Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Keitaro; Murata, Isao*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi*; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Konno, Chikara; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(8), p.1146 - 1157, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)We carried out a detailed measurement of the double-differential cross sections of fluorine for emitted protons, deuterons, tritons and  -particles with 14.2 MeV neutron incidence. An improved charged-particle spectrometer with a pencil DT-neutron beam furnished at the FNS facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency enabled us to obtain precise data with a fine energy resolution in wide energy range and angular range from 15 to 150
-particles with 14.2 MeV neutron incidence. An improved charged-particle spectrometer with a pencil DT-neutron beam furnished at the FNS facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency enabled us to obtain precise data with a fine energy resolution in wide energy range and angular range from 15 to 150  . The obtained data were compared with the nuclear data evaluated in JENDL-3.3 and ENDF/B-VII.0. As a result, large differences in the energy and angular distributions of emitted particles and the charged-particle production cross sections were found between the measured and evaluated data. Angular-differential cross sections for several discrete peaks corresponding to excited states of residual nuclei were extracted to discuss the reaction mechanism of charged-particle emission. The obtained data suggest that the charged-particle emission reaction of fluorine has a quite complicated mechanism where both the direct reaction process and the pre-equilibrium process contribute. The present experiment is the first simultaneous measurement of the four different kinds of charged particles and would provide useful data to confirm previous experimental data as well as to establish a nuclear reaction model of fluorine.
. The obtained data were compared with the nuclear data evaluated in JENDL-3.3 and ENDF/B-VII.0. As a result, large differences in the energy and angular distributions of emitted particles and the charged-particle production cross sections were found between the measured and evaluated data. Angular-differential cross sections for several discrete peaks corresponding to excited states of residual nuclei were extracted to discuss the reaction mechanism of charged-particle emission. The obtained data suggest that the charged-particle emission reaction of fluorine has a quite complicated mechanism where both the direct reaction process and the pre-equilibrium process contribute. The present experiment is the first simultaneous measurement of the four different kinds of charged particles and would provide useful data to confirm previous experimental data as well as to establish a nuclear reaction model of fluorine.
Kondo, Keitaro; Murata, Isao*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi*; Konno, Chikara; Nishitani, Takeo
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology (ND 2007), Vol.1, p.407 - 410, 2008/05
Beryllium and carbon are candidate materials of fusion reactors and the  Be(n,2n+2
Be(n,2n+2 ) and
) and  C(n,n'+3
C(n,n'+3 ) reactions are important from engineering requirements. In order to estimate double-differential cross sections (DDX) for emitted particles, we have to accurately grasp details of the reaction mechanism. Understanding of the reaction mechanism is also interesting from a viewpoint of nuclear physics. Recently we developed a new spectrometry system with a pencil-beam DT neutron source. Using the system, we carried out detailed measurements of DDX for
) reactions are important from engineering requirements. In order to estimate double-differential cross sections (DDX) for emitted particles, we have to accurately grasp details of the reaction mechanism. Understanding of the reaction mechanism is also interesting from a viewpoint of nuclear physics. Recently we developed a new spectrometry system with a pencil-beam DT neutron source. Using the system, we carried out detailed measurements of DDX for  -particles emitted from beryllium and carbon. The reaction mechanism was investigated by a Monte Carlo calculation of DDX. For the
-particles emitted from beryllium and carbon. The reaction mechanism was investigated by a Monte Carlo calculation of DDX. For the  Be(n,2n+2
Be(n,2n+2 ) reaction, the result suggests importance of the contribution from the
) reaction, the result suggests importance of the contribution from the  Be(n,
Be(n, )
) He*(Ex
He*(Ex 1.8MeV) reaction. For the
1.8MeV) reaction. For the  C(n,n'+3
C(n,n'+3 ) reaction, the contribution from the
) reaction, the contribution from the  C(n,
C(n, )
) Be*(Ex
Be*(Ex 2.43MeV) reaction was appeared and its ratio was investigated to explain the shape of DDX for neutrons in lower energy.
2.43MeV) reaction was appeared and its ratio was investigated to explain the shape of DDX for neutrons in lower energy.
Kondo, Keitaro; Murata, Isao*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi*; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Konno, Chikara; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(2), p.103 - 115, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56(Nuclear Science & Technology)We carried out a detailed measurement of neutron induced  -particle emission double-differential cross-section of carbon at 14.2 MeV, for which there were few measured data in spite of its importance in many applications. The obtained cross-section for the
-particle emission double-differential cross-section of carbon at 14.2 MeV, for which there were few measured data in spite of its importance in many applications. The obtained cross-section for the  C(n,
C(n,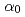 )
) Be
Be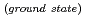 reaction agreed well with previous experiments and evaluated nuclear data. The obtained angular-differential cross-section of the
reaction agreed well with previous experiments and evaluated nuclear data. The obtained angular-differential cross-section of the  C(n,n'+3
C(n,n'+3 ) reaction for
) reaction for  -particles showed a strong forward-peaked distribution that suggested significant contribution of the direct reaction process to the 3
-particles showed a strong forward-peaked distribution that suggested significant contribution of the direct reaction process to the 3 breakup. We attempted to calculate the emitted particle spectra by means of a Monte Carlo method and estimate the branching ratio of the channels which contribute to the
breakup. We attempted to calculate the emitted particle spectra by means of a Monte Carlo method and estimate the branching ratio of the channels which contribute to the  C(n,n'+3
C(n,n'+3 ) reaction. As a result, it was found that the
) reaction. As a result, it was found that the  C(n,
C(n, )
) Be* channels play an important role in generating the experimental double-differential cross-section both of emitted
Be* channels play an important role in generating the experimental double-differential cross-section both of emitted  -particles and neutrons. The estimated ratio of the
-particles and neutrons. The estimated ratio of the  C(n,
C(n, )
) Be* channels was around 40%, somewhat larger than those evaluated in previous studies.
Be* channels was around 40%, somewhat larger than those evaluated in previous studies.
Kondo, Keitaro; Murata, Isao*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Takagi, Satoshi*; Shido, Shoichi*; Konno, Chikara; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2786 - 2793, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ochiai, Kentaro; Sato, Satoshi; Wada, Masayuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Yamauchi, Michinori; Abe, Yuichi; Nishitani, Takeo; Konno, Chikara
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2794 - 2798, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron streaming experiments have been conducted by using the FNS D-T neutron source at Japan Atomic Energy Agency under the ITER/ITA Task 73-10 in order to evaluate effects of the slit on nuclear properties and validate prediction accuracies on numerical simulations. The experimental assembly with a slit of 2 cm in width and 55 cm in depth was prepared with two iron blocks of 30 cm in height, 100 cm in width and 55cm in thickness as first campaign. The slit was located in the 12-cm upper part from the D-T neutron source point. In order to evaluate distributions of the neutron fluxes along the slit as a function of the depth from the assembly surface, fission reaction rates were measured by U-238 and U-235 micro-fission chambers. The experimental accuracies of these fission reaction rates are within 5%. Monte-Carlo calculation code, MCNP-4c, was used to calculate the U-238 and U-235 reaction rates and neutron energy spectra due to each measured position. From our first experiment, the following facts were found: (1) At d = 20 and 40 cm, reaction rates on U-238, which represent fast neutron flux, decreased by about three orders of magnitude along slits with 50 cm in depth. Monte Carlo calculation results agree well with measured values within 6 %. (2) Reaction rates on U-235, which represent thermal neutron flux, decrease by about one order of magnitude along slits with 50 cm in depth. Values of C/E of U-238 and U-235 reaction rates were 1.10-1.22 and 1.10-1.23 respectively and the calculated values overestimated slightly.
Kubota, Naoyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1596 - 1600, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The Neutron Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (NERDA) using a neutron beam was proposed to extend the analyzing depth of hydrogen isotopes up to several hundreds micrometers. The 14.1 MeV neutrons beam produced by the Fusion Neutronics Source facility in Japan Atomic Energy Agency entered a sample from the normal direction. Emitted particles from the sample were measured using a  E-E counter telescope detector. Incident neutron fluence was monitored with a
E-E counter telescope detector. Incident neutron fluence was monitored with a  U fission chamber located behind the target chamber. The proof-of-principle experiment was performed using a standard sample of deuterated polyethylene film containing a known concentration of deuterium with the thickness of 100
U fission chamber located behind the target chamber. The proof-of-principle experiment was performed using a standard sample of deuterated polyethylene film containing a known concentration of deuterium with the thickness of 100  m. The depth resolution was evaluated to be 99
m. The depth resolution was evaluated to be 99  m corresponding to 12% of the maximum probing depth of 801
m corresponding to 12% of the maximum probing depth of 801  m for the sample. For a carbon-based Plasma Facing Component (PFC) sample the depth resolution was expected to be 61
m for the sample. For a carbon-based Plasma Facing Component (PFC) sample the depth resolution was expected to be 61  m, which was enough to reveal hydrogen isotope distributions of co-deposited layers. Also, we applied NERDA to analyses of hydrogen isotope distributions in PFCs of JT-60U.
m, which was enough to reveal hydrogen isotope distributions of co-deposited layers. Also, we applied NERDA to analyses of hydrogen isotope distributions in PFCs of JT-60U.
