Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Morita, Hisashi; Daigo, Fumihisa; Sayato, Natsuki; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Kojima, Kazuki; Nakayama, Kazuhiko; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-030, 166 Pages, 2022/05
When the roof of the JMTR Hot Laboratory (HL) building was repaired for rain leaks in January, 2015, thinning was found at one of the anchor bolts on base of the HL exhaust stack. Moreover, the thinning of some anchor bolts and gaps between the anchor bolt nuts and flange plate was found in the later investigation for the exhaust stack. Since the possibility of the exhaust stack collapsing cannot be denied, it was removed. Therefore, it became necessary to rebuild a new exhaust stack as soon as possible. The design of the new exhaust stack was based on the measures to prevent rainwater intrusion into the base, which was the cause of the thinning of the anchor bolts found in the investigation, and on the new regulatory standards established after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Furthermore, since the new exhaust stack corresponds to buildings and structures that must undergo building confirmation, the soundness of the new exhaust stack against seismic force and wind load was evaluated based on the Building Standards Law and the Stack Structure Design Guideline. This report described the basic design of the new exhaust stack.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Okada, Michio*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Oka, Kohei*; Kojima, Kazuki*; Di o, W. A.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Kasai, Hideaki*
o, W. A.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Kasai, Hideaki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.31101_1 - 31101_8, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:73.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We report results of our experimental and theoretical studies on the oxidation of Cu-Au alloy surfaces, viz., Cu Au(111), CuAu(111), and Au
Au(111), CuAu(111), and Au Cu(111), using hyperthermal O
Cu(111), using hyperthermal O molecular beam (HOMB). We observed strong Au segregation to the top layer of the corresponding clean (111) surfaces. This forms a protective layer that hinders further oxidation into the bulk. The higher the concentration of Au in the protective layer formed, the higher the protective efficacy. As a result, of the three Cu-Au surfaces studied, Au
molecular beam (HOMB). We observed strong Au segregation to the top layer of the corresponding clean (111) surfaces. This forms a protective layer that hinders further oxidation into the bulk. The higher the concentration of Au in the protective layer formed, the higher the protective efficacy. As a result, of the three Cu-Au surfaces studied, Au Cu(111) is the most stable against dissociative adsorption of O
Cu(111) is the most stable against dissociative adsorption of O , even with HOMB. We also found that this protective property breaks down for oxidations occurring at temperatures above 300 K.
, even with HOMB. We also found that this protective property breaks down for oxidations occurring at temperatures above 300 K.

Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 108(20), p.205501_1 - 205501_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:67.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen atoms absorbed in a metal occupy the interstitial sites of the metal lattice. In an fcc metal lattice, each metal atom has two tetrahedral (T) and one octahedral (O) sites that can accommodate hydrogen. Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied LaH and fully occupied LaH
and fully occupied LaH . O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH
. O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH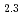 into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD
confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD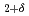 by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Kojima, Atsushi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02B121_1 - 02B121_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:46.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)JAEA has developed the MeV accelerator to demonstrate 1 MeV, 200 A/m H
H ion beam acceleration required for ITER NBI. A key to realize such a high power accelerator is improvement of voltage holding capability. Based on detailed investigation of the voltage holding characteristics, MeV accelerator was modified to reduce electric field concentration by extending gaps between the grid supports and increasing curvature radiuses at the support corners. After the modifications, accelerator succeeded in sustaining -1 MV in vacuum without beam acceleration. Moreover, beam deflection due to the magnetic field for electron suppression and space charge repulsion was compensated by aperture displacement technique. As the result, beam deflection was compensated and voltage holding during the beam acceleration was improved. Beam parameter of the MeV accelerator was increased to 980 keV, 185 A/m
ion beam acceleration required for ITER NBI. A key to realize such a high power accelerator is improvement of voltage holding capability. Based on detailed investigation of the voltage holding characteristics, MeV accelerator was modified to reduce electric field concentration by extending gaps between the grid supports and increasing curvature radiuses at the support corners. After the modifications, accelerator succeeded in sustaining -1 MV in vacuum without beam acceleration. Moreover, beam deflection due to the magnetic field for electron suppression and space charge repulsion was compensated by aperture displacement technique. As the result, beam deflection was compensated and voltage holding during the beam acceleration was improved. Beam parameter of the MeV accelerator was increased to 980 keV, 185 A/m , which is close to the requirement of ITER accelerator.
