Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwase, Hiroki*; Akamatsu, Masaaki*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Kazuki*; Sakai, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(1), p.110 - 115, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:85.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)With the increasing importance of light-responsive materials, it is vital to analyze the relationship between function and structural changes induced by light irradiation. Small-angle scattering (SAS) is effective for such structural analysis. However, quantitatively capturing local molecular structure formation and molecular reactions at a scale of less than 1 nm via SAS is difficult. In this study, to analyze the structure of non-equilibrium phenomena in light-responsive materials, a new sample environment has been developed for a time-of-flight small- and wide-angle neutron scattering instrument (TAIKAN), comprising a UV-Vis irradiation system, UV-Vis absorption measurement equipment and photodetector. Simultaneous measurement of small-angle neutron scattering and UV-Vis absorption was achieved. This system was used to demonstrate the in situ observation of UV-Vis irradiation-induced structural change of micelles formed by a light-responsive surfactant sample in an aqueous solution.
 Cs discharge from a forested catchment
Cs discharge from a forested catchmentSakuma, Kazuyuki; Hayashi, Seiji*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Malins, A.; Funaki, Hironori; Tsuji, Hideki*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; Kitamura, Akihiro; Iijima, Kazuki
Water Resources Research, 58(8), p.e2021WR031181_1 - e2021WR031181_16, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:39.28(Environmental Sciences)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Kobayashi, Hideki*; Suzuki, Rikie*; Yang, W.*; Ikawa, Hiroki*; Inoue, Tomoharu*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Kim, Y.*
Polar Data Journal (Internet), 2, p.14 - 29, 2018/11
The Arctic and boreal regions have been experiencing a rapid warming in the 21st century. It is important to understand the dynamics of boreal forest at the continental scale under the climate and environmental changes. While the role of understory vegetation in boreal forest ecosystems on carbon and nutrient cycling cannot be ignored, they are still one of least understood components in boreal ecosystems. Spectroscopic measurements of vegetation are useful to identify species and their biochemical characteristics. In this data paper, we present spectral reflectances of 44 typical understory formations and five 30-m long transects. The spectral reflectance covers the spectral region of visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared (350-2500 nm). For the transect measurements, we decided the length of transect at 30 m, similar to the scale of one pixel of a Landsat type satellite imagery. The photographs at all positions, where spectral reflectances were obtained, are included to understand the structure and status of each sample. The data set contains six dwarf shrubs (blueberry (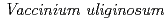 ), cowberry (
), cowberry (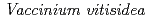 ), feltleaf willow (
), feltleaf willow (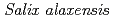 ), young birch (
), young birch (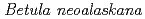 ), young aspen (
), young aspen ( ), and young black spruce (
), and young black spruce ( )), two herbaceous (cottongrass (
)), two herbaceous (cottongrass ( ) and marsh Labrador tea (
) and marsh Labrador tea ( )), three mosses (Sphagnum moss, splendid feather moss (
)), three mosses (Sphagnum moss, splendid feather moss (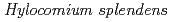 ), and polytrichum moss (
), and polytrichum moss (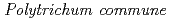 )), and reindeer lichen (
)), and reindeer lichen (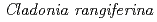 ). Spectral reflectances from several non-vegetative such as snow, litter, and soil are also included. This spectral and photographic data set can be used for understanding the spectral characteristics of understory formations, designing newly planned spectral observations, and developing and validating the remote sensing methodology of large scale understory monitoring.
). Spectral reflectances from several non-vegetative such as snow, litter, and soil are also included. This spectral and photographic data set can be used for understanding the spectral characteristics of understory formations, designing newly planned spectral observations, and developing and validating the remote sensing methodology of large scale understory monitoring.
