Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Kenji; Lahaye, S.*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.109 - 116, 2020/10
CEA/DEN/DM2S/SERMA and JAEA/NSEC are working on benchmarks for burnup, isotopic concentrations and decay heat calculations in the collaboration framework between both organisms. Both actors of this benchmark are independently developing their own simulation code systems for computing quantities of interest in nuclear fuel cycle domain: MENDEL in CEA and MARBLE in JAEA. The purpose of the benchmark is to verify each system by comparing both calculation results on specific applications. MENDEL uses a several solvers for the resolution of Bateman equation. Runge-Kutta method or Chebyshev Rational Approximation method (CRAM) are used for irradiation computations. An analytical solver can also be used for decay calculations. MARBLE can use Krylov subspace method or CRAM method. As the first phase of the benchmark, we compared the calculated results of decay heat and isotropic concentrations following by a Pu-239 fast fission pulse. We applied nuclear data from three libraries: (1) JEFF-3.1.1, (2) JENDL/DDF-2015 + JENDL/FPY-2011, and (3) ENDF/B-VII.1. Nuclear data and burnup chain were generated from these libraries independently on each system. We confirmed that the results for both systems were in very good agreement with each other. Numerical results were also compared to experimental data. As the second phase of the benchmark, we are proceeding with a burnup calculation benchmark of MENDEL and MARBLE using the nuclear data and burnup chain provided by ORLIBJ33, which is a set of cross-section data based on JENDL-3.3 for ORIGEN-2 code system. We will also compare with calculation results by the ORIGEN-2 code with ORLIBJ33. Since the series of ORLIB, that is, ORLIBJ32, ORLIBJ33, and ORLIBJ40, have been widely used especially in Japan for many years, the comparison with ORLIB is effective for confirming the performance of MENDEL and MARBLE.
 and MVP on the MCNP criticality validation suite
and MVP on the MCNP criticality validation suiteBrun, E.*; Zoia, A.*; Trama, J. C.*; Lahaye, S.*; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2015) (DVD-ROM), p.351 - 360, 2015/09
This paper presents a joint work conducted at CEA Saclay and JAEA Tokai aimed at comparing the Monte Carlo codes TRIPOLI and MVP on a selection of ICSBEP benchmarks. Our goal is to establish a common set of Monte Carlo input decks, as a basis for rigorous inter-code comparison in criticality-safety. As a reference, we will use the MCNP Criticality Validation Suite: other Monte Carlo developers might easily join that effort in the future. For the purpose of inter-code comparison, the TRIPOLI
and MVP on a selection of ICSBEP benchmarks. Our goal is to establish a common set of Monte Carlo input decks, as a basis for rigorous inter-code comparison in criticality-safety. As a reference, we will use the MCNP Criticality Validation Suite: other Monte Carlo developers might easily join that effort in the future. For the purpose of inter-code comparison, the TRIPOLI and MVP input decks have been translated from those of MCNP, without any further assumptions. Both TRIPOLI
and MVP input decks have been translated from those of MCNP, without any further assumptions. Both TRIPOLI and MVP have been run with the same ENDF/B-VII.0 evaluated nuclear data, and as far as possible the same simulation options as in the original LANL work. In this abstract, we present preliminary results on the BIGTEN benchmark. In the full paper these will be extended to the 31 benchmarks of the MCNP Criticality Validation Suite. In the future, this database will also help in the analysis of sensitivity to nuclear data, CPU times and figures of merit.
and MVP have been run with the same ENDF/B-VII.0 evaluated nuclear data, and as far as possible the same simulation options as in the original LANL work. In this abstract, we present preliminary results on the BIGTEN benchmark. In the full paper these will be extended to the 31 benchmarks of the MCNP Criticality Validation Suite. In the future, this database will also help in the analysis of sensitivity to nuclear data, CPU times and figures of merit.