Sato, Satoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Verzilov, Y.*; Wada, Masayuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishitani, Takeo; Konno, Chikara
Nuclear Fusion, 47(7), p.517 - 521, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:60.47(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kubota, Naoyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kutsukake, Chuzo; Hayashi, Takao; Shu, Wataru; Kondo, Keitaro; Verzilov, Y.*; Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishi, Masataka; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/03
Fuel and impurity particles show complicated behavior on the surface of plasma facing components (PFC) in fusion devices. The study is important for the design of the fuel recycling, safety management of the tritium inventory, etc. Quantitative measurements of hydrogen and lithium isotopes together with other impurities on the PFC surface exposed to D-T plasmas in TFTR were performed using the deuteron-induced nuclear reaction analysis, imaging plate method, full combustion method and activation analysis. The tritium depth profile was different from deuterium one. The surface tritium largely contributed to the whole tritium in the sample. On the other hand, the retained amount of lithium-6 was lager than that of lithium-7. This relates to the injection of enriched lithium-6 pellets in some campaigns. No other impurities were detected. So the large amount of tritium remained near the surface and did not diffuse more deeply, which gives a bright prospect for tritium safety.
Sato, Satoshi; Verzilov, Y.*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Wada, Masayuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishitani, Takeo; Konno, Chikara
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
 rays from D(
rays from D( ,
, )
) Li and
Li and  F(
F( ,n)
,n) Na to alpha particle diagnostics
Na to alpha particle diagnosticsOchiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Taniike, Akira*; Kitamura, Akira*; Kondo, Keitaro*; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.262 - 264, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the density of 3.5-MeV  particle and the leakage
particle and the leakage  particle in D-T plasmas, we propose the observation of 2.186-MeV
particle in D-T plasmas, we propose the observation of 2.186-MeV  -ray produced by D(
-ray produced by D( ,
, )
) Li reaction and the use of the activation method by
Li reaction and the use of the activation method by  F(
F( ,n)
,n) Na reaction, respectively. In order to verify these reaction rates, we have carried out the irradiation experiments by means of helium ion bombardment into a deuteride polyethylene and a calcium floride crystal samples. From our experiment, D(
Na reaction, respectively. In order to verify these reaction rates, we have carried out the irradiation experiments by means of helium ion bombardment into a deuteride polyethylene and a calcium floride crystal samples. From our experiment, D( ,
, )
) Li reaction rate is estimated to be 10
Li reaction rate is estimated to be 10 m
m s
s in the ITER typical plasma condition. So we obtained good prospect of the
in the ITER typical plasma condition. So we obtained good prospect of the  -ray measurement as the confined
-ray measurement as the confined  diagnostics by using high efficiency detector. Also, it was found that The number of leakage alpha particles in order of 10
diagnostics by using high efficiency detector. Also, it was found that The number of leakage alpha particles in order of 10 m
m could be estimated by the activation method with
could be estimated by the activation method with  F(
F( ,n)
,n) Na.
Na.
Kondo, Keitaro; Murata, Isao*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Takagi, Satoshi*; Shido, Shoichi*; Takahashi, Akito*; Nishitani, Takeo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 568(2), p.723 - 733, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:70.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)Deuteron-tritium (DT) neutron induced charged-particle emission double-differential cross section (DDXc) is quite important to estimate nuclear heating, material damages for a fusion reactor. In order to realize the accurate measurement of the DDXc data especially for light nuclei, we propose a unique spectrometer system and a data processing method in this paper. The spectrometer overcomes the fundamental difficulty of the DDXc measurement with a pencil-beam neutron source and a counter telescope consisting of silicon surface barrier detectors. A superior S/N ratio, fine energy and angular resolutions, a wide detection energy range, and a excellent particle discrimination are realized. In order to confirm the validity of the spectrometer, measurements of the emitted  -particle from
-particle from  Al(
Al(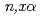 ) reaction and the recoiled proton from
) reaction and the recoiled proton from  H(
H(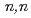 ) reaction are carried out. Based on the results, we conclude the validity and the superiority of the present spectrometry technique.