Kobayashi, Hideki*; Nagai, Shin*; Kim, Y.*; Yan, W.*; Ikeda, Kyoko*; Ikawa, Hiroki*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Suzuki, Rikie*
Remote Sensing, 10(7), p.1071_1 - 1071_19, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:51.57(Environmental Sciences)Plant phenology timings, such as spring green-up and autumn senescence, are essential state information characterizing biological responses and terrestrial carbon cycles. Current efforts for the in situ reflectance measurements are not enough to obtain the exact interpretation of how seasonal spectral signature responds to phenological stages in boreal evergreen needleleaf forests. This study shows the first in situ continuous measurements of canopy scale (overstory + understory) and understory spectral reflectance and vegetation index in an open boreal forest in interior Alaska. Two visible and near infrared spectroradiometer systems were installed at the top of the observation tower and the forest understory, and spectral reflectance measurements were performed in 10 min intervals from early spring to late autumn. We found that canopy scale normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) varied with the solar zenith angle. On the other hand, NDVI of understory plants was less sensitive to the solar zenith angle. Due to the influence of the solar geometry, the annual maximum canopy NDVI observed in the morning satellite overpass time (10-11 am) shifted to the spring direction compared with the standardized NDVI by the fixed solar zenith angle range (60-70 degree). We also found that the in situ NDVI time-series had a month-long high NDVI plateau in autumn, which was completely out of photosynthetically active periods when compared with eddy covariance net ecosystem exchange measurements. The result suggests that the onset of an autumn high NDVI plateau is likely to be the end of the growing season. In this way, our spectral measurements can serve as baseline information for the development and validation of satellite-based phenology algorithms in the northern high latitudes.
Wakai, Takashi; Kobayashi, Sumio; Kato, Shoichi; Ando, Masanori; Takasho, Hideki*
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/07
This paper describes a thermal fatigue test on a structural model with a dissimilar welded joint. In the present design of JSFR, there may be dissimilar welded joints between ferritic and austenitic steels especially in IHX and SG. Creep-fatigue is one of the most important failure modes in JSFR components. However, the creep-fatigue damage evaluation method has not been established for dissimilar welded joint. To investigate the evaluation method, structural test will be needed for verification. Therefore, a thermal fatigue test on a thick-wall cylinder with a circumferential dissimilar welded joint between Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel and 304SS was performed. Since the coefficients of thermal expansion of these steels were significantly different, buttering layer of Ni base alloy was installed between them. After the completion of the test, deep cracks were observed at the HAZ in 304SS, as well as at HAZ in Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. There were many tiny surface cracks in BM of 304SS. According to the fatigue damage evaluation based on the finite element analysis results, the largest fatigue damage was calculated at HAZ in 304SS. Large fatigue damage was also estimated at BM of 304SS. Fatigue cracks were observed at HAZ and BM of 304SS in the test, so that analytical results are in a good agreement with the observations. However, though relatively small fatigue damage was estimated at HAZ in Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel, deep fatigue cracks were observed in the test. To identify the cause of such a discrepancy between the test and calculations, we performed a series of finite element analyses. Some metallurgical investigations were also performed.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamichi, Hideo; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Nishimura, Kazuaki; Fujisaku, Sakae; Tanaka, Hideki; Isomae, Hidemi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Kurita, Tsutomu; Iida, Masayoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/04
TRP has stored the plutonium in solution state for long-term since the last PCDF operation in 2007 was finished. After the great east Japan earthquake in 2011, JAEA had investigated the risk against potential hazard of these solutions which might lead to make hydrogen explosion and/or boiling of the solution accidents with the release of radioactive materials to the public when blackout. To reduce the risk for storing Pu solution (about 640 kg Pu), JAEA planned to perform the process operation for the solidification and stabilization of the solution by converted into MOX powder at PCDF in 2013. In order to perform PCDF operation without adaption of new safety regulation, JAEA conducted several safety measures such as emergency safety countermeasures, necessary security and safeguards (3S) measures with understanding of NRA. As a result, the PCDF operation had stared on 28th April, 2014, and successfully completed to convert MOX powder on 3rd August, 2016 for about 2 years as planned.
Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki; Kobayashi, Jun; Kamide, Hideki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 4(1), p.16-00217_1 - 16-00217_15, 2017/02
In the design of the Advanced Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor in Japan, the Reynolds number in the primary hot leg (H/L) piping reaches 4.2 10
10 . Furthermore, a short elbow is used in the H/L piping to achieve a compact plant layout. In the H/L piping, flow-induced vibration is a concern due to the excitation force caused by pressure fluctuation in the short elbow. In this report, the influence of inlet velocity condition on the unsteady velocity characteristics in the short elbow was studied by controlling the flow patterns at the elbow inlet. Measured velocity distributions indicated that the inlet velocity profiles affected a circumferential secondary flow, which then affected an area of flow separation at the elbow. It was also found that the velocity fluctuation at low frequency components observed upstream of the elbow could remain in downstream of the elbow though its intensity was attenuated.
. Furthermore, a short elbow is used in the H/L piping to achieve a compact plant layout. In the H/L piping, flow-induced vibration is a concern due to the excitation force caused by pressure fluctuation in the short elbow. In this report, the influence of inlet velocity condition on the unsteady velocity characteristics in the short elbow was studied by controlling the flow patterns at the elbow inlet. Measured velocity distributions indicated that the inlet velocity profiles affected a circumferential secondary flow, which then affected an area of flow separation at the elbow. It was also found that the velocity fluctuation at low frequency components observed upstream of the elbow could remain in downstream of the elbow though its intensity was attenuated.
Kobayashi, Jun; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 10th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2016/11
JAEA has been conducting a design study for an advanced large-scale sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). Hot sodium from the fuel subassembly can mix with the cold sodium from the control rod (CR) channel at the bottom of Upper Internal Structure (UIS). Temperature fluctuation due to the fluid mixing at the core outlet may cause high cycle thermal fatigue at the bottom of UIS. JAEA had performed a water experiment to examine countermeasures for the significant temperature fluctuation generated at the bottom of SFRs UIS. Meanwhile, a self-actuated shutdown system (SASS) is equipped in a backup control rod (BCR) channel to ensure reactor shutdown. The BCR guide tubes have a flow guide structure "flow-collector" to provide reliable operation of SASS. Flow-collector may affect the thermal mixing behavior at the bottom of the UIS. This study has investigated the influence of the flow- collector on characteristics of the temperature fluctuation around the BCR channels.
Ono, Ayako; Kamide, Hideki; Kobayashi, Jun; Doda, Norihiro; Watanabe, Osamu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(9), p.1385 - 1396, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:71.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)Decay heat removal by natural circulation is a significant passive safety measure of a fast reactor against station blackout. The decay heat removal system (DHRS) of the loop type sodium fast reactor being designed in Japan comprises a direct reactor auxiliary cooling system and primary reactor auxiliary cooling system (PRACS). The thermal hydraulic phenomena in the plant under natural circulation conditions need to be understood for establishing a reliable natural circulation driven DHRS. In this study, sodium experiments were conducted using a plant dynamic test loop to understand the thermal-hydraulic phenomena considering natural circulation in the plant. The experiments simulating the scram transient confirmed that PRACS started up smoothly under natural circulation, and the simulated core was stably cooled after the scram. Moreover, the experiments varying the pressure loss coefficients of the loop as the experimental parameters showed robustness of the PRACS.
