Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
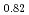 La
La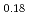 Fe
Fe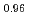 Ni
Ni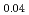 As
As
Xie, T.*; Liu, C.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Li, S.*; Luo, H.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(47), p.474001_1 - 474001_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Condensed Matter) -dependent collective relaxation dynamics of glass-forming liquid Ca
-dependent collective relaxation dynamics of glass-forming liquid Ca K
K (NO
(NO )
)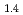 investigated by wide-angle neutron spin-echo
investigated by wide-angle neutron spin-echoLuo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Falus, P.*; Garc a Sakai, V.*; Hartl, M.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Z, Y.*
a Sakai, V.*; Hartl, M.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Z, Y.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.2092_1 - 2092_9, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:58.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luo, M.-Y.*; Lam, T.-N.*; Wang, P.-T.*; Tsou, N.-T.*; Chang, Y.-J.*; Feng, R.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Liaw, P. K.*; Yeh, A.-C.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 210, p.114459_1 - 114459_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:91.45(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Lam, T.-N.*; Luo, M.-Y.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Jain, J.*; Lee, S.-Y.*; Yeh, A.-C.*; Huang, E.-W.*
Crystals (Internet), 12(2), p.157_1 - 157_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:87.21(Crystallography)Zhai, Y.*; Luo, P.*; Nagao, Michihiro*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kienzle, P. A.*; Z, Y.*; Faraone, A.*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23(12), p.7220 - 7232, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27(Chemistry, Physical)Saito, Shimpei*; De Rosis, A.*; Fei, L.*; Luo, K. H.*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Physics of Fluids, 33(2), p.023307_1 - 023307_21, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:98.32(Mechanics)A Boiling phenomenon in a liquid flow field is known as forced-convection boiling. We numerically investigated the boiling system on a cylinder in a flow at a saturated condition. To deal with such a phenomenon, we developed a numerical scheme based on the pseudopotential lattice Boltzmann method. The collision was performed in the space of central moments (CMs) to enhance stability for high Reynolds numbers. Furthermore, additional terms for thermodynamic consistency were derived in a CMs framework. The effectiveness of the model was tested against some boiling processes, including nucleation, growth, and departure of a vapor bubble for high Reynolds numbers. Our model can reproduce all the boiling regimes without the artificial initial vapor phase. We found that the Nukiyama curve appears even though the focused system is the forced-convection system. Also, our simulations support experimental observations of intermittent direct solid-liquid contact even in the film-boiling regime.
 at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeakLuo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Leao, J. B.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 12(1), p.392 - 398, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27(Chemistry, Physical)Using neutron spin-echo spectroscopy, we studied the microscopic structural relaxation of a prototypical network ionic liquid ZnCl at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is 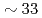 % higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point
% higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point 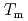 . Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the
. Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the 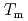 . These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl
. These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
 As
As
Xie, T.*; Wei, Y.*; Gong, D.*; Fennell, T.*; Stuhr, U.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Li, S.*; Hu, J.*; Luo, H.*
Physical Review Letters, 120(26), p.267003_1 - 267003_7, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:84.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary) (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor
superconductorHu, D.*; Yin, Z.*; Zhang, W.*; Ewings, R. A.*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Roessli, B.*; Wei, Y.*; Zhao, L.*; Chen, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(9), p.094504_1 - 094504_7, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:59.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The temperature and energy dependence of spin excitations in an optimally P-doped BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor (T
superconductor (T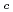 = 30 K) were studied by using inelastic neutron scattering. Experimental results are consistent with calculations from a combined density functional theory and dynamical mean field theory, and suggest that the decreased average pnictogen height in BaFe
= 30 K) were studied by using inelastic neutron scattering. Experimental results are consistent with calculations from a combined density functional theory and dynamical mean field theory, and suggest that the decreased average pnictogen height in BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) reduces the strength of electron correlations and increases the effective bandwidth of magnetic excitation.
reduces the strength of electron correlations and increases the effective bandwidth of magnetic excitation.