) reaction are carried out. Based on the results, we conclude the validity and the superiority of the present spectrometry technique.
Nakao, Makoto*; Hori, Junichi*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori; Ishioka, Noriko; Suto, Hiroyuki*; Nishitani, Takeo
JAEA-Research 2006-071, 37 Pages, 2006/11
In the design of IFMIF, long-term operation with total facility availability of at least 70 % is required. However, activation of structural materials by deuteron beam limits maintenance, which causes lower facility availability. Thus it is essential to prepare deuteron-induced activation cross section database and to select low activation materials based on it. In this work, we measured deuteron-induced activation cross sections of aluminum, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, nickel, copper, tantalum, tungsten and gold. The measured cross sections were compared with other experimental data and calculations. Deuteron-induced activities of nuclides produced in SS316 and F82H alloys used as the accelerator structural material were also measured to validate the measured cross sections comprehensively. It demonstrated that the measured activities of almost all the nuclides were in agreement with evaluated ones based on the measured cross sections within error.
Kubota, Naoyoshi; Fujiwara, Yoshio*; Okumura, Kazutaka*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kitamura, Akira*; Furuyama, Yuichi*; Taniike, Akira*; Nishitani, Takeo
JAEA-Research 2006-019, 15 Pages, 2006/06
Surface analysis of lithium-6 ( Li) was performed for both 95 % and 40 %
Li) was performed for both 95 % and 40 %  Li-enriched lithium titanate (Li
Li-enriched lithium titanate (Li TiO
TiO ) samples as the candidate tritium breeding material using 2.6 MeV-proton Rutherford Backscattering Spectroscopy (RBS). The depth resolution of this method was enough to measure the
) samples as the candidate tritium breeding material using 2.6 MeV-proton Rutherford Backscattering Spectroscopy (RBS). The depth resolution of this method was enough to measure the  Li depth profile in terms of the evaluation of thermal neutron transportation. The atomic density of
Li depth profile in terms of the evaluation of thermal neutron transportation. The atomic density of  Li could be measured within the error of 27 % for both samples although the accuracy of 5 % was not achieved for the evaluation of tritium breeding. It was confirmed that the sample atomic compositions agreed with Li
Li could be measured within the error of 27 % for both samples although the accuracy of 5 % was not achieved for the evaluation of tritium breeding. It was confirmed that the sample atomic compositions agreed with Li TiO
TiO within errors of 30 % for Li/Ti and 15 % for O/Ti. The whole errors were caused by the data accuracy of scattering cross sections predominately. Providing more accurate cross section data can lead to the utilization of the RBS method for tritium breeding materials analysis.
within errors of 30 % for Li/Ti and 15 % for O/Ti. The whole errors were caused by the data accuracy of scattering cross sections predominately. Providing more accurate cross section data can lead to the utilization of the RBS method for tritium breeding materials analysis.
Nakao, Makoto*; Hori, Junichi*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Ishioka, Noriko; Nishitani, Takeo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 562(2), p.785 - 788, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Activation cross sections for deuteron-induced reactions on aluminum, iron, copper, tantalum and tungsten were measured by using stacked-foil method. The stacked-foils were irradiated with deuteron beam at the AVF cyclotron in TIARA facility, JAERI. We obtained the activation cross-sections for  Al(d,x)
Al(d,x)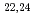 Na,
Na,  Fe(d,x)
Fe(d,x)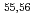 Co,
Co,  Cu(d,x)
Cu(d,x) Cu,
Cu,  Cu(d,x)
Cu(d,x) Zn,
Zn,  Ta(d,x)
Ta(d,x)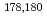 Ta and
Ta and  W(d,x)
W(d,x)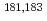 Re in 20-40MeV region. These cross-sections were compared with other experimental ones and the data in the ACSELAM library calculated by the ALICE-F code.
Re in 20-40MeV region. These cross-sections were compared with other experimental ones and the data in the ACSELAM library calculated by the ALICE-F code.