Ikuta, Masafumi*; Niwa, Masakazu; Danhara, Toru*; Yamashita, Toru*; Maruyama, Seiji*; Kamataki, Takanobu*; Kobayashi, Tetsuo*; Kurosawa, Hideki*; Kokubu, Yoko; Hirata, Takafumi*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 122(3), p.89 - 107, 2016/03
We carried out mineral composition analysis, morphological classification of volcanic glass shards and refractive index measurements of the glass shards and orthopyroxene from the eruption products from Sakurajima volcano. In this study, refractive indexes of hydrated and non-hydrated parts within each individual glass shard were measured separately. This measurements in consideration of hydration in glass shards made possible distinct discrimination of the pumice samples from the three eruption events of Bunmei, An-ei, and Taisho. Pumice layers in the core samples obtained from the southern part of the Miyazaki Plain were also identified as the Sakurajima-Bunmei tephra by the above mentioned analyses, and also by the data of radiocarbon dating for coaly materials included in the pumice layers. Occurrences of the pumice layers suggest that the Sakurajima-Bunmei tephra could have reached the southern part of Miyazaki Plain as pumice falls.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Shirai, Yasuyuki*; Shiotsu, Masahiro*; Naruo, Yoshihiro*; Kobayashi, Hiroaki*; Nonaka, Satoshi*; Inatani, Yoshifumi*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 101, p.012177_1 - 012177_8, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Thermodynamics)Transient heat transfers from PtCo wire heaters inserted into vertically-mounted pipes, through which forced flow subcooled liquid hydrogen was passed, were measured by increasing the exponential heat input with various time periods at a pressure of 0.7 MPa and inlet temperature of 21 K. The flow velocities ranged from 0.3 to 7 m/s. The PtCo wire heaters had a diameter of 1.2 mm and lengths of 60 mm, 120 mm and 200 mm and were inserted into the pipes with diameters of 5.7mm, 8.0 mm, and 5.0 mm, respectively. With increase in the heat flux to the onset of nucleate boiling, surface temperature increased along the curve predicted by the Dittus-Boelter correlation for longer period, where it can be almost regarded as steady-state. For shorter period, the heat transfer became higher than the Dittus-Boelter correlation. In nucleate boiling regime, the heat flux steeply increased to the transient critical heat flux (CHF), which became higher for shorter period. Effect of flow velocity, period, and heated geometry on the transient CHF was clarified.
Kobayashi, Jun; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.6664 - 6677, 2015/08
Numerical simulation is recognized an essential tool for the physical phenomena analysis and plant design study of a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). In order to enhance credibility of the numerical results in the activities for plant design by using numerical simulations, it is recognized that verification and validation (V&V) process is very important. In this study, experiments for planar triple parallel jets mixing phenomena conducted in JAEA were proposed as benchmark problems for the code validation in the area of thermal striping study in the SFR development.
Tomita, Masanori*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Maeda, Munetoshi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Life Sciences in Space Research, 6, p.36 - 43, 2015/07
A radiation-induced bystander response is generally known as a cellular response induced in unirradiated cell by receiving bystander signaling factors released from directly irradiated cells of a cell population. Bystander responses induced by high-LET heavy ions at low fluence are an important problem concerning the health of astronauts in the space environment. Here we set out NO-mediated bystander signal transductions induced by high-LET heavy-ion microbeam irradiation in normal human fibroblasts. Our findings suggest that Akt- and NF- B-dependent signaling pathway involving COX-2 plays an important role in the NO-mediated high-LET heavy-ion-induced bystander responses. Additionally, COX-2 may be used as a molecular marker of high-LET heavy-ion-induced bystander cells, which are distinguish form directly irradiated cells.
B-dependent signaling pathway involving COX-2 plays an important role in the NO-mediated high-LET heavy-ion-induced bystander responses. Additionally, COX-2 may be used as a molecular marker of high-LET heavy-ion-induced bystander cells, which are distinguish form directly irradiated cells.
