Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 18(3), p.134 - 135, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
 that stimulates DNA ligation
that stimulates DNA ligationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Cui, S.*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Molecular Microbiology, 54(1), p.278 - 285, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:133 Percentile:91.37(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The extraordinary radiation resistance of  results from the efficient capacity of the bacterium to repair DNA double-strand breaks. By analyzing the DNA damage repair-deficient mutant, KH311, a unique radiation-inducible gene (designated
results from the efficient capacity of the bacterium to repair DNA double-strand breaks. By analyzing the DNA damage repair-deficient mutant, KH311, a unique radiation-inducible gene (designated  ) responsible for loss of radiation resistance was identified. Investigations in vitro showed that the gene product of
) responsible for loss of radiation resistance was identified. Investigations in vitro showed that the gene product of  (PprA) preferentially bound to double-stranded DNA carrying strand breaks, inhibited
(PprA) preferentially bound to double-stranded DNA carrying strand breaks, inhibited  exonuclease III activity, and stimulated the DNA end-joining reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent and NAD-dependent DNA ligases. These results suggest that
exonuclease III activity, and stimulated the DNA end-joining reaction catalyzed by ATP-dependent and NAD-dependent DNA ligases. These results suggest that  has a radiation-induced nonhomologous end-joining repair mechanism in which PprA plays a critical role.
has a radiation-induced nonhomologous end-joining repair mechanism in which PprA plays a critical role.

Hua, Y.*; Narumi, Issei; Gao, G.*; Tian, B.*; Sato, Katsuya; Kitayama, Shigeru; Shen, B.*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306(2), p.354 - 360, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:95.76(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have identified a unique deinococcal gene,  , as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which
, as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which  is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with
is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with  . In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of
. In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of  and
and  and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
 UV-endonuclease
UV-endonuclease 
Kitayama, Shigeru; Narumi, Issei; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 67(3), p.613 - 616, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.16(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
 irradiated by heavy ions
irradiated by heavy ionsShikazono, Naoya; Tanaka, Atsushi; Kitayama, Shigeru*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Tano, Shigemitsu*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 41(2), p.159 - 162, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:69.98(Biology)no abstracts in English

Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Yamamoto, Kazuo; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Journal of Biochemistry, 131(1), p.121 - 129, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:38.54(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)RecA protein is considered to be the most important participant in the radiation resistance of  . We identified a new
. We identified a new  mutation (
mutation (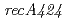 ) in the DNA-repair deficient mutant strain KI696, the phenotype of which is remarkably different from mutant strain rec30 carrying
) in the DNA-repair deficient mutant strain KI696, the phenotype of which is remarkably different from mutant strain rec30 carrying 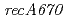 . In vitro, neither RecA424 nor RecA670 could promote DNA strand exchange, indicating that both RecA424 and Rec670 are defective in recombination activity. RecA424 promoted the autocleavage reaction of LexA in vitro, whereas RecA670 did not. The LexA level in KI696 was decreased following
. In vitro, neither RecA424 nor RecA670 could promote DNA strand exchange, indicating that both RecA424 and Rec670 are defective in recombination activity. RecA424 promoted the autocleavage reaction of LexA in vitro, whereas RecA670 did not. The LexA level in KI696 was decreased following  -irradiation. However, the LexA level in strain rec30 was constant irrespective of irradiation. These results indicate that RecA424 retains co-protease activity, whereas RecA670 does not. While strain rec30 is extremely radiation sensitive, strain KI696 is only slightly sensitive. Together, these observations suggest that the co-protease activity rather than the recombination activity of RecA contributes to the radiation resistance in
-irradiation. However, the LexA level in strain rec30 was constant irrespective of irradiation. These results indicate that RecA424 retains co-protease activity, whereas RecA670 does not. While strain rec30 is extremely radiation sensitive, strain KI696 is only slightly sensitive. Together, these observations suggest that the co-protease activity rather than the recombination activity of RecA contributes to the radiation resistance in  .
.
Kitayama, Shigeru*; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 461(3), p.179 - 187, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei; Kitayama, Shigeru*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo*
FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 174, p.151 - 157, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:32.92(Microbiology)no abstracts in English
Funayama, Tomoo; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 435, p.151 - 161, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 435(3), p.233 - 243, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei; K.Cherdchu*; Kitayama, Shigeru*; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Gene, 198, p.115 - 126, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:66.63(Genetics & Heredity)no abstracts in English