Kondo, Keitaro; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Nishitani, Takeo; Murata, Isao*; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Akito*
JAEA-Research 2006-016, 50 Pages, 2006/03
Charged-particle emission double- differential cross section (DDXc) is quite important to estimate nuclear heating, material damages of a fusion reactor. We have developed a new technique for detailed measurement of DDXc. The technique overcomes fundamental difficulties of DDXc measurement with a pencil-beam neutron source and a counter telescope consisting of silicon surface barrier detectors. A superior S/N ratio, fine energy and angular resolutions, a wide detection energy range, and an excellent particle discrimination are realized together with a reasonable measurement time. In order to confirm the validity of the spectrometer, measurements of the emitted  -particle from
-particle from  Al(n,x
Al(n,x ) reaction and the recoiled proton from
) reaction and the recoiled proton from  H(n,n) reaction are carried out. Based on the results, we conclude the validity and the superiority of the present spectrometry technique.
H(n,n) reaction are carried out. Based on the results, we conclude the validity and the superiority of the present spectrometry technique.
Nakao, Makoto; Hori, Junichi*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori; Ishioka, Noriko; Nishitani, Takeo
FAPIG, (172), p.3 - 7, 2006/03
The IFMIF (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility) is in the design planning stage as neutron source to test fusion reactor materials for high fluence neutron. In the design of it long-term operation that total facility is 70 % at least is required. However, deuteron beam activates the structural materials and these activation limits maintenance and makes long-term operation difficult. Thus the accurate estimation of deuteron-induced activity and the selection of structural materials are important. In this work, measurements of deuteron-induced activation cross sections for aluminum, iron, copper, tantalum, and tungsten were performed.
Kubota, Naoyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kutsukake, Chuzo; Kondo, Keitaro*; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.227 - 231, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hydrogen isotopes play important roles in the fuel recycling, the plasma condition etc. at the surface region of plasma facing components. The Fusion Neutronics Source (FNS) of Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute has started microanalysis studies for fusion components since 2002 by applying the beam analyses. In this study, we have measured tritium depth profiles of TFTR tiles exposed to the deuterium-tritium plasma to reveal the hydrogen isotope behavior at the surface region using some microscopic techniques for material analyses at FNS. As the result of the deuteron nuclear reaction analysis, four kinds of elements; deuterium, tritium, lithium-6 and lithium-7, were identified from the energy spectra. Using the spectra, depth profiles of each element were also calculated. The tritium profile had a peak at 0.5 micron, whereas the deuterium and lithium profiles were uniform from the surface to 1.0 micron depth. In addition, the surface region of the TFTR tile has retained the tritium more than one order of magnitude in the bulk.
Kondo, Keitaro; Takagi, Satoshi*; Murata, Isao*; Miyamaru, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Akito*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1527 - 1533, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:68.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fusion reactor development, double-differential charged-particle emission cross sections(DDXc) are necessary to estimate nuclear heating and material damages of candidate materials irradiated with neutrons. Especially in light nuclei such as Be, Li, and C, nuclear reactions are complicated and difficult to estimate energy spectra of emitted particles based only on theoretical calculations Therefore development of a new technique for precise measurements of DDXc is quite important. Recently we successfully developed a new spectrometer for measurement of DDXc using a pencil-beam DT neutron source of FNS in JAERI. In the present study we carried out measurements of DDXc of  Be,
Be,  C,
C,  F, and
F, and  Al using the spectrometer. The present technique was valid from the result of measurement for the
Al using the spectrometer. The present technique was valid from the result of measurement for the  Al(n,x
Al(n,x ) reactions. Slight differences appeared between measured data and evaluation or previous experimental values for
) reactions. Slight differences appeared between measured data and evaluation or previous experimental values for  Be(n,x
Be(n,x ) reactions at backward scattering angle and in lower energy region.
) reactions at backward scattering angle and in lower energy region.
Sato, Satoshi; Verzilov, Y. M.; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nakao, Makoto*; Wada, Masayuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Nishitani, Takeo
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1183 - 1193, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.5(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nakao, Makoto*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Sato, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Nishitani, Takeo
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.283 - 285, 2006/01
Measurements of deuteron-induced activation cross sections for IFMIF accelerator structural materials (vanadium, iron, nickel and tantalum) were performed. In this work, we have obtained the cross sections for 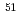 V(d,x)
V(d,x)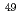 Cr,
Cr,  Fe(d,x)
Fe(d,x)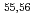 Co,
Co,  Ni(d,x)
Ni(d,x) Co,
Co, 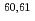 Cu and
Cu and  Ta(d,x)
Ta(d,x)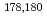 Ta reactions in 14-40 MeV region. These cross sections will be compared with other experimental ones and calculated value.
Ta reactions in 14-40 MeV region. These cross sections will be compared with other experimental ones and calculated value.