Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 =1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl
=1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurements
in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurementsKimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okunishi, Koichi*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kikuchi, Hikomitsu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(9), p.094701_1 - 094701_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Suekuni, Koichiro*; Lee, C. H.*; Tanaka, Hiromi*; Nishibori, Eiji*; Nakamura, Atsushi*; Kasai, Hidetaka*; Mori, Hitoshi*; Usui, Hidetomo*; Ochi, Masayuki*; Hasegawa, Takumi*; et al.
Advanced Materials, 30(13), p.1706230_1 - 1706230_6, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:89.35(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric materials for highly efficient devices must satisfy conflicting requirements of high electrical conductivity and low thermal conductivity. In this paper, we studied the crystal structure and phonon dynamics of tetrahedrites (Cu,Zn) (Sb,As)
(Sb,As) S
S . The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
. The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Aoki, Kazufumi; Okamoto, Akiko; Kawakami, Takeshi; Kume, Nobuhide; Nakanishi, Chika; Koie, Masahiro; Kawamata, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-048, 69 Pages, 2015/02
JAEA was assigned as a designated public institution under the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and under the Armed Attack Situations Response Act. Based on these Acts, the JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the national government and/or local governments in case of disaster responses or response in the event of a military attack, etc. In order to fulfill the tasks, the JAEA has established the Emergency Action Plan and the Civil Protection Action Plan. In case of a nuclear emergency, NEAT dispatches specialists of JAEA, supplies the national government and local governments with emergency equipment and materials, and gives technical advice and information. In normal time, NEAT provides various exercises and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response institutions of the national and local governments, police, fire fighters, self-defense forces, etc. in addition to the JAEA itself. The NEAT also researches nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and cooperates with international organizations. In the FY2013, the NEAT accomplished the following tasks: (1) Technical support activities as a designated public institution in cooperation with the national and local governments, etc. (2) Human resource development, exercise and training of nuclear emergency response personnel for the national and local governments, etc. (3) Researches on nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and sending useful information (4) International contributions to Asian countries on nuclear disaster preparedness and response in collaboration with the international organizations
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Goto, Ichiro*; Kibe, Satoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-040, 115 Pages, 2015/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Okuno, Hiroshi; Katagiri, Hiromi; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Okamoto, Akiko; Koie, Masahiro; Ikeda, Takeshi; Nemotochi, Toshimasa; Saito, Toru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-046, 65 Pages, 2014/02
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire stations and nuclear operators etc., because the JAEA has been designated as the Designated Public Institution under the Basic Act on Disaster Control Measures and the Act on Response to Armed Attack Situations, etc.. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, dispatches specialists as required, and supplies the National Government and local governments with emergency equipments and materials. NEAT provides various exercise and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal times. The tasks of NEAT, with its past experiences as a designated public institution including the responses to TEPCO's Fukushima Accident, have been shifted to technical supports to the national government for strengthening its abilities to emergency responses; the NEAT therefore focused on maintenance and operation of its functions, and strengthening its response abilities in cooperation with the national government. This annual report summarized these activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2012.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-041, 115 Pages, 2014/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2012, from 1st April 2012 to 31st March 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
 -ray irradiation in HNO
-ray irradiation in HNO media
mediaNogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 296(1), p.423 - 427, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.62(Chemistry, Analytical)Stability of polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP), a resin with adsorption selectivity to U(VI) in nitric acid media, against  -ray irradiation has been examined using HNO
-ray irradiation has been examined using HNO solutions of various concentrations. As the result, no clear decrease in the capacity was observed for any samples. Or rather, it was found that the capacity increased by approximately 50% for the PVPP slurry irradiated in 6 M HNO
solutions of various concentrations. As the result, no clear decrease in the capacity was observed for any samples. Or rather, it was found that the capacity increased by approximately 50% for the PVPP slurry irradiated in 6 M HNO . The infrared spectroscopic study indicates that PVPP degrades by
. The infrared spectroscopic study indicates that PVPP degrades by  -ray irradiation in HNO
-ray irradiation in HNO from the cleavage of the pyrrolidone ring by the addition of oxygen atom originating from HNO
from the cleavage of the pyrrolidone ring by the addition of oxygen atom originating from HNO , followed by the formation of chain monoamides with multiple coordinative atoms by the continuous addition of oxygen, finally leading to the generation of primary-amine type anion exchange resin. It is also indicated that all generated functional groups possess adsorptivity to U(VI) in 3 M HNO
, followed by the formation of chain monoamides with multiple coordinative atoms by the continuous addition of oxygen, finally leading to the generation of primary-amine type anion exchange resin. It is also indicated that all generated functional groups possess adsorptivity to U(VI) in 3 M HNO .
.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationNogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Science China; Chemistry, 55(9), p.1739 - 1745, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.69(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Stability of N-alkylated pyrrolidone derivatives (NRPs) against radiation was examined by irradiation tests with  Co
Co  -ray. We have been developed a novel reprocessing system using NRPs which have precipitation ability to haxa- and tetravalent actinides in nitric acid media. Degradation rates of NRPs are evaluated by irradiation in 3M nitric acid solutions and mechanism of degradation are discussed in the present paper.
-ray. We have been developed a novel reprocessing system using NRPs which have precipitation ability to haxa- and tetravalent actinides in nitric acid media. Degradation rates of NRPs are evaluated by irradiation in 3M nitric acid solutions and mechanism of degradation are discussed in the present paper.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Okamoto, Akiko; Ikeda, Takeshi; Tamura, Kenichi; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Abe, Minako; Sato, Sohei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-033, 70 Pages, 2012/08
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, etc., by the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. NEAT of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies with the National Government and local governments emergency equipment and materials. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for emergency response organizations at normal time. Concerning the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its the utmost effort. This annual report summarized these activities of NEAT in the fiscal year 2011.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Sawahata, Masayoshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-037, 66 Pages, 2011/12
When a Nuclear emergency occurs, Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies emergency equipment and materials to the National Government and local governments. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. NEAT also researches on nuclear disaster prevention and cooperates with international organizations. Concerning about the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake at 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its full scale effort. NEAT served as the center of these supporting activities of JAEA.
Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Nogami, Masanobu*; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Morita, Yasuji; Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Someya, Hiroshi*; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/12
An advanced reprocessing system for spent FBR fuels based on two precipitation processes using pyrrolidone derivatives as precipitants has been developed. Experimental results of precipitation behavior of U, Pu and other elements, the heat- and radiation-resistance of precipitants, the thermal decomposition properties of precipitates showed that N-n-butyl-2-pyrrolidone and N-neopentyl-2-pyrrolidone are the appropriate precipitants for the first and second precipitation steps, respectively. From the engineering investigation, We confirmed that the precipitation and the filtration can be done efficiently using the engineering scale equipment and that the fuel pellets are directly prepared by the calcination of the precipitates. On the basis of these results, we evaluated that the proposed system is expected to be one of candidates of the future reprocessing systems for spent FBR fuels.
Nogami, Masanobu*; Harada, Masayuki*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 53(7), p.948 - 951, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The precipitation ability of 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidone (DMI) to U(VI) and U(IV) was examined using nitric acid solutions. While DMI precipitated U(VI) from 3 M nitric acid, no precipitate was observed in the solution containing 0.15 M U(IV) and 3 M nitric acid by adding DMI at the ratio of [DMI]/[U(IV)]=5. This indicates that the selectivity of DMI to U(VI) than U(IV). In spite of the excellent selectivity to U(VI), DMI has a disadvantage on the stability in nitric acid, because gradual acid hydrolysis of DMI is inevitable due to the nature of the chemical structure. Experiments on the stability of DMI in  -ray irradiation and heating in nitric acid solutions showed that the stability is strongly affected by the concentration of nitric acid and that DMI may be applicable in nitric acid solutions up to ca. 2 M.
-ray irradiation and heating in nitric acid solutions showed that the stability is strongly affected by the concentration of nitric acid and that DMI may be applicable in nitric acid solutions up to ca. 2 M.
Kanamori, Masashi; Shirakawa, Yusuke; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Okuno, Hiroshi; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-037, 60 Pages, 2010/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are designated public organizations conforming to the basic law on emergency preparedness and the basic plan for disaster countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an off-site center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the national government and municipal office. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2009.
Nogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 283(2), p.541 - 546, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.77(Chemistry, Analytical)Adsorptivity of polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) to various metal ions was examined as a part of the development of resins with selectivity to U(VI) in nitric acid media. It was found that PVPP has a strong adsorptivity to U(VI) in wide concentration range of nitric acid. The mechanism of U(VI) adsorption by PVPP was discussed by results of Scatchard plot analysis and infrared spectroscopic analysis. Furthermore, it was found that fission productions except for Re(VII) as the simulant of Tc(VII) and Pd(II) are not adsorbed on to PVPP and that Pd(II) and Re(VII) species are weakly adsorbed in the lower concentration ranges of nitric acid, where the adsorption rates of Pd(II) are extremely slower than those of U(VI). These results indicate that U(VI) can be separated from other metal ions by PVPP.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationNogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Kawata, Yoshihisa; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 25, 2009/12
As a part of the development of a novel reprocessing system for spent FBR fuels based on the precipitation method, influence of concentrations of HNO on the stability by
on the stability by  -ray irradiation was examined for
-ray irradiation was examined for  -
- -butyl-2-pyrrolidone (NBP), a candidate precipitant for the first precipitation step for selectively precipitating U(VI). The residual ratios of the samples for HNO
-butyl-2-pyrrolidone (NBP), a candidate precipitant for the first precipitation step for selectively precipitating U(VI). The residual ratios of the samples for HNO solutions up to 3 M were found to be decreased identically, where ca. 20% of NBP was degraded after the irradiation of 1 MGy. It was found that the degradation of the samples of 6 M HNO
solutions up to 3 M were found to be decreased identically, where ca. 20% of NBP was degraded after the irradiation of 1 MGy. It was found that the degradation of the samples of 6 M HNO is more distinguished, where ca. 30% was degraded after the irradiation of 0.1 MGy. As the result of the investigation of the degradation mechanism of NBP, it was revealed that the degradation started from the cleavage of the pyrrolidone ring of NBP by the addition of oxygen atom, followed by the formation of chain monoamides and C4 compounds by the continuous addition of oxygen, leading to the generation of oxalic acid.
