Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.2(Physics, Applied)Kobayashi, Taishi*; Fushimi, Tomokazu*; Mizukoshi, Hirofumi*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 38(48), p.14656 - 14665, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Shimamura, Keisuke*; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Nagai, Takayuki; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 570, p.153962_1 - 153962_13, 2022/11
Simulated nuclear waste glass samples containing phosphorus, which increase the solubility of molybdenum, were prepared and analyzed using synchrotron X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS) analysis for some constituent elements and Raman spectroscopic analysis of their complex structure. Changes in local structure and chemical state due to different phosphorus additions and waste loading rates were systematically studied. Consequently, no crystalline phase due to the molybdate compound was observed even at a maximum waste content of 30 wt% (corresponding to 1.87 mol% MoO ). Oxidation proceeded when the waste-loading rate was increased, whereas the reduction proceeded when phosphorus was added. In some cases, the effects of oxidation and reduction were offset. The local structure around specific elements can be classified as follows; Zn that is affected mainly by the waste-loading rate, Ce that is affected by both the waste-loading rate and phosphorus addition, and Zr element that is not affected by either of them. From the comparison between the analytical results of Mo and other elements, it was considered that the added phosphorus exists as a free PO
). Oxidation proceeded when the waste-loading rate was increased, whereas the reduction proceeded when phosphorus was added. In some cases, the effects of oxidation and reduction were offset. The local structure around specific elements can be classified as follows; Zn that is affected mainly by the waste-loading rate, Ce that is affected by both the waste-loading rate and phosphorus addition, and Zr element that is not affected by either of them. From the comparison between the analytical results of Mo and other elements, it was considered that the added phosphorus exists as a free PO structural unit and may deprive the alkali metal coordinated to the molybdate ion.
structural unit and may deprive the alkali metal coordinated to the molybdate ion.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
 and Eu
and Eu ions onto sedimentary rock in the presence of gamma-irradiated humic acid
ions onto sedimentary rock in the presence of gamma-irradiated humic acidZhao, Q.*; Saito, Takeshi*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, p.128211_1 - 128211_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:62.11(Engineering, Environmental)The influence of humic acid and its radiological degradation on the sorption of Cs and Eu
and Eu by sedimentary rock was investigated to understand the sorption process of metal ions and humic substances. Aldrich humic acid (HA) solution was irradiated with different doses of gamma irradiation using a Co-60 gamma-ray source prior to the contact between the metal ions and the solid sorbent. The HA molecule decomposed to smaller molecules with a lower complexation affinity. Batch sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effect of gamma-irradiated HA on the sorption of Cs
by sedimentary rock was investigated to understand the sorption process of metal ions and humic substances. Aldrich humic acid (HA) solution was irradiated with different doses of gamma irradiation using a Co-60 gamma-ray source prior to the contact between the metal ions and the solid sorbent. The HA molecule decomposed to smaller molecules with a lower complexation affinity. Batch sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effect of gamma-irradiated HA on the sorption of Cs and Eu
and Eu ions. The addition of non-irradiated HA weakened the sorption of Eu because of the lower sorption of the neutral or negatively charged Eu-HA complexes compared with free Eu ions. The sorption of monovalent Cs ions was barely affected by the presence of HA and its gamma irradiation. The concentration ratio of HA complexed species and non-complexed species in the solid and liquid phases was evaluated by sequential filtration and chemical equilibrium calculations. The ratios supported the minimal contribution of HA to Cs sorption. However, the concentration ratio for Eu
ions. The addition of non-irradiated HA weakened the sorption of Eu because of the lower sorption of the neutral or negatively charged Eu-HA complexes compared with free Eu ions. The sorption of monovalent Cs ions was barely affected by the presence of HA and its gamma irradiation. The concentration ratio of HA complexed species and non-complexed species in the solid and liquid phases was evaluated by sequential filtration and chemical equilibrium calculations. The ratios supported the minimal contribution of HA to Cs sorption. However, the concentration ratio for Eu in the liquid phase was high, indicating that the complexing ability of HA to Eu
in the liquid phase was high, indicating that the complexing ability of HA to Eu was higher than that of HA to Cs
was higher than that of HA to Cs ions. Therefore, the sorption of free Eu
ions. Therefore, the sorption of free Eu would predominate with the gamma irradiation dose applied to the HA solution under a radiation field near the HLW package.
would predominate with the gamma irradiation dose applied to the HA solution under a radiation field near the HLW package.
 Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.69(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Motoshima, Takayuki*; Matsui, Hiroya; Kawakubo, Masahiro*; Kobayashi, Masato*; Ichimura, Tetsuhiro*; Sugita, Yutaka
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(3), p.163 - 167, 2022/03
, 64(3), p.163 - 167, 2022/03
no abstracts in English
Kimata, Tetsuya*; Kakitani, Kenta*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Iwase, Akihiro*; Mao, W.*; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Terai, Takayuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(3), p.035801_1 - 035801_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takeda, Shino*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kobayashi, Taishi*
The Chemistry of Thorium, Plutonium and MA, 254 Pages, 2022/03
The chemistry of nuclear materials such as Thorium (Part 1) and Plutonium (Part 2) was described in relation from the fundamentals on solid chemistry and solution chemistry to the practicals on the experiment and evaluation method in detail. Minor actinides such as Neptunium, Americium, Curium and Protoactinium, was introduced the basics on the solid and solution chemistry.
Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Oba, Yojiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Heller, W. T.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 578, p.121352_1 - 121352_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.84(Materials Science, Ceramics)Hasegawa, Yuta; Aoki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Hiromichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Parallel Computing, 108, p.102851_1 - 102851_12, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.94(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)The aerodynamics simulation code based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) using forest-of-octrees-based block-structured local mesh refinement (LMR) was implemented, and its performance was evaluated on GPU-based supercomputers. We found that the conventional Space-Filling-Curve-based (SFC) domain partitioning algorithm results in costly halo communication in our aerodynamics simulations. Our new tree cutting approach improved the locality and the topology of the partitioned sub-domains and reduced the communication cost to one-third or one-fourth of the original SFC approach. In the strong scaling test, the code achieved maximum 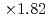 speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega- lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs. In the weak scaling test, the code achieved 9620 MLUPS at 128 GPUs with 4.473 billion grid points, while the parallel efficiency was 93.4% from 8 to 128 GPUs.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Aoki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Hiromichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 6 Pages, 2021/05
We introduce an improved domain partitioning method called "tree cutting approach" for the aerodynamics simulation code based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) with the forest-of-octrees-based local mesh refinement (LMR). The conventional domain partitioning algorithm based on the space-filling curve (SFC), which is widely used in LMR, caused a costly halo data communication which became a bottleneck of our aerodynamics simulation on the GPU-based supercomputers. Our tree cutting approach adopts a hybrid domain partitioning with the coarse structured block decomposition and the SFC partitioning in each block. This hybrid approach improved the locality and the topology of the partitioned sub-domains and reduced the amount of the halo communication to one-third of the original SFC approach. The code achieved 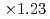 speedup on 8 GPUs, and achieved
speedup on 8 GPUs, and achieved 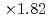 speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega-lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs with strong scaling test.
speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega-lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs with strong scaling test.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Sasage, Kenichi; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Nagai, Takayuki
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 551, p.120393_1 - 120393_8, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.89(Materials Science, Ceramics)The chemical state of ruthenium in simulated iron phosphate radioactive waste glass was investigated by conventional X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and imaging XAFS analyses. The EXAFS analysis suggested that ruthenium was contained as glass phase when content of the waste components was less than 10wt.% in 30 mol%Fe O
O -P
-P O
O base glass. In other samples, crystalline RuO
base glass. In other samples, crystalline RuO was predominant. According to the imaging XAFS analysis, RuO
was predominant. According to the imaging XAFS analysis, RuO particles in all samples had length smaller than 50
particles in all samples had length smaller than 50 m. Aggregations of RuO
m. Aggregations of RuO , which are found in nuclear waste borosilicate glass, were not seen in any of the iron phosphate glass samples.
, which are found in nuclear waste borosilicate glass, were not seen in any of the iron phosphate glass samples.
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs in soils near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Cs in soils near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationSasaki, Takayuki*; Matoba, Daisuke*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Iijima, Kazuki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 326(1), p.303 - 314, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.51(Chemistry, Analytical) -isosaccharinic acid
-isosaccharinic acidKobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 138, p.151 - 158, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.74(Thermodynamics)The effect of  -isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH
-isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) range of 6
) range of 6 13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]
13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]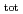 ) = 10
) = 10
 10
10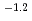 mol/dm
mol/dm . The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH
. The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH and [ISA]
and [ISA] suggested the existence of U(OH)
suggested the existence of U(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 as a dominant species within the investigated pH
as a dominant species within the investigated pH range of 6
range of 6 12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO
12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO (OH)
(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 was suggested as a dominant species at pH
was suggested as a dominant species at pH 7
7 13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sekimoto, Shun*
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 105, 2019/08
To understand this structural change of a borosilicate glass by a neutron irradiation in detail, the irradiation test was carried out in KUR in 2017FY. The glass structure was estimated by using Raman spectrometry in 2018FY. Comparing with the Raman spectra of glass samples before and after irradiation, it could be observed the change of peak height of Si-O bridging structure by the irradiation.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Nakajima, Shogo*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Langmuir, 35(24), p.7995 - 8006, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.5(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kano, Shigeru; Himeno, Haruyuki*; Kobayashi, Hiroshi*; Nakatani, Mikio*
JAEA-Research 2018-013, 18 Pages, 2019/03
The chemical state and local structure of some elements in the simulated nuclear waste glass samples (20 batches) prepared by bottom drain test in the full scale mock-up tests using KMOC melter were investigated by synchrotron radiation based X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analysis. As a result of the analysis of cerium element, it was confirmed that the oxidation proceeds gently as the batch advanced. For manganese, iron, and zinc, there was almost no difference between batches, which seemed to be stabilized by getting into the frame structure of the borosilicate glass. There were no elements that seemed to be clearly crystalline except for platinum group elements. Remarkable precipitation was hardly observed in zirconium and molybdenum with the imaging analysis.