Schaffer, M. J.*; Snipes, J. A.*; Gohil, P.*; de Vries, P.*; Evans, T. E.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Gao, X.*; Garofalo, A. M.*; Gates, D. A.*; Greenfield, C. M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103028_1 - 103028_11, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:80.59(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Experiments at DIII-D investigated the effects of ferromagnetic error fields similar to those expected from proposed ITER Test Blanket Modules (TBMs). Studied were effects on: plasma rotation and locking; confinement; L-H transition; edge localized mode (ELM) suppression by resonant magnetic perturbations; ELMs and the H-mode pedestal; energetic particle losses; and more. The experiments used a 3-coil mock-up of 2 magnetized ITER TBMs in one ITER equatorial port. The experiments did not reveal any effect likely to preclude ITER operations with a TBM-like error field. The largest effect was slowed plasma toroidal rotation v across the entire radial profile by as much as 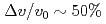 via non-resonant braking. Changes to global
via non-resonant braking. Changes to global 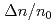 ,
, 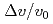 and
and 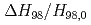 were
were  3 times smaller. These effects are stronger at higher
3 times smaller. These effects are stronger at higher  and lower
and lower 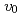 . Other effects were smaller.
. Other effects were smaller.
Chapman, I. T.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Coda, S.*; Gerhardt, S.*; Graves, J. P.*; Howell, D. F.*; Isayama, Akihiko; La Haye, R. J.*; Liu, Y.*; Maget, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 50(10), p.102001_1 - 102001_7, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:87.41(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Moreau, D.*; Mazon, D.*; Walker, M. L.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Flanagan, S. M.*; Gohil, P.*; Groebner, R. J.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Schuster, E.*; Ou, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
La Haye, R. J.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Maraschek, M.*
Nuclear Fusion, 49(4), p.045005_1 - 045005_8, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:83.81(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hender, T. C.*; Wesley, J. C.*; Bialek, J.*; Bondeson, A.*; Boozer, A. H.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Garofalo, A.*; Goodman, T. P.*; Granetz, R. S.*; Gribov, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S128 - S202, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:916 Percentile:100(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Prater, R.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Petty, C. C.*; Strait, E. J.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Humphreys, D. A.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Lohr, J.*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(5), p.371 - 377, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:87.07(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The 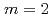 /
/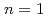 neoclassical tearing mode (NTM) has been observed to strongly degrade confinement and frequently lead to a disruption in high
neoclassical tearing mode (NTM) has been observed to strongly degrade confinement and frequently lead to a disruption in high  discharges in DIII-D if allowed to grow to large size. Stabilization of grown NTMs by application of highly localized electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) at the island location has led to operation at increased plasma pressure, up to the no-wall kink limit. After the NTM is stabilized by the ECCD, the correct location for the current drive is maintained using information from real-time equilibrium reconstructions which include measurements from the motional Stark effect diagnostic. This same process is used alternatively to prevent the mode from ever growing, leading to performance at the pressure limit in high performance hybrid discharges with
discharges in DIII-D if allowed to grow to large size. Stabilization of grown NTMs by application of highly localized electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) at the island location has led to operation at increased plasma pressure, up to the no-wall kink limit. After the NTM is stabilized by the ECCD, the correct location for the current drive is maintained using information from real-time equilibrium reconstructions which include measurements from the motional Stark effect diagnostic. This same process is used alternatively to prevent the mode from ever growing, leading to performance at the pressure limit in high performance hybrid discharges with  above 4%. Modeling using the modified Rutherford equation shows that the required power is in close agreement with the experimental threshold for prevention of the 2/1 NTM.
above 4%. Modeling using the modified Rutherford equation shows that the required power is in close agreement with the experimental threshold for prevention of the 2/1 NTM.
