Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sawada, Shinichi*; Kimura, Takehiro*; Nishijima, Haruyuki*; Kodaira, Takahide*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Imabayashi, Shinichiro*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45(27), p.13814 - 13820, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.8(Chemistry, Physical)An electrochemical membrane Bunsen reaction using a cation exchange membrane (CEM) is a key to achieving an iodine-sulfur (IS) thermochemical water splitting process for mass-production of hydrogen. In this study, we prepared both the radiation-grafted CEM with a high ion exchange capacity (IEC) and the highly-porous Au-electroplated anode, and then used them for the membrane Bunsen reaction to reduce the cell overvoltage. The high-IEC grafted CEM exhibited low resistivity for proton transport, while the porous Au anode had a large effective surface area for anodic SO oxidation reaction. As a result, the cell overvoltage for the membrane Bunsen reaction was significantly reduced to 0.21 V at 200 mA/cm
oxidation reaction. As a result, the cell overvoltage for the membrane Bunsen reaction was significantly reduced to 0.21 V at 200 mA/cm , which was only one-third of that of the previous test using the commercial CEM and non-porous anode. From the analysis of the current-voltage characteristics, employment of the grafted CEM was found to be more effective for the overvoltage reduction compared to the porous Au anode.
, which was only one-third of that of the previous test using the commercial CEM and non-porous anode. From the analysis of the current-voltage characteristics, employment of the grafted CEM was found to be more effective for the overvoltage reduction compared to the porous Au anode.
Sugiyama, Daisuke*; Kimura, Hideo; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kawata, Yosuke*; Ogino, Haruyuki*; Okoshi, Minoru*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 38(1), p.456 - 462, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Experience after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station has shown that there is a need to establish radiation protection criteria for radioactive waste management consistent with the criteria adopted for the remediation of existing exposure situations. A stepwise approach to setting such criteria is proposed. Initially, a reference level for annual effective dose from waste management activities in the range 1-10 mSv should be set, with the reference level being less than the reference level for ambient dose. Subsequently, the reference level for annual effective dose from waste management activities should be reduced in one or more steps to achieve a final target value of 1 mSv. The dose criteria at each stage should be determined with relevant stakeholder involvement. Illustrative case studies show how this stepwise approach might be applied in practice.
Wakai, Eiichi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi*; Ito, Yuzuru*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yagi, Juro*; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 11, p.2405112_1 - 2405112_4, 2016/11
Kimura, Haruyuki; Hoashi, Eiji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(5), p.327 - 340, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Curved magnetically guided lithium target (MGLT) without a back plate was proposed for accelerator-based intense neutron source such as IFMIF. The curved MGLT can replace conventional lithium target with a curved back plate under the most severe condition on neutron irradiation. The magnetic field suited for MGLT is produced in combination of radiation-proof resistive coils and F82H parts (yokes, nozzles and high flux test module (HFTM)). Shape of the magnetic field becomes curved in the target region by setting HFTM closely to MGLT. Lithium flow on MGLT was analyzed in detail by two dimensional equations of motion with magnetic field calculated by the Poisson Superfish code. The necessary magnetic flux density at the target region was found to be about 0.5 T to fulfill the IFMIF target conditions; flow speed of 15 m/s, curvature radius of 1-1.6 m and flow thickness of 0.025 m. A narrow gap (a few mm) between MGLT and HFTM could be controlled via control of the coil current.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Fukada, Satoshi*; Yagi, Juro*; Ida, Mizuho; Kanemura, Takuji; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(12), p.691 - 705, 2012/12
no abstracts in English
Nishitani, Takeo; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Clement Lorenzo, S.*; Baluc, N.*; Hayashi, Kimio; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Kimura, Haruyuki; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Heidinger, R.*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 62(1), p.210 - 218, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recent progress in the material related researches and the IFMIF/EVEDA project, which are carried out under the Broader Approach (BA) framework, is reported. In the International Fusion Energy Research Center (IFERC) project of BA, the R&D building was completed March 2010 at the Rokkasho BA site. R&Ds on reduced activation ferritic/ martensitic (RAFM) steels as structural material, SiC/SiC composites as a flow channel insert material and/or alternative structural material, advanced tritium breeders and neutron multipliers, and tritium technology relevant to the DEMO operational condition are progressed in Japan and EU. In the IFMIF/EVEDA project, the fabrication of the injector for the IFMIF prototype accelerator was completed at the CEA Saclay, and the first proton beam was obtained in May, 2011. The IFMIF lithium target test loop was completed in March 2011, and a lithium flow of 5 m/s was obtained.