Li, B.; Luo, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Ren, W. J.*; Yano, S.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Gardner, J. S.*; Liss, K.-D.*; Miao, P.*; Lee, S.-H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(22), p.224405_1 - 224405_6, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:85.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ding, F.*; Luo, G.-N.*; Pitts, R.*; Litnovsky, A.*; Gong, X.*; Ding, R.*; Mao, H.*; Zhou, H.*; Wampler, W. R.*; Stangeby, P. C.*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 455(1-3), p.710 - 716, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:88.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Hu, P.*; Yin, Y.-G.; Ishikawa, Satoru*; Suzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Fujimaki, Shu; Igura, Masato*; Yuan, C.*; Huang, J.*; Li, Z.*; et al.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(9), p.6306 - 6316, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:77.23(Environmental Sciences)Shu, Wataru; Nakamichi, Masaru; Alimov, V.; Luo, G.-N.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.1017 - 1021, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:95.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shu, Wataru; Luo, G.; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1463 - 1467, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:96.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The mechanisms of retention and blistering in the near-surface region of tungsten exposed to high glux deuterium plasmas of tens of eV were studied with a variety of techniques, such as XRD, TEM, SEM, TDS, NRA and ERDA. The results of small angle XRD at a fixed incident angle of 1.5 indicated that within the experimental error there was a zero change in the lattice parameter after the plasma exposure. This implies that deuterium does not exist in the lattice interstitial sites, but instead forms a deuterium-vacancy complex and then clusters and further bubbles (deuterium molecules in vacancy clusters and voids) in near-surface region. Cross-sectional TEM observations showed that small blisters with a diameter of around 30 nm and nano-cracks formed in the near-surface region before the formation of larger blisters with diameters of up to a few microns (comparable to grain size). The TDS results strongly indicated that deuterium existed in the molecular form in tungsten after the plasma exposure. The NRA and ERDA results suggest that the maximum atomic ratio of deuterium against tungsten reached as high as 1-2% in the near-surface region. These evidences suggest that crystal defects like vacancies should be generated due to lowering of the formation energy of vacancies by the intrusion of a great number of hydrogen isotope atoms into the near-surface region of tungsten.
indicated that within the experimental error there was a zero change in the lattice parameter after the plasma exposure. This implies that deuterium does not exist in the lattice interstitial sites, but instead forms a deuterium-vacancy complex and then clusters and further bubbles (deuterium molecules in vacancy clusters and voids) in near-surface region. Cross-sectional TEM observations showed that small blisters with a diameter of around 30 nm and nano-cracks formed in the near-surface region before the formation of larger blisters with diameters of up to a few microns (comparable to grain size). The TDS results strongly indicated that deuterium existed in the molecular form in tungsten after the plasma exposure. The NRA and ERDA results suggest that the maximum atomic ratio of deuterium against tungsten reached as high as 1-2% in the near-surface region. These evidences suggest that crystal defects like vacancies should be generated due to lowering of the formation energy of vacancies by the intrusion of a great number of hydrogen isotope atoms into the near-surface region of tungsten.
Shu, Wataru; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Miwa, Yukio; Wakai, Eiichi; Luo, G.-N.*; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Physica Scripta, T128, p.96 - 99, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:92.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The dependence of deuterium retention and blistering upon the microstructures of tungsten exposed to 38 eV plasma were studied with TDS, PA and SEM. For samples exposed to higher fluences (up to 10 D/m
D/m ), a peculiar phenomenon of bursting release of deuterium was found obviously in TDS spectra, where sudden spikes appeared. SEM observations also confirmed the phenomenon of bursting of blisters, even for the single crystal tungsten (111) exposed to 10
), a peculiar phenomenon of bursting release of deuterium was found obviously in TDS spectra, where sudden spikes appeared. SEM observations also confirmed the phenomenon of bursting of blisters, even for the single crystal tungsten (111) exposed to 10 D/m
D/m at room temperature. The preliminary PA measurements suggested that the vacancy concentration in the near-surface region of the partially-recrystallized tungsten increased after the exposure, and electron back-scattering diffraction (EBSD) results showed that blisters appeared predominantly on the grains with nearly (111) surface orientation.
at room temperature. The preliminary PA measurements suggested that the vacancy concentration in the near-surface region of the partially-recrystallized tungsten increased after the exposure, and electron back-scattering diffraction (EBSD) results showed that blisters appeared predominantly on the grains with nearly (111) surface orientation.