La Haye, R. J.*; Prater, R.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Maraschek, M. E.*; Urso, L.*; Zohm, H.*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Resistive neoclassical tearing mode (NTM) islands will be the principal limit on stability and performance in ITER as beta is well below the ideal kink limit. NTM island control in ITER is predicted to be challenging both because of the relatively narrower marginal island widths and the relatively broader electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD). Measurements from ASDEX Upgrade, DIII-D, and JET in beta rampdown experiments are used to determine the marginal island size for m/n=3/2 NTM removal. This is compared to data from ASDEX Upgrade, DIII-D and JT-60U with elimination of the m/n=3/2 island by continuous ECCD at near constant beta. The empirical marginal island size is consistent in both sets of removal experiments and found to be about twice the ion banana width. A common methodology is developed for fitting the saturated m/n=3/2 island before (or without) ECCD in all four experimental devices. To this is added (and model tested to experiments) the effect of unmodulated co-ECCD on island stabilization including both replacing the missing bootstrap current and making the classical tearing stability index more negative. The experimentally benchmarked model is then used to evaluate ITER. The ITER ECCD upper launcher with up to 20 MW of injected power is appraised with or without modulation for both the m/n=3/2 mode and the m/n=2/1 NTM (which can lock to the resistive wall and induce disruption). An m/n=2/1 rotating island model with drag from eddy current induced in the resistive wall is used to predict the necessary ECCD to keep the island from locking as a function of the rotation in ITER. The planned relatively wide ECCD should be capable of regulating the island width to avoid mode locking with the anticipated rotation in ITER but there is little margin available for inevitable misalignment. Narrower ECCD of more power and/or more rotation in ITER would increase confidence in island control and successful operation.
Prater, R.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Petty, C. C.*; Strait, E. J.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Humphreys, D. A.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Lohr, J.*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Onset of the m/n=2/1 neoclassical tearing mode (NTM) has been prevented in high-performance DIII-D discharges using localized electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD). Active tracking of the  =2 surface location, using real-time equilibrium reconstructions with motional Stark effect data, allows the current drive to be maintained at the rational surface even in the absence of a detectable mode. With the application of this technique in DIII-D hybrid discharges, the 2/1 mode is avoided and good energy confinement is maintained for more than 1 second with
=2 surface location, using real-time equilibrium reconstructions with motional Stark effect data, allows the current drive to be maintained at the rational surface even in the absence of a detectable mode. With the application of this technique in DIII-D hybrid discharges, the 2/1 mode is avoided and good energy confinement is maintained for more than 1 second with  at the estimated n=1 no-wall stability limit for ideal kink modes (
at the estimated n=1 no-wall stability limit for ideal kink modes (
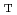 approximately equals 3.9 % and normalized beta
approximately equals 3.9 % and normalized beta 
 approximately equals 3.2). The results can be understood through modeling using the modified Rutherford equation.
approximately equals 3.2). The results can be understood through modeling using the modified Rutherford equation.
La Haye, R. J.*; Prater, R.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Maraschek, M. E.*; Urso, L.*; Zohm, H.*
Nuclear Fusion, 46(4), p.451 - 461, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:151 Percentile:97.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Zohm, H.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; La Haye, R. J.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Maraschek, M. E.*; Sauter, O.*; Urso, L.*
Proceedings of 14th Joint Workshop on Electron Cyclotron Emission and Electron Cyclotron Resonance Heating (EC-14), p.334 - 339, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Zohm, H.*; Gantenbein, G.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Keller, A.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Maraschek, M.*; M ck, A.*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Pinches, S. D.*; Strait, E. J.*
ck, A.*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Pinches, S. D.*; Strait, E. J.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12A), p.A163 - A173, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:59.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A review of magnetohydrodynamic limits to tokamak operation in terms of current, density and pressure is given. Although the current and density limits in a tokamak usually lead to disruptive termination of the discharge, it is argued that these can be avoided by staying away from the respective limits. This is especially true since operation close to these limits is not really desirable, due to the decreased confinement at very high density and the high disruptivity at low q. On the other hand, the limit to plasma pressure set by neoclassical tearing modes (NTMs) and resistive wall modes (RWMs) is too low to guarantee economic operation of future fusion reactors. Therefore, active control of these two instabilities is now being studied. Noticeable progress has been made by NTM stabilization with ECCD. Avoidance of NTMs and RWMs by tailoring sawteeth and spinning the plasma, shows promising results. Also, experiments on direct RWM stabilization by active coils are showing their first encouraging results.
Buttery, R. J.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Coda, S.*; Gohil, P.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Jackson, G.*; Raju, D.*; Reimerdes, H.*; Sabbagh, S.*; Sen, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English