Kondo, Hiroo; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Ida, Mizuho; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Kanemura, Takuji; Wakai, Eiichi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(12), p.123008_1 - 123008_12, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.4(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity (EVEDA) for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is proceeded as one of the ITER Broader Approach (BA) activities. The EVEDA Li test loop (ELTL) is aimed at validating stability of the Li target and feasibility of a Li purification system as the key issues. In this paper, the design of the ELTL especially of a target assembly in which the Li target is produced by the contraction nozzle is presented.
Garin, P.*; Diegele, E.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ibarra, A.*; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Kimura, Haruyuki; M slang, A.*; Muroga, Takeo*; Nishitani, Takeo; Poitevin, Y.*; et al.
slang, A.*; Muroga, Takeo*; Nishitani, Takeo; Poitevin, Y.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.611 - 614, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:87.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper summarizes the proposals and findings of the IFMIF Specification Working Group established to update the Users requirements and top level specifications for the Facility. Special attention is given to the different roadmaps of fusion path way towards power plants, of materials R&D and of facilities and their interactions. The materials development and validation activities on structural materials, blanket functional materials and non-metallic materials are analyzed and specific objectives and requirements to be implemented in IFMIF are proposed. Emphasis is made in additional potential validation activities that can be developed in IFMIF for ITER TBM qualification as well as for DEMO-oriented mock-up testing.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Kogawara, Takafumi; Kimura, Haruyuki; Yokomine, Takehiko*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Nogami, Shuhei*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Saito, Masahiro*; Nishimura, Arata*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/03
Japanese activities of test facilities in IFMIF-EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility-Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities) project have three subjects of engineering design of post irradiation examination (PIE) facilities, small specimen test technique (SSTT), and engineering design of high flux test module (HFTM), and this paper is summarized about present status. Functional analysis and design of 2-D and 3-D models of PIE facility were performed. In HFTM, as materials of heater, W-3Re alloy and/or SiC/SiC composite were selected in the points of high temperature materials, fabrication technology and some suitable properties such as resistance of thermal shock, high temperature re-crystallization, ductility, resistance of irradiation degradation, and low-activation. In SSTT, a test machine of fracture toughness was designed and developed for small specimens with 10 mm square, and it had high accuracy controllability for stress and displacement.
Kondo, Hiroo; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Nakamura, Hiroo*; Ida, Mizuho; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Miyashita, Makoto*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Kanemura, Takuji; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
The Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity (EVEDA) for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is proceeded as one of the ITER Broader Approach (BA) activities. The EVEDA Li test loop (ELTL) is aimed at validating stability of the Li target and feasibility of a Li purification system as the key issues. In this paper, the design of the ELTL especially of a target assembly in which the Li target is produced by the contraction nozzle is presented.
Ohira, Shigeru; Utsumi, Shigeo*; Kubo, Takashi; Yonemoto, Kazuhiro; Kasuya, Kenichi; Ejiri, Shintaro; Kimura, Haruyuki; Okumura, Yoshikazu
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.665 - 669, 2010/08
Under the Agreement Between the Government of Japan and the EURATOM for the Joint Implementation of the Broader Approach Activities (BA Activities) in the Field of Fusion Energy Research, JAEA develop a new site at Rokkasho-mura in Aomori prefecture of Japan as the Japanese Implementing Agency. In this new site, two of the three projects of the BA Activities are to be implemented, namely, International Fusion Energy Research Center (IFERC) Project and International Fusion Material Irradiation Facility/Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity (IFMIF/EVEDA) Project. In March 2009, the Administration and Research Building was completed, and the other research facilities; CSC&REC Building, DEMO R&D Building and IFMIF/EVEDA Accelerator Building will be completed in March 2010. In this presentation, the specifications and construction schedule of the individual research buildings will be presented, especially special features of the IFMIF/EVEDA Accelerator Building.
Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Garin, P.*; Vermare, C.*; Shidara, Hiroyuki; Kimura, Haruyuki; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Ohira, Shigeru; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Mosnier, A.*; Facco, A.*; et al.