Luo, G.-N.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Plasma Science and Technology, 7(4), p.2982 - 2984, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Hellgren, N.*; Guo, J.*; Luo, Y.*; S the, C.*; Agui, Akane; Kashtanov, S.*; Nordgren, J.*;
the, C.*; Agui, Akane; Kashtanov, S.*; Nordgren, J.*;  gren, H.*; Sundgren, J.-E.*
gren, H.*; Sundgren, J.-E.*
Thin Solid Films, 471(1-2), p.19 - 34, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:133 Percentile:96.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Ohira, Shigeru; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2004-031, 27 Pages, 2004/03
A plasma source has been constructed for investigating plasma-surface interactions in a tokamak. It is a compact device with a total length less than 1 m, compared to other existing facilities in the world. However, it can provide with stable plasma beams of low energy ( 100 eV) and high flux (
100 eV) and high flux ( 10
10 /m
/m /s), close to the predicted edge plasma conditions near the ITER divertor. This report presents mainly its configuration and its characteristics, including influence of filament, arc discharge, magnetic field, bias voltage parameters, and so on, on plasma beam being delivered towards the sample. Also shown are the results of preliminary experiments of blister formation on tungsten samples irradiated by a deuterium plasma beam generated with the source.
/s), close to the predicted edge plasma conditions near the ITER divertor. This report presents mainly its configuration and its characteristics, including influence of filament, arc discharge, magnetic field, bias voltage parameters, and so on, on plasma beam being delivered towards the sample. Also shown are the results of preliminary experiments of blister formation on tungsten samples irradiated by a deuterium plasma beam generated with the source.
Shu, Wataru; Kawakubo, Yukio*; Luo, G.; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(12), p.1019 - 1026, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recovery of tritium from co-deposited layers is a crucial issue for fusion machines that use carbon as plasma facing materials. In this study, the removal rate of the JT-60 and TFTR co-deposited layers by KrF laser was measured for varying laser energy density. The removal rate of 5.0  m/pulse was achieved for the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density of 11 J/cm
m/pulse was achieved for the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density of 11 J/cm for KrF excimer laser. Hydrogen (tritium) was released in the form of hydrogen molecules and readily recovered. The formation of cones due to local surface melting was observed at the KrF laser energy density of 0.8 J/cm
for KrF excimer laser. Hydrogen (tritium) was released in the form of hydrogen molecules and readily recovered. The formation of cones due to local surface melting was observed at the KrF laser energy density of 0.8 J/cm , whereas strong melting was determined to be the mechanism of the ablative removal of the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density greater than the ablation threshold.
, whereas strong melting was determined to be the mechanism of the ablative removal of the JT-60 co-deposited layers at the energy density greater than the ablation threshold.
Luo, G.-N.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 349(1-2), p.211 - 216, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.49(Chemistry, Physical)Lithium ceramics, Li O, LiAlO
O, LiAlO and Li
and Li SiO
SiO , under ion or electron beam irradiation have been studied using a Kelvin probe that measures work function changes of materials. Surface charging was observed to influence greatly the probe output, which can be explained qualitatively employing a model concerning polarization effect in insulating ceramics due to free charges on their surfaces. It is found that the insulating ceramics could not be studied properly with the Kelvin probe. A probable solution has been presented, i.e., to heat the ceramics, so as to raise their electric conductivities high enough to root out the surface charges
, under ion or electron beam irradiation have been studied using a Kelvin probe that measures work function changes of materials. Surface charging was observed to influence greatly the probe output, which can be explained qualitatively employing a model concerning polarization effect in insulating ceramics due to free charges on their surfaces. It is found that the insulating ceramics could not be studied properly with the Kelvin probe. A probable solution has been presented, i.e., to heat the ceramics, so as to raise their electric conductivities high enough to root out the surface charges