 106401_4, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.71(Physics, Applied)A nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) experiment was performed on a  U target with quasi-monochromatic
U target with quasi-monochromatic  -rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr
-rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr (Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr
(Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr (Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr
(Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr (Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
(Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
 rays
raysHayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Minehara, Eisuke; Kii, Toshiteru*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 80(4), p.045110_1 - 045110_5, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:71.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)A non-destructive assay method for measuring a shielded chemical compound has been proposed. The chemical compound is measured by using a nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) measurement technique with an energy tunable laser Compton scattering (LCS)  -ray source. This method has an advantage that hidden materials can be detected through heavy shields such as iron plates of a thickness of several centimeters. A detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C
-ray source. This method has an advantage that hidden materials can be detected through heavy shields such as iron plates of a thickness of several centimeters. A detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C H
H N
N , shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates is demonstrated. The NRF
, shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates is demonstrated. The NRF  -rays of
-rays of  C and
C and  N of the melamine are measured by using the LCS
N of the melamine are measured by using the LCS  -rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio (
-rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio ( C/
C/ N)
N)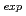 = 0.39
= 0.39  0.12 is consistent with (C/N)
0.12 is consistent with (C/N)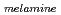 = 0.5.
= 0.5.
Yoshikawa, Kiyoshi*; Inoue, Nobuyuki*; Yamazaki, Tetsuo*; Makino, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Yasushi*; Toku, Hisayuki*; Masuda, Kai*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Onishi, Masami*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2002-020, 63 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
 -rays
-raysHayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Katsumura, Soichiro; Seya, Michio; Harada, Hideo; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Ogaki, Hideaki
no journal, ,
We propose a non-destructive assay method for measuring an isotope and a chemical compound hidden by heavy shields such as iron plates of a thickness of several centimeters. We use a nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) measurement technique with an energy tunable laser Compton scattering (LCS)  -ray source. Isotope mapping of a block of
-ray source. Isotope mapping of a block of  Pb concealed in an iron box of 1.5 cm thickness has been demonstrated. We also demonstrate detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C
Pb concealed in an iron box of 1.5 cm thickness has been demonstrated. We also demonstrate detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C H
H N
N , shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates. We measure NRF
, shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates. We measure NRF  -rays of
-rays of  C and
C and  N of the melamine by using the LCS
N of the melamine by using the LCS  -rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio (
-rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio ( C/
C/ N)
N)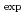 = 0.39
= 0.39  0.12 is consistent with (C/N)
0.12 is consistent with (C/N)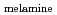 = 0.5.
= 0.5.
Hayakawa, Takehito; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Zen, H.*; Omer, M.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi
no journal, ,
Recently, a nondestructive measurement method of shielded fissional isotopes such as  U or
U or  Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy
Pu has been proposed for the nuclear security. These isotopes are measured by using nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) with monochromatic energy  -ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered
-ray beams generated by laser Compton-scattering (LCS). We have proposed that one measure scattered  -rays from NRF with LCS
-rays from NRF with LCS  -ray beams using the LaBr
-ray beams using the LaBr (Ce) detectors. The LaBr
(Ce) detectors. The LaBr (Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope
(Ce) crystals include internal radioisotopes of a meta-stable isotope 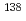 La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as
La and alpha decay chains from some actinides as 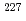 Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of
Ac. There is a broad pump at about 2 MeV. This pump is considered to be an overlap of  -rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of
-rays from decay chains of some actinides but its detailed structure has not been established. Here we have measured NRF spectra of  U using the LCS
U using the LCS  -rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF
-rays with energy of about 2.5 MeV at the HIgS facility of the Duke University. The background has been evaluated using a simulation code GEAT4. The 9 peaks, 8 NRF  -rays plus the Compton scattered
-rays plus the Compton scattered  -ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr
-ray of the incident beam, are finally assigned in an energy range of about 200 keV at about 2.5 MeV. The 8 integrated NRF cross-sections measured by LaBr (Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr
(Ce) have been consistent with results by an HPGe detector. The three levels are newly assigned using the HPGe detector. Two of them are also measured by LaBr (Ce).
(Ce).