Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied) FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; Fukatsu, Yuta
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.24(Energy & Fuels)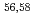 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 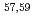 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 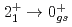 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 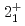 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 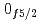 and
and 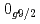 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
Onuki, Toshihiko*; Ye, J.*; Kato, Tomoaki; Liu, J.; Takano, Masahide; Kozai, Naofumi; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Environmental Science; Processes & Impacts, 25(7), p.1204 - 1212, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)To elucidate chemical forms of Cs and I in microparticles produced via the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident and released into the atmosphere, we analyzed Cs and I in condensed vaporized particles (CVP) produced by melting experiments using nuclear fuel components containing CsI with concrete. CVPs consisted of many round particles containing Cs and I of diameters less than several tens of micrometers. Two kinds of particles were present: one containing large amounts of Cs and I, suggesting the presence of CsI, and the other containing small amounts of Cs and I with large Si contents. Most of CsI from both particles were dissolved in water. On the contrary, some fractions of Cs remained from the latter particles. These results suggest that Cs was incorporated in CVPs along with Si to form water low-soluble CVPs
Liu, H.*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Lei, J.*; Ren, Z.*
Physical Review C, 108(1), p.014617_1 - 014617_8, 2023/07
In this paper, we study deuteron-induced inclusive breakup reaction and explore the 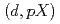 and
and 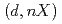 reactions for light and medium mass nuclei. Using the models of Ichimura, Austern, and Vincent and Glauber, we scrutinize the double differential cross-section of nonelastic breakup and compare the results for various reaction systems. Our findings indicate that the Glauber model, combined with a quantum
reactions for light and medium mass nuclei. Using the models of Ichimura, Austern, and Vincent and Glauber, we scrutinize the double differential cross-section of nonelastic breakup and compare the results for various reaction systems. Our findings indicate that the Glauber model, combined with a quantum  -matrix, produces remarkable results in the deuteron-induced inclusive breakup reaction. While both models are proficient in predicting the outcomes of light and medium mass nuclei, the
-matrix, produces remarkable results in the deuteron-induced inclusive breakup reaction. While both models are proficient in predicting the outcomes of light and medium mass nuclei, the 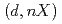 reaction showcases higher consistency than the
reaction showcases higher consistency than the 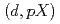 reaction. Nevertheless, there are still significant discrepancies between experimental and theoretical cross-sections that require further investigation and analysis. This study opens up a new realm of possibilities for future research in the field.
reaction. Nevertheless, there are still significant discrepancies between experimental and theoretical cross-sections that require further investigation and analysis. This study opens up a new realm of possibilities for future research in the field.
 X-ray synchrotron diffraction
X-ray synchrotron diffractionLi, H.*; Liu, Y.*; Zhao, W.*; Liu, B.*; Tominaga, Aki; Shobu, Takahisa; Wei, D.*
International Journal of Plasticity, 165, p.103612_1 - 103612_20, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.7(Engineering, Mechanical)In order to clarify the strength properties of Co-free maraging steel,  tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
tensile experiment using high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction was performed. Diffraction profiles from the martensitic and austenitic phases were obtained, and their strength and width were observed to vary as loading. Analysis of the diffraction profiles showed that the content of martensite in the as-aged material decreased slowly at low stress levels and decreased rapidly at high stress levels. On the other hand, the austenite phase in the as-solution materials was significantly transformed the martensite phase as the stress increased. It was clarified to be responsible for their respective strength properties.
Liu, Y.*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Shundo, Atsuomi*; Kawaguchi, Daisuke*; Tanaka, Keiji*; Aoki, Hiroyuki
Langmuir, 39(29), p.10154 - 10162, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.07(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) ; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activity
; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activityFang, Y.*; Kong, L.*; Wang, R.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Bu, K.*; Liu, X.*; Yan, S.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Materials Today Physics (Internet), 34, p.101083_1 - 101083_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered van der Waals halides are particularly sensitive to external pressure, suggesting a feasible route to pinpoint their structure with extraordinary behavior. However, a very sensitive pressure response usually lead to a detrimental phase transition and/or lattice distortion, making the approach of materials manipulation in a continuous manner remain challenging. Here, the extremely weak interlayer coupling and high tunability of layered RhI crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
Zhang, T.*; Yao, Y.*; Morita, Koji*; Liu, X.*; Liu, W.*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
Yamano, Hidemasa; Chenaud, M.-S.*; Tsige-Tamirat, H.*; Sumner, T.*; Lee, J.*; Liu, S.*; Peregudova, O.*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The Generation IV (GEN-IV) international forum is a framework for international co-operation in research and development for the next generation of nuclear energy systems. Within the GEN-IV sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) system arrangement, the SFR Safety and Operation (SO) project addresses the areas of safety technology and reactor operation technology developments. The aims of the SO project include (1) analyses and experiments that support establishment of the safety approaches and validate the performance of specific safety features, (2) development and verification of computational tools and validation of models employed in safety assessment and facility licensing, and (3) acquisition of reactor operation technology, as determined largely from experience and testing in operating SFR plants. The tasks in the SO topics are categorized into the following three work packages (WP): WP-SO-1 "Methods, Models and Codes" is devoted to the development of tools for the evaluation of safety. WP-SO-2 "Experimental Programs and Operational Experience" includes the operation, maintenance and testing experiences in experimental facilities and SFRs, and WP-SO-3 "Studies of Innovative Design and Safety Systems" relates to safety technologies for GEN-IV reactors such as active and passive safety systems and other specific design features. This paper reports recent activities within the SO project.
 by monolayer hexagonal boron nitride coating for improved photo- and thermionic-cathodes
by monolayer hexagonal boron nitride coating for improved photo- and thermionic-cathodesYamaguchi, Hisato*; Yusa, Ryunosuke*; Wang, G.*; Pettes, M. T.*; Liu, F.*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Moody, N. A.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 122(14), p.141901_1 - 141901_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:85.09(Physics, Applied)A lowering of work function for LaB by monolayer hexagonal BN coating is reported. Photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM) and thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) both revealed that the hBN coated region of a LaB
by monolayer hexagonal BN coating is reported. Photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM) and thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) both revealed that the hBN coated region of a LaB (100) single crystal has lower work function compared to the bare (i.e., non-coated) and graphene coated regions. A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB
(100) single crystal has lower work function compared to the bare (i.e., non-coated) and graphene coated regions. A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB (100) compared to graphene coated LaB
(100) compared to graphene coated LaB (100) was qualitatively supported by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adding an oxide layer in the calculations improved consistency between the calculation and experimental results. We followed up our calculations with synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) and confirmed the presence of an oxide layer on our LaB
(100) was qualitatively supported by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adding an oxide layer in the calculations improved consistency between the calculation and experimental results. We followed up our calculations with synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) and confirmed the presence of an oxide layer on our LaB .
.
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
 particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linac
particles generated by residual gas stripping in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex linacTamura, Jun; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Liu, Y.*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Okabe, Kota; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1049, p.168033_1 - 168033_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) linac is a high-intensity accelerator in which beam loss is a critical issue. In the J-PARC linac, H beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H
beams are accelerated to 191~MeV by a separated drift tube linac (SDTL) and subsequently to 400~MeV by an annular-ring coupled structure (ACS). Because there are more beam loss mechanisms in H linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H
linacs than in proton linacs, it is imperative to investigate the beam loss circumstances for beam loss mitigation. Electron-stripping phenomena, which generate uncontrollable H particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H
particles, are characteristic beam loss factors of H linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H
linacs. To clarify the beam loss causes in the J-PARC linac, a new diagnostic line was installed in the beam transport between the SDTL and ACS. In this diagnostic line, H particles were separated from the H
particles were separated from the H beam, and the intensity profiles of the H
beam, and the intensity profiles of the H particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H
particles were successfully measured by horizontally scanning a graphite plate in the range where H particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H
particles were distributed. By examining the intensity variation of the H particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H
particles with different residual pressure levels, we proved that half of the H particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
particles in the SDTL section are generated by the residual gas stripping in the nominal beam operation of the J-PARC linac.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:85.05(Mechanics)Madokoro, Hiroshi; Yamashita, Takuya; Gaus-Liu, X.*; Cron, T.*; Fluhrer, B.*; Sato, Ikken; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 209(2), p.144 - 168, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Ma, J.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.23(Physics, Applied)