Kasokuki, 7(2), p.110 - 118, 2010/07
International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is an accelerator-based neutron irradiation facility dedicated for development of fusion materials. Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities (EVEDA) phase of IFMIF project has been initiated in June 2007 and a prototype of the IFMIF accelerator (40 MeV - 125 mA CW Deuteron) is under construction in Rokkasho, Aomori. The target of the prototype is 9 MeV - 125 mA CW beam operation, which is full scale prototyping up to the first tank of superconducting linac section. In this report, the major technical specifications and issues of this extremely high-power machine are overviewed and expected results through operation in future are summarized.
Vermare, C.*; Garin, P.*; Shidara, H.*; Beauvais, P. Y.*; Mosnier, A.*; Ibarra, A.*; Heidinger, R.*; Facco, A.*; Pisent, A.*; Maebara, Sunao; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.777 - 779, 2010/05
Mosnier, A.*; Beauvais, P. Y.*; Branas, B.*; Comunian, M.*; Facco, A.*; Garin, P.*; Gobin, R.*; Gournay, J. F.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ibarra, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.588 - 590, 2010/05
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Vermare, C.*; Asahara, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Garin, P.*; Maebara, Sunao; Takahashi, Hiroki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kojima, Toshiyuki; Ohira, Shigeru; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.668 - 670, 2010/03
Progress of the IFMIF/EVEDA prototype accelerator in fiscal year of 2008 is described. All the sub-systems of the prototype accelerator have started to design, settled the plan of the manufacturing and component tests and fixed the design parameters. As a result of the analysis of planning for the engineering validation of the IFMIF accelerator system, the project duration to be prolonged to the end of 2014 including some months for contingency was approved by the BA Steering Committee. In this article, the design status of each accelerator component, the interface between the accelerator components and the IFMIF/EVEDA Accelerator Building settled in International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) in Rokkasho and the proposed accelerator commissioning plan for the engineering validation will be presented.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Haruyuki; Inutake, Masaaki*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Ozeki, Takahisa; Naito, Osamu; Takase, Yuichi*; Ide, Shunsuke; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(1), p.81 - 93, 2007/01
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Koji; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Isei, Nobuaki; Tani, Takashi; Kikuchi, Kazuo; Shibata, Takatoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.187 - 196, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)In JFT-2M, the toroidal field ripple was reduced by ferritic insert. Two kinds of ripple reduction were carried out. In the first case, ferritic steel was installed between toroidal field coil and vacuum vessel, just under toroidal field coil, outside vacuum vessel. In the second one, ferritic steel was installed inside vacuum vessel covering almost whole inside wall. The ripple was successfully reduced in the both cases. The temperature increment on the first wall measured by infrared TV was also reduced. A new version of OFMC code was also developed to analyze fast ion behavior in the complex structure of the toroidal field. The TF ripple reduction with ferritic insert in JFT-2M is summarized in this article.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Kimura, Haruyuki; Okano, Fuminori; Kawashima, Hisato; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shinohara, Koji; JFT-2M Group; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.241 - 248, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)JFT-2M has been modified three times in the Advanced Material Tokamak Experiment (AMTEX) program to investigate compatibility of the low activation ferritic steel F82H with tokamak plasmas as a structural material for future reactors. The ferritic steel plate/wall was installed inside and/or outside of the vacuum vessel to reduce the ripple of toroidal magnetic field step by step through three modifications. This paper focuses on engineering aspects in these modifications; electromagnetic analysis to find a suitable way for fixing these plates, installation procedure to keep small tolerance, a three-dimensional magnetic field measurement device used to obtain information of the actual shape of the vacuum vessel used as a installation standard surface. To keep a good surface condition of the ferritic steel plate/wall that rusts easily, careful treatment was executed before the installation. To reduce oxygen impurities further, a boronization system with tri-methyl boron, which is safe and easy to operate, was developed.
Kawashima, Hisato; Sengoku, Seio; Uehara, Kazuya; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shoji, Teruaki*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.168 - 186, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental efforts on JFT-2M have been devoted to understand SOL/Divertor plasmas and to investigate power and particle controllability. Open divertor configuration was used for the first decade of JFT-2M started in 1984. We found out the SOL/Divertor plasma properties such as in/out asymmetry, heat and particle diffusivities, and SOL current at ELMs. Handling of power and particle was demonstrated by active control methods such as local pumping, edge ergodization, divertor biasing, and edge heating. For improvement of power and particle control capability of divertor, it was modified to closed configuration in 1995, which demonstrated the baffling effects with narrower divertor throat. Dense and cold divertor state (n
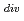 = 4
= 4 10
10 m
m and T
and T
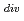 = 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.
= 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.