is more distinguished, where ca. 30% was degraded after the irradiation of 0.1 MGy. As the result of the investigation of the degradation mechanism of NBP, it was revealed that the degradation started from the cleavage of the pyrrolidone ring of NBP by the addition of oxygen atom, followed by the formation of chain monoamides and C4 compounds by the continuous addition of oxygen, leading to the generation of oxalic acid.
Kanamori, Masashi; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Omura, Akiko; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-023, 61 Pages, 2009/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are Designated Public Organizations conforming to the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the Joint Council of Nuclear Disaster Countermeasures, which meets at the Off-Site Center. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2008.
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Yamamoto, Takumi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Oasa, Kazumi; Kawashima, Hisato; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Toshihide; Shoji, Teruaki*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Kikuchi, Kazuo; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.139 - 167, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)The main results obtained by the various heating and current drive systems, external coil system and divertor bias system are reviewed from the viewpoint of the advanced active control of the tokamak plasma. Also, the features of each system are described. The contribution of the JFT-2M in these areas are summarized.
Yamasaki, Kazuhiko*; Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Tamaki, Yoshihisa*; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Morita, Yasuji; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Mineo, Hideaki; Koshino, Nobuyoshi*; Asanuma, Noriko*; Harada, Masayuki*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/10
N-cyclohexyl-2-pyrrolidone (NCP), can selectively precipitate U(VI) ions in aqueous nitric acid solutions. Utilizing this property, we have been developing a simple reprocessing process of spent nuclear fuel based only on precipitation method. In the first precipitation step, only U is separated by precipitation in a yield of about 70%, and in the second precipitation step both U and Pu are recovered and separated from fission products (FP) and other transuranium elements (TRU). In the present study, a precipitator and a precipitate separator were designed and built up, and were tested with aspets of operationability and system performance.
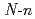 -butyl-2-pyrrolidone,
-butyl-2-pyrrolidone,  -cyclohexylmethyl-2-pyrrolidone, and 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidone
-cyclohexylmethyl-2-pyrrolidone, and 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidoneKoshino, Nobuyoshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Nogami, Masanobu*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Inorganica Chimica Acta, 358(6), p.1857 - 1864, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:88.15(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Structural analyses of UO (NO
(NO )
) L
L [L=
[L=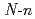 -butyl-2-pyrrolidone, N-cyclohexylmethyl-2-pyrrolidone, and 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidone] have been carried out using X-ray diffraction method. These uranyl complexes were found to have a hexagonal bipyramidal structure. The bond distances of U=O and U-O (ligand), and bond angles of U-O-C(carbonyl) are determined. In uranyl nitrate complexes with cyclic amides such as 2-pyrrolidone, urea, and caprolactam derivatives, a linear correlation was found to hold between U-O (ligand) bond distances and U-O-C(carbonyl) bond angles. Vibrational frequencies of UO
-butyl-2-pyrrolidone, N-cyclohexylmethyl-2-pyrrolidone, and 1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidone] have been carried out using X-ray diffraction method. These uranyl complexes were found to have a hexagonal bipyramidal structure. The bond distances of U=O and U-O (ligand), and bond angles of U-O-C(carbonyl) are determined. In uranyl nitrate complexes with cyclic amides such as 2-pyrrolidone, urea, and caprolactam derivatives, a linear correlation was found to hold between U-O (ligand) bond distances and U-O-C(carbonyl) bond angles. Vibrational frequencies of UO (NO
(NO )
) L
L have also been measured by IR and Raman spectrophotometers. Using relationships between vibrational frequencies of O=U=O bonds and donor numbers (DNs) of ligands, donicities of N-substituted-2-pyrrolidones were determined.
have also been measured by IR and Raman spectrophotometers. Using relationships between vibrational frequencies of O=U=O bonds and donor numbers (DNs) of ligands, donicities of N-substituted-2-pyrrolidones were determined.