Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kakinouchi, Keisuke*; Nakamura, Tsutomu*; Tamada, Taro; Adachi, Hiroaki*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; Maruyama, Mihoko*; Takahashi, Yoshinori*; Takano, Kazufumi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Inoue, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 43(4), p.937 - 939, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A method for growing large protein crystals is described. In this method, a cut pipette tip is used to hang large-scale droplets (maximum volume 200  l) consisting of protein and precipitating agents. A crystal grows at the vapor-liquid interface; thereafter the grown crