Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042006_1 - 042006_7, 2021/10
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
Proceedings of International Youth Nuclear Congress 2020 (IYNC 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/05
Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
 acidic solutions
acidic solutionsYokoyama, Akihiko*; Kitayama, Yuta*; Fukuda, Yoshiki*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Murakami, Masashi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Yano, Shinya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 107(1), p.27 - 32, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 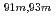 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Sugita, Yutaka*; Takahashi, Yoshiaki*; Uragami, Manabu*; Kitayama, Kazumi*; Fujita, Tomoo; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2007-023, 70 Pages, 2007/03
The sealing performance of a repository is very important for the safety assessment of the geological disposal system for high-level radioactive waste. NUMO and JAEA set up a technical commission to investigate sealing technology in a repository in 2004 following a cooperation agreement between these two organisations. The objectives of this commission were to present a concept of sealing performance required in the disposal system and to direct future R&D for design requirements of closure components (backfilling material, clay plug, etc.). Hydraulic analyses on tunnel intersections were carried out during the first year in 2004. This was expanded into a hydraulic analysis of a complete disposal panel with all tunnels during the second year in 2005. Since the model structure in 2005 was more complicated than the one used in 2004, the concept of equivalent permeability was adopted in and around each tunnel in the hydraulic analyses. Parameters used in the hydraulic analyses were installation positions of clay plugs, permeability of the backfilling material, permeability of disposal tunnel and directions of hydraulic gradient to estimate influences to the analytical results preliminary. Analytical results showed that flow rate in a disposal tunnel was influenced by directions of hydraulic gradient, installation of the clay plug at the both ends of each disposal tunnel and permeability of the main tunnel.
Sugita, Yutaka; Fujita, Tomoo; Takahashi, Yoshiaki*; Kawakami, Susumu; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Yui, Mikazu; Uragami, Manabu*; Kitayama, Kazumi*
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 32(1-7), p.32 - 41, 2007/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.74(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The H12 repository concept for vitrified high-level radioactive waste was developed based on a multi-barrier system with the emphasis on robust engineered barrier performance to ensure its feasibility for a wide range of geological conditions typically observed in Japan. The buffer is clay-based and plays a very important role in the engineered barrier system (EBS). The decision to use a volunteer siting process requires maximum flexibility of the repository concept to allow it to be adapted to potential sites and hence a wide range of variants of the basic H12 repository design has been developed. In order to evaluate the feasibility and the applicability of different repository options to specific siting environments, NUMO has established a set of "design factors" which classify the aspects that need to be considered when evaluating the pros and cons of different repository options. A Na-type bentonite from Japan is used as the reference material for all clay-based repository components (buffer, backfill, clay plug, etc.). The characteristics of this bentonite (thermal, mechanical, chemical, hydraulic) have been examined with consideration of various practical constraints (limitation on the repository footprint, the influence of saline water, the interaction of hyperalkaline leachates and practical working environment, etc.). Clay-based seals, which close off the tunnels after emplacement of the EBS, may also be key components for assessment of the repository. Full analyses considering all engineered barrier components (buffer, backfill, clay plug, concrete lining, tunnel, concrete plug, host rock) that may be used in a repository will be an essential future task. As a first step towards this goal, a numerical analysis focusing on hydraulic behaviour at the intersections of the disposal tunnels and the main tunnel is presented to illustrate how the design requirements of clay-based seals can be determined.
Oe, Kazuhiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Lerum, H. V.*; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Lerum, H. V.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We are planning to investigate the redox behavior of element 106, seaborgium (Sg). For the Sg study, we newly developed a continuous dissolution apparatus which dissolves the gas-jet transported nuclides produced in nuclear reactions into aqueous solution. The new apparatus has a hydrophobic membrane filter for separation of aqueous solution from the gas. We investigated the dissolution efficiencies with the apparatus for short-lived nuclides of molybdenum and tungsten which are lighter homologues of Sg. In the meeting, the dependence of the efficiencies on the aqueous- and gas-flow rates will be reported.
Miyashita, Sunao; Oe, Kazuhiro; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Omtvedt, J. P.*; et al.
no journal, ,
For the experiments of the redox potentials of Sg, rapid separation between different oxidation states of Sg is needed. In this study, solvent extraction of hexavalent Mo and W, as the lighter homologues of Sg, from 1.0 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution into di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (HDEHP), 1-phenyl-3-metyl-4-benzoyl-5-pyrazolone (PMBP), N-benzoyl-N-pheny-hydroxylamine (BPHA) and 4-isopropyl-tropolone (HT) in toluene was carried out. When HDEHP and PMBP were used as extractant, extraction equilibrium of  W was achieved within 5 and 1 hours respectively. On the other hand, when BPHA and HT were used, extraction equilibrium of
W was achieved within 5 and 1 hours respectively. On the other hand, when BPHA and HT were used, extraction equilibrium of  W was quickly achieved within 1 minute in both extractants. Extraction kinetics of
W was quickly achieved within 1 minute in both extractants. Extraction kinetics of 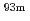 Mo using BPHA and HT was examined. Extraction kinetics of Mo was slower than that of W. Extraction equilibrium of Mo was achieved within 10 by BPHA and 3 minutes by HT. We concluded that HT is a suitable extractant for the Sg reduction experiment.
Mo using BPHA and HT was examined. Extraction kinetics of Mo was slower than that of W. Extraction equilibrium of Mo was achieved within 10 by BPHA and 3 minutes by HT. We concluded that HT is a suitable extractant for the Sg reduction experiment.
Miyashita, Sunao; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Solvent extraction of  Mo and
Mo and  W using 4-isopropyltropolone (Hinokitiol, HT) was investigated. Extraction mechanism of Mo and W with HT was examined by slope analysis. The slopse of the distribution ratio of Mo and W vs. [HT] in logarithmic scale are 1.88 and 1.54, respectively.
W using 4-isopropyltropolone (Hinokitiol, HT) was investigated. Extraction mechanism of Mo and W with HT was examined by slope analysis. The slopse of the distribution ratio of Mo and W vs. [HT] in logarithmic scale are 1.88 and 1.54, respectively.
Miyashita, Sunao; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
del, M.; Kaneya, Yusuke; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
no journal, ,
The extraction behavior of hexavalent and reduced Mo and W were investigated when aqueous phase was 0.1 M HCl/0.9 M LiCl solution. The D value of Mo was changed from 10 to 1 when applied potential was near 0 to -0.2 V. On the other hand, the D value of W was not changed at all applied potentials in this experimental condition. Those results indicated that Mo was reduced by FEC, and the extraction behavior of reduced Mo was different from hexavalent Mo. In the case of W, W was not reduced or the D values of reduced W was same as hexavalent W.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sch del, M.; Lerum, H. V.*; et al.
del, M.; Lerum, H. V.*; et al.
no journal, ,
To carry out a continuous reduction experiment of Sg with the low production rates and the short half-life, we are developing a new chemistry assembly consisting of a membrane degasser (MDG), a flow electrolytic column (FEC), the continuous liquid-liquid extraction apparatus, and the liquid scintillation counting system (SISAK). Recently, we have begun preparatory studies with Mo and W isotopes. Aqueous solution dissolving Mo and W was successfully separated from a carrier gas. Redox couples of Mo(VI)/Mo(V) and W(VI)/W(V) in HCl have been characterized for their macro amounts. Extraction behavior of Mo(VI) and W(VI) between toluene containing hinokitiol (HT) and HCl was successfully observed by a batch method. On-line extractions of short-lived Mo and W were also carried out using SISAK and MDG. In the symposium, our present status of the preparation with Mo and W will be presented.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Attallah, M. F.*; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Towards electrolytic reduction of Sg, batch-wise electrolytic reduction of carrier-free  Mo and
Mo and 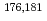 W radiotracers was studied using a flow electrolytic column (FEC). The electrolyzed samples from a FEC were chemically analyzed by solvent extraction with TOA and HDEHP to separate and identify reduced species from the stable Mo(VI) and W(VI) ones based on their different extraction behavior.
W radiotracers was studied using a flow electrolytic column (FEC). The electrolyzed samples from a FEC were chemically analyzed by solvent extraction with TOA and HDEHP to separate and identify reduced species from the stable Mo(VI) and W(VI) ones based on their different extraction behavior.  Mo and
Mo and 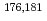 W were applied as radiotracers. We also performed cyclic voltammetry and UV/Vis absorption spectrometry of macro amounts of Mo and W in acidic solutions to obtain information on redox reactions of these elements under given conditions. In the conference, the present status of the preparatory reduction experiments with Mo and W will be presented.
W were applied as radiotracers. We also performed cyclic voltammetry and UV/Vis absorption spectrometry of macro amounts of Mo and W in acidic solutions to obtain information on redox reactions of these elements under given conditions. In the conference, the present status of the preparatory reduction experiments with Mo and W will be presented.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Kitayama, Yuta*; Lerum, H. V.*; Goto, Naoya*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Komori, Yukiko*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Vascon, A.; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Asai, Masato; Attallah, M. F.*; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Kaneko, Masashi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Due to short half-lives less than 10 s and extremely low production rates, transactinide elements heavier than seaborgium (Sg) are produced on an atom per hour scale. Therefore, a continuous rapid chemistry assembly is required to study aqueous-phase chemistry of these heaviest elements. In the present study, we started developments of a continuous chemistry assembly. Our first attempt was made in on-line experiments with Mo and W, lighter homologs of Sg, to optimize a chemistry assembly consisting of a newly developed membrane degasser as an interface between gas-jet and aqueous phase, a flow electrolytic column apparatus utilized to control oxidation states of Mo and W ions, and the continuous liquid-liquid extraction apparatus of SISAK for separation. In the conference, present status of the developments will be presented.
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
To ensure the safety of workers working at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), a technology to measure the distribution of radioactive materials in the working environment is required. In order to develop a new gamma-ray imager that can compensate for the shortcomings of existing gamma-ray imagers, the feasibility of a gamma-ray detector that does not require a shield was examined by simulation. There are pinhole cameras and a Compton camera as a technology for imaging radioactive material distribution. Since the pinhole camera can identify the source direction in one event, the image reconstruction is easy, and there is a possibility that it can be applied to quantitative measurement. However, the total weight is too heavy to be suitable for remote measurement because a shield is required. Since the Compton camera does not require a shield, it is small and light, and remote measurement is possible. However, multiple events are required to estimate the source direction, and the cone drawn at that time becomes noise, and the S/N ratio of the image is lowered. We propose a novel gamma-ray imager such as a pinhole camera that does not require shields. In this study, we verified the principle of a directional gamma-ray detector that does not require a shield.
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagata, Shuhei*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kitayama, Ayami; Dobashi, Ryuta*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kitayama, Ayami; Nagata, Shuhei*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Dobashi, Ryuta*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English