Kobayashi, Jun; Ezure, Toshiki; Kamide, Hideki; Oyama, Kazuhiro*; Watanabe, Osamu*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
A column type upper internal structure (UIS) is installed in the upper plenum of reactor vessel in JSFR. High cycle thermal fatigue may occur at the bottom plate (CIP) of the UIS where the hot sodium from the fuel subassembly can mix with the cold sodium from the control rod channel and the blanket fuel subassembly. We have been conducted a water experiment using a reactor upper plenum model to grasp the thermal-hydraulic phenomena around control rod (CR) channels, and to obtain countermeasures for significant temperature fluctuation on the CIP. The experimental apparatus has 1/3 scale and 60 sector model of the reactor upper plenum. By the experiment, characteristics of fluid temperature fluctuation between the handling head of the assemblies and the CIP are measured and countermeasure for the significant temperature fluctuation generation will be discussed on the influence of the distance from the handling head outlet to the lower surface of the CIP.
sector model of the reactor upper plenum. By the experiment, characteristics of fluid temperature fluctuation between the handling head of the assemblies and the CIP are measured and countermeasure for the significant temperature fluctuation generation will be discussed on the influence of the distance from the handling head outlet to the lower surface of the CIP.
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Tomita, Masanori*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Maeda, Munetoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Hiroko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 76, 2015/03
The objective of this project is to elucidate molecular mechanisms for the induction of radioadaptive response through radiation-induced bystander responses induced by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams in JAEA. We found that the adaptive response was induced by Ar (520 MeV  Ar
Ar ) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that
) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that 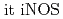 expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
Tomita, Masanori*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 77, 2015/03
Radiation-induced bystander responses are defined as responses in cells that have not been directly targeted by radiation but are in the neighborhood of cells that have been directly exposed. In this study, we aim to clarify a role of bystander response to sustain the homeostasis of damaged tissue using heavy-ion microbeams. We established the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation method to a 3D cultured human epidermis. Using this method, a viable cell rate of the 3D cultured human epidermis irradiated with 260 MeV  Ne-ion microbeams or broadbeams was analyzed by the MTT method.
Ne-ion microbeams or broadbeams was analyzed by the MTT method.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Kobayashi, Jun; Onojima, Takamitsu; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohno, Shuji; Kamide, Hideki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*
Proceedings of 10th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 13 Pages, 2014/12
Thermal striping phenomenon is one of the most important issues in an advanced loop type sodium cooled reactor JSFR. Temperature fluctuation caused by mixing of fluids at different temperature from the control rod channels and the core fuel assemblies may touch the Core Instrument Plane (CIP) at bottom of the Upper Internal Structure (UIS) and cause high cycle thermal fatigue there. In JAEA, the 1/3-scaled Five Jets Water Test (FIWAT) has been performed in order to investigate thermal striping phenomena around the CIP. In the FIWAT, the test section was simulating a control rod channel, adjacent four fuel subassemblies and a part of the CIP. The flow rate ratio and the absolute velocity of hot jets as the reference experimental condition were equal to that of the JSFR and a third of JSFR, respectively. In the experiment, it was shown that the fluid temperature fluctuation characteristics around the structure depended on the flow rate ratio. The temperature fluctuation which showed sudden decrease and recovery like a spike form was intermittently observed in the fluid near the structure. The amplitude of such spike-like temperature fluctuation in the fluid was much mitigated on the structure surface.
Ono, Ayako; Tanaka, Masaaki; Kobayashi, Jun; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 9th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-9) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/11
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Kobayashi, Jun; Kameyama, Yuri*; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Ezure, Toshiki; Ono, Ayako; Kamide, Hideki
JAEA-Research 2014-009, 104 Pages, 2014/07
In this study, water experiments (WATLON) were carried out to clarify the unsteady behavior of heat transfer under wall jet condition in the mixing tee. In experiments, heat transfer coefficients between fluid and wall in the mixing region were obtained from temperature measurements using thermocouples (movable tree type in fluid and embedded type in wall). To clarify the relation between the local velocity and the wall temperature, those were measured simultaneously by the Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) and the thermocouple measurement, respectively. Sampling time of the velocity by the PIV and the temperature by the thermocouple were synchronized in the measurement. The experimental results showed that the heat transfer coefficient was from 2 - 6 time larger than the reference value predicted by the Dittus-Boelter correlation in straight pipes and was increased as the local velocity near the wall.