Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
FeShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Homma, Michio*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
Physical Review C, 87(2), p.024301_1 - 024301_7, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.29(Physics, Nuclear)Electro-magnetic dipole transitions in  Fe were measured in photon scattering experiments with a linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Fe were measured in photon scattering experiments with a linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. While the summed magnetic dipole (
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. While the summed magnetic dipole ( ) strength was determined as
) strength was determined as 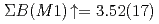
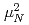 at excitation energies between 7 and 10 MeV, the summed electric dipole (
at excitation energies between 7 and 10 MeV, the summed electric dipole ( ) strength below 10 MeV was obtained as
) strength below 10 MeV was obtained as 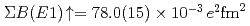 . The observed
. The observed  strength was compared with shell-model predictions in the
strength was compared with shell-model predictions in the 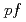 -shell using the GXPF1J and KB3G effective interactions. In addition, the
-shell using the GXPF1J and KB3G effective interactions. In addition, the  strength was compared with random-phase approximation calculations with the Skyrme interaction.
strength was compared with random-phase approximation calculations with the Skyrme interaction.
 Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
Physical Review C, 78(6), p.061303_1 - 061303_4, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:95.33(Physics, Nuclear)Spin-flip  strength in
strength in  Pb has been measured in photon scattering experiments with a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The data resolve an
Pb has been measured in photon scattering experiments with a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The data resolve an  giant resonance into at least seven, possibly eight, discrete transitions at excitation energies between 7.1 and 7.4 MeV below the neutron separation energy. The measured
giant resonance into at least seven, possibly eight, discrete transitions at excitation energies between 7.1 and 7.4 MeV below the neutron separation energy. The measured  strength in this region is found to be larger than the previous report. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
strength in this region is found to be larger than the previous report. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Wada, Kunihiko*; Matsubara, Hideaki*; Kawamura, Masashi*
Zairyo, 57(7), p.674 - 680, 2008/07
Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Wada, Kunihiko*; Matsubara, Hideaki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, A, 74(739), p.370 - 376, 2008/03
Thickness of the bond coating was about 0.18 mm, and the thickness of the top coating was about 0.12 mm. The rotation speeds of specimens in the EB-PVD process were 5 rpm, 10 rpm and 20 rpm. The specimens were oxidized at 1273 K for 200 h. The in-plane residual stress was measured by a conventional X-ray method, and the out-of-plane residual strain was measured by a strain scanning method with hard synchrotron X-rays. For the specimens with 5 rpm and 10 rpm, the in-plane compressive residual stresses were released by the oxidization. For the specimen with 20 rpm, the in-plane residual stress did not change by the oxidization, because it was very small before the oxidization. The in-plane residual stresses were large compression near the interface. For the specimens with 5 rpm and 10 rpm, the out-of-plane stresses were small from the coating surface but became a compression near the interface. Both in-plane and out-of-plane residual stresses of the specimen with 20 rpm were very small. In the effect of decreasing the residual stress, the rotation speed of 20 rpm was the excellent condition. According to the observation with a scanning electron microscope, the featherlike columnar structure decreased after the oxidization. This volume decrease caused the release of the in-plane residual stresses.
Suzuki, Kenji*; Wada, Kunihiko*; Matsubara, Hideaki*; Shobu, Takahisa; Kawamura, Masashi*; Tanaka, Keisuke*
Zairyo, 56(7), p.588 - 593, 2007/07
The Ni-based superalloy IN738LC was used as the substrate material, and CoNiCrAlY powder was pressureless plasma-sprayed on the substrate as the bond coating. Zirconia was coated as the top coating by the electron beam-physical vapor deposition (EV-PVD) method. In the EB-PVD process, the specimens were kept at 1223 K and rotated with 5 rpm, 10 rpm and 20 rpm. According to the microscopic observation and the result of the pole figures, the top coatings had a columnar structure, which was made by the piling up of (111) planes. The cross section of the column had a diamond shape, and its diagonal was parallel to the rotation axis. The residual stress on the surface of the top coatings was evaluated by the X-ray diffraction method. Each diffraction profile was separated into the 133 and the 331 peak, and the residual stress was measured by the sin
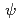 method. The measured residual stresses were -76.6 MPa for 5 rpm, -63.0 MPa for 10 rpm and -25.1 MPa for 20 rpm.
method. The measured residual stresses were -76.6 MPa for 5 rpm, -63.0 MPa for 10 rpm and -25.1 MPa for 20 rpm.
 Pb using laser Compton scattering
Pb using laser Compton scattering  rays
raysShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray beam from inverse Compton scattering
-ray beam from inverse Compton scatteringShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
no journal, ,
The knowledge of the M1 response allows one to elucidate the details of nuclear dynamics. It is also important for the estimate neutral current neutrino-nucleus cross sections for supernova explosion. Low-lying electromagnetic transitions can be studied by the method of nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). Recently, it has been shown that quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beams from inverse laser Compton scattering has considerably increased experimental sensitivity and to enable one to detect the fine structure of relatively weak M1 transitions. In this report, results of the NRF measurements on  Pb using a linearly polarized photon beam will be presented. The M1 resonance below the neutron separation energy is resolved into several individual transitions. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
Pb using a linearly polarized photon beam will be presented. The M1 resonance below the neutron separation energy is resolved into several individual transitions. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
 Fe using laser Compton scattering
Fe using laser Compton scattering  rays
raysShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Homma, Michio*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
no journal, ,
Low-lying electromagnetic transitions can be studied by the method of nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). Recently, it has been shown that quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beams from inverse laser Compton scattering has considerably increased experimental sensitivity and to enable one to detect the fine structure of relatively weak M1 transitions. In this report, results of the NRF measurements on nuclei around lead and iron region will be presented. The M1 resonance below the neutron separation energy is resolved in to individual transitions. The experimental results are compared with theoretical predictions based on self-consistent RPA and Shell model calculations. The role of the tensor interaction in giant M1 resonance region is discussed.
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*
no journal, ,
Nuclear electromagnetic (EM) transitions can be studied by nuclear photon scattering, or nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). Recently, it was shown that a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam produced by inverse Compton scattering increased experimental sensitivities to distinguish between electric and magnetic dipole transitions. Here we report the results of the nuclear photon scattering measurements on  Fe using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam derived at National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba. Many dipole resonances below the neutron separation energy of
Fe using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam derived at National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba. Many dipole resonances below the neutron separation energy of  Fe (11.2 MeV) have been observed. The multi-polarities of these transitions were determined by intensity asymmetry relative to the polarization of the incident photon beam. The experimental results are compared with a shell model calculation.
Fe (11.2 MeV) have been observed. The multi-polarities of these transitions were determined by intensity asymmetry relative to the polarization of the incident photon beam. The experimental results are compared with a shell model calculation.
 rays
raysShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*
no journal, ,
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) measurements on iron nuclei have been carried out by using laser Compton  rays with high polarization. NRF scattering
rays with high polarization. NRF scattering  rays were measured by a Ge detector with a relative detection efficiency of 140%. Multi-polarities of the transitions were determined by intensity asymmetry of the transitions with respect to the polarization. Many electric- and magnetic- dipole transitions were observed. The measurement method and the experimental results will be reported.
rays were measured by a Ge detector with a relative detection efficiency of 140%. Multi-polarities of the transitions were determined by intensity asymmetry of the transitions with respect to the polarization. Many electric- and magnetic- dipole transitions were observed. The measurement method and the experimental results will be reported.