, which is close to the requirement of ITER accelerator.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Kojima, Atsushi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.449 - 456, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.22(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)At JAEA, MeV accelerator has been developed as a proof-of-principle accelerator for ITER NBI. To achieve the acceleration of 1 MeV, 200 A/m beam required for ITER, improvement of the voltage holding capability is essential. Review of voltage holding results ever obtained with various geometries of the accelerators showed that voltage holding capability was about a half of that for ideal small electrode. This is due to local electric field concentration in the accelerators, such as edge and corner between grids and its support structures. Based on these results, accelerator was modified to reduce the electric field concentration by reshaping the support structures and expanding the gap length. After the modifications, voltage holding capability in vacuum was increased from 835 kV to 1 MV. Voltage holding progressed the energy and current to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m
beam required for ITER, improvement of the voltage holding capability is essential. Review of voltage holding results ever obtained with various geometries of the accelerators showed that voltage holding capability was about a half of that for ideal small electrode. This is due to local electric field concentration in the accelerators, such as edge and corner between grids and its support structures. Based on these results, accelerator was modified to reduce the electric field concentration by reshaping the support structures and expanding the gap length. After the modifications, voltage holding capability in vacuum was increased from 835 kV to 1 MV. Voltage holding progressed the energy and current to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m ).
).
Hayashi, Takashi; Chino, Masamichi; Yamazawa, Hiromi; Nagai, Haruyasu; Moriuchi, Shigeru*; Ishikawa, Hirohiko*; Adachi, Takashi*; Kojima, Hiromi*; Okano, Hiroshi*; Odagawa, Fumiaki*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-034, 137 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Atsuko*; Ichikawa, Kazuki*; Kojima, Kazuaki*; Ono, Yutaka; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tanaka, Shigeo*; Sakata, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Phytochelatin (PC) has been shown to play an important role in heavy metal detoxification. However, Arabidopsis transgenic plants overexpressing the PC synthase gene failed to show an increase in Cd tolerance. To explore a novel heavy metal detoxification mechanism, we screened for an Arabidopsis Cd-sensitive mutant (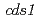 ) by carbon ion beam mutagenesis, which causes large base pair deletions at random loci in the genome. Genetic analyses and GSH synthesis inhibitor studies revealed that the
) by carbon ion beam mutagenesis, which causes large base pair deletions at random loci in the genome. Genetic analyses and GSH synthesis inhibitor studies revealed that the 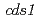 phenotype was different from those of PC synthesis mutants. Moreover, Cd content in shoots of
phenotype was different from those of PC synthesis mutants. Moreover, Cd content in shoots of 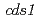 cultured on Cd-containing media was similar to wild type, suggesting that Cd-sensitive phenotype of
cultured on Cd-containing media was similar to wild type, suggesting that Cd-sensitive phenotype of 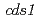 was not attributed to the Cd transport system from roots to shoots. In the rough mapping,
was not attributed to the Cd transport system from roots to shoots. In the rough mapping, 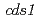 was localized to approximately 300kbp region of chromosome 4. One of the genes was found to have a 2.5 kbp deletion in the promoter region.
was localized to approximately 300kbp region of chromosome 4. One of the genes was found to have a 2.5 kbp deletion in the promoter region.
Kojima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Aoki, Katsutoshi; Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Otomo, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction measurements have revealed that LaD undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD
undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD , move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD
, move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH
both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH
is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results. Enthalpy comparison shows that unusual volume contraction in LaH
at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results. Enthalpy comparison shows that unusual volume contraction in LaH than LaH
than LaH explains the phase separation phenomena. Lattice dynamics calculations on these lanthanum hydrides shed light on the detailed mechanism.
explains the phase separation phenomena. Lattice dynamics calculations on these lanthanum hydrides shed light on the detailed mechanism.

Aoki, Katsutoshi; Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Otomo, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements have revealed that LaD undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Synchrotron X-ray and neutron experiments were made at BL22XU, SPring-8 and a total scattering device, NOVA, J-PARC. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD
undergoes phase separation at high pressure with the relocation of deuterium atoms in the interstitial sites of La metal lattice. Synchrotron X-ray and neutron experiments were made at BL22XU, SPring-8 and a total scattering device, NOVA, J-PARC. Deuterium atoms, which occupy the tetrahedral sites of the fcc metal lattice in LaD , move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD
, move into the empty octahedral sites at 11 GPa to form LaD and LaD both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH
both having fcc metal lattices. Mono-hydride with an NaCl structure, which is common for mono-hydrides of transition metals, is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. The first-principle calculations showed that LaH is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH
is stable at low pressure and it undergoes a phase separation into LaH and LaH at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results.
at 10 GPa, which is excellent agreement with the experimental results.
Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Formation of an NaCl-type mono-deuteride LaD has been found by neutron diffraction experiments at high pressure. The NaCl-type structure has been reported for alkaline hydrides and transition metal hydrides, but not for rare-earth metal hydrides. The NaCl-type mono-hydride is formed in rare-earth metals for the first time. Lanthanum mono-deuteride is formed as a result of the phase separation of the di-deuteride under high pressure. This result suggests that the three different hydrides, mono-, di-, and tri-hydrides, with the fcc metal lattice are realized. The hydrogen atoms occupy only O-sites, only T-sites and both O-sites and T-sites in the mono-, di-, and tri-hydrides, respectively. Hence, it is expected that the H-M bonding nature is different for each hydride.

Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated the pressure-induced phase separation in rare-earth metal dihydrides by synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction experiments. Rare-earth metal hydrides exhibit the stoichiometoric dihydride and trihydride. The dihydride is a metallic while trihydride is an insulator. Recently, we have found the pressure induced phase separation in the lanthanum dihydride. This phenomenon is understood as the decomposition into the hydrogen-poor and rich phases under high pressure. However, the hydrogen occupancy and position have been unclear yet. Our neutron diffraction experiments have revealed that an NaCl-type mono-deuteride is formed as a counterpart of the deuterium-rich phase.
Aoki, Katsutoshi; Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Otomo, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied fcc-LaH and fully occupied fcc-LaH
and fully occupied fcc-LaH , the former is metallic and the latter is insulating. Our previous synchrotron X-ray and infrared measurements revealed that the dihydride decomposed into hydrogen-rich and hydrogen-poor phases upon compression to 11 GPa at ambient temperature; the hydrogen rich phase was identified as LaH
, the former is metallic and the latter is insulating. Our previous synchrotron X-ray and infrared measurements revealed that the dihydride decomposed into hydrogen-rich and hydrogen-poor phases upon compression to 11 GPa at ambient temperature; the hydrogen rich phase was identified as LaH but the hydrogen composition and occupation sites of the hydrogen-poor phase remained undetermined. The crystal structure of the hydrogen-poor phase was investigated for LaD
but the hydrogen composition and occupation sites of the hydrogen-poor phase remained undetermined. The crystal structure of the hydrogen-poor phase was investigated for LaD by neutron diffraction measurement with a total diffractometer NOVA at J-PARC. The formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of LaD
by neutron diffraction measurement with a total diffractometer NOVA at J-PARC. The formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of LaD by the decomposition was confirmed from the diffraction profiles. First-principle enthalpy and lattice dynamic calculations have demonstrated that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures.
by the decomposition was confirmed from the diffraction profiles. First-principle enthalpy and lattice dynamic calculations have demonstrated that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures.
Machida, Akihiko; Hattori, Takanori; Honda, Mitsunori*; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated the structural properties of rare-earth metal hydrides under high pressure. LaH has the CaF
has the CaF type structure in which the H atoms locate at the tetrahedral interstitial sites (T-sites) of the fcc metal lattice. Synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection experiments revealed disproportionation reaction of LaH
type structure in which the H atoms locate at the tetrahedral interstitial sites (T-sites) of the fcc metal lattice. Synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection experiments revealed disproportionation reaction of LaH into the H-poor and H-rich phases around 11 GPa. Before the disproportionation reaction, we have found that the fcc metal lattice transformed into tetragonal lattice. The ordering of the H atoms in the octahedral-sites (O-sites) causes the tetragonal distortion of LaH
into the H-poor and H-rich phases around 11 GPa. Before the disproportionation reaction, we have found that the fcc metal lattice transformed into tetragonal lattice. The ordering of the H atoms in the octahedral-sites (O-sites) causes the tetragonal distortion of LaH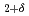 . The tetragonal transformation and successive disproportionation reaction of LaH
. The tetragonal transformation and successive disproportionation reaction of LaH would closely relate to the inter-site transfer of the H atoms between the T- and O-sites. We have performed the neutron diffraction experiments of LaD
would closely relate to the inter-site transfer of the H atoms between the T- and O-sites. We have performed the neutron diffraction experiments of LaD to investigate the change of the positions and occupancies of the hydrogen atoms under high pressure.
to investigate the change of the positions and occupancies of the hydrogen atoms under high pressure.
Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Hydrogen atoms absorbed in a metal occupy the interstitial sites of the metal lattice. In an fcc metal lattice, each metal atom has two tetrahedral (T) and one octahedral (O) sites that can accommodate hydrogen. Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied LaH and fully occupied LaH
and fully occupied LaH . Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH
. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. We performed the neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. We performed the neutron diffraction measurements on LaD , and found the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a phase separation products. We have first found the NaCl-type rare-earth metal monohydride.
, and found the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a phase separation products. We have first found the NaCl-type rare-earth metal monohydride.
Fujita, Masateru; Kojima, Kazuki; Hashimura, Hirohiko; Uryu, Mitsuru; Odagawa, Masanobu*; Maenaka, Toshinobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Kazuki; Kojima, Keidai; Fujita, Masateru; Hashimura, Hirohiko; Takaji, Kazuhiko*; Maenaka, Toshinobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Kazuki; Fujita, Masateru; Nakanishi, Ryuji; Uryu, Mitsuru; Takaji, Kazuhiko*; Maenaka, Toshinobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English