Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kowatari, Munehiko*; Nagamoto, Keisuke*; Nakagami, Koichi*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Moritake, Takashi*; Kunugita, Naoki*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(17), p.1303 - 1312, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Environmental Sciences)Kowatari, Munehiko; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radioisotopes, 70(1), p.1 - 18, 2021/01
 scintillation spectrometer due to terrestrial gamma ray components; Application in environmental radiation monitoring
scintillation spectrometer due to terrestrial gamma ray components; Application in environmental radiation monitoringKowatari, Munehiko; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Kessler, P.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Measurements, 138, p.106431_1 - 106431_6, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology) Cf neutron source with the spherical protection case
Cf neutron source with the spherical protection caseKowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Romallosa, K. M. D.*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(4), p.436 - 443, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)The anisotropic emission of neutrons from a cylindrical X1  Cf source with the spherical external casing was experimentally determined. The influence of metal materials and shapes of the external casing to the anisotropy factor,
Cf source with the spherical external casing was experimentally determined. The influence of metal materials and shapes of the external casing to the anisotropy factor, 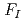 (
( ) was assessed by the Monte Carlo calculation, before performing the measurement. The results of the calculation result implied that light and spherical-shaped external casing decreases the anisotropic emission of neutrons from a cylindrical source and the nature of the material does not affect the anisotropic emission to a large extent. The experimental results obtained when a spherical-shaped aluminum protection case was employed also revealed that the anisotropy factor was close to 1.0 with a wide zenith angle range.
) was assessed by the Monte Carlo calculation, before performing the measurement. The results of the calculation result implied that light and spherical-shaped external casing decreases the anisotropic emission of neutrons from a cylindrical source and the nature of the material does not affect the anisotropic emission to a large extent. The experimental results obtained when a spherical-shaped aluminum protection case was employed also revealed that the anisotropy factor was close to 1.0 with a wide zenith angle range.
 Am and
Am and  Sr/
Sr/ Y sources in terms of the eye lens monitoring in the nuclear facilities
Y sources in terms of the eye lens monitoring in the nuclear facilitiesYoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 188(2), p.191 - 198, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Environmental Sciences)Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 187(1), p.61 - 68, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Environmental Sciences)Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 186(4), P. 538, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:1.45(Environmental Sciences)In the original version of this article an error occurred in Table 5. In section (b), the unit  Sv h
Sv h has been amended to nSv h
has been amended to nSv h . The corrected table appears below. The author apologises for this error.
. The corrected table appears below. The author apologises for this error.
Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi
Radioisotopes, 68(9), p.595 - 603, 2019/09
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Nagaguro, Seiji*; Nakamura, Hajime*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(2), p.179 - 188, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Environmental Sciences) scintillation detector coupled with lead shielding
scintillation detector coupled with lead shieldingKowatari, Munehiko; Tanimura, Yoshihiko
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011037_1 - 011037_7, 2019/01
Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Nishino, Sho; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko; Oishi, Tetsuya
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.134 - 138, 2019/01
At the severe nuclear accidents like the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, various radionuclides will be dispersed into the environment and raise the dose rate. The 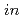 -
-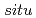 measurements of
measurements of  ray spectra and identifying radionuclides using the results are important for the radiological protection from both external and internal exposure. For this application a commercially available CdZnTe spectrometer (Kromek GR-1) was characterized at the calibration fields of FRS/JAEA. The angular dependence of the detection efficiency was studied and the efficiency was kept within 15 % degradation in
ray spectra and identifying radionuclides using the results are important for the radiological protection from both external and internal exposure. For this application a commercially available CdZnTe spectrometer (Kromek GR-1) was characterized at the calibration fields of FRS/JAEA. The angular dependence of the detection efficiency was studied and the efficiency was kept within 15 % degradation in  135 degree incident angle, which covers 85 % of all. The usable dose range was evaluated and the spectrometer could correctly measure the
135 degree incident angle, which covers 85 % of all. The usable dose range was evaluated and the spectrometer could correctly measure the  ray spectra below 200
ray spectra below 200  Gy/h.
Gy/h.
 and SrI
and SrI (Eu) scintillation detectors for environmental monitoring
(Eu) scintillation detectors for environmental monitoringKowatari, Munehiko; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; Roettger, A.*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.81 - 85, 2019/01
Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.86 - 90, 2019/01
Kowatari, Munehiko; Zutz, H.*; Hupe, O.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 178(1), p.48 - 56, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)In high energy photon reference fields the value of the air kerma rate is determined by using ionization chambers. From the charge collected inside the ionization chamber the dose can be calculated using a set of calibration and correction factors according to ISO 4037-2. A crucial parameter is the correction for the attenuation and scattering of the primary radiation due to the chamber wall. This parameter can be determined using Monte Carlo calculations. The evaluation of the factor was performed for a commercially available ionization chamber of the type Victoreen 550-3 under different build-up conditions. The results were verified by measurements in the R-F high energy photon fields according to ISO 4037-1 at the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA).
Nishino, Sho; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshida, Tadayoshi
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1258 - 1263, 2017/11
In order to investigate how neutron dosimeters respond in the continuous neutron fields in workplaces, we performed performance tests of four widely-used neutron survey meters in various simulated workplace neutron calibration fields established in two calibration facilities (FRS and ICF) in JAEA. As a result, we found that survey meters significantly over or underestimate neutron dose in the fields which have spectral components only in the energy range below 1 MeV, while those show good performance in the fields which have spectral components in the energy range above 1 MeV.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwase, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1188 - 1195, 2017/11
The equivalent doses to the lens of the eye and extremities for radiation workers should be assessed properly to ensure that the dose limits are not exceeded. Recently, the following two issues has pressed demand on more appropriate evaluation of the equivalent doses of the lens of the eye and extremity. One is the new occupational dose limit for the lens of the eye the ICRP recommended. The other is growing demand on handling of highly activated materials in the maintenance works of an accelerator and contaminated materials during the decommissioning works of nuclear facility, which increases the potential exposure risk to the extremities to a wider variety of radio-nuclides. Since the points to be assessed for the exposures to the lens of the eye and the extremities are apart from the trunk, the homogeneity of the radiation fields would be significantly impact on the assessment of these equivalent doses. However, there has been no sufficient and available method to identify the nonhomogeneous situations systematically in terms of the eye lens or extremity monitoring. The goal of this study is to provide the framework to identify the nonhomogeneous exposure situations. In order to fulfil this purpose, newly proposed indices to represent the homogeneity were calculated by Monte Carlo simulation incorporated with mathematical phantom, verifying the benchmark measurements. Important parameters that significantly impact on these indices were also shown from the various trials of calculations of homogeneity indices.
Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1230 - 1238, 2017/11
The Facility of Radiation Standards (FRS) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) offers various kinds of radiation calibration fields for calibration and testing for over three decades. The FRS-JAEA offers reliable X-ray,  -ray, beta-ray and neutron calibration fields with a vast range of variety. The quality and a set of neutron calibration fields are particularly mentioned. Neutron calibration fields with energies ranging between 0.025 eV and 19 MeV enable users to check the whole items for performance test. Two different sets of beta-ray calibration fields were established and served for regular calibration of dosimeters mainly used in nuclear industries. Resent research accomplishments on
-ray, beta-ray and neutron calibration fields with a vast range of variety. The quality and a set of neutron calibration fields are particularly mentioned. Neutron calibration fields with energies ranging between 0.025 eV and 19 MeV enable users to check the whole items for performance test. Two different sets of beta-ray calibration fields were established and served for regular calibration of dosimeters mainly used in nuclear industries. Resent research accomplishments on  -ray calibration fields can extend the upper limit of the energy up to 6 MeV. In addition to them, a simulated workplace neutron calibration field has been newly established for calibration of neutron dosimeters used inside the nuclear reactors.
-ray calibration fields can extend the upper limit of the energy up to 6 MeV. In addition to them, a simulated workplace neutron calibration field has been newly established for calibration of neutron dosimeters used inside the nuclear reactors.
Kowatari, Munehiko
Hamon, 27(3), p.109 - 112, 2017/08
A various kinds of radioactive neutron sources have been developed since neutron had been first discovered. The reactions which are mainly taken advantage for generating neutrons as radioactive neutron source are ( ,n) reaction, (
,n) reaction, ( ,n) reaction and nuclear fission reaction. Only
,n) reaction and nuclear fission reaction. Only  Am-Be and
Am-Be and  Cf neutron sources are now available due to reliable reproducibility of neutron emission, long half-lives and less disturbing
Cf neutron sources are now available due to reliable reproducibility of neutron emission, long half-lives and less disturbing  ray emission. Both are designated as a "reference neutron source" by ISO 8529 series describing principle of establishment of neutron calibration field. Total neutron emission rate from neutron source must be well defined in terms of sophisticated method by national metrological laboratory. Correction factor for anisotropic emission from cylindrical-shaped neutron source must be experimentally determined for neutron fluence rate at a point of test in the calibration laboratory.
ray emission. Both are designated as a "reference neutron source" by ISO 8529 series describing principle of establishment of neutron calibration field. Total neutron emission rate from neutron source must be well defined in terms of sophisticated method by national metrological laboratory. Correction factor for anisotropic emission from cylindrical-shaped neutron source must be experimentally determined for neutron fluence rate at a point of test in the calibration laboratory.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko
Hoken Butsuri, 51(3), p.160 - 166, 2016/09
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 170(1-4), p.199 - 203, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.53(Environmental Sciences)Both cylinder and slab phantoms have been recommended for the calibration phantoms for eye lens dosimetry in the |IAEA TECDOC. This study aims to investigate the influence of these phantoms on the calibration of dosemeters for eye lens dosimetry. In order to fulfill the purpose, the backscatters of photons and electrons from practically used water-filled phantoms were evaluated by calculations and experiments. Calculations showed cylinder phantom and slab phantom were found to well-simulate the effect of backscattered photons within 10% and 5%, respectively. It was also found that a cylinder phantom had 10% lower backscattered effect over the range of 50-100 keV. Due to this, the measured calibration factors of cylinder phantom for non-filtered Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) and Radio-Photo Luminescence (RPL) dosemeters increased by 20% and 10%, respectively when compared to the slab phantom. For electrons, no difference was found between cylinder and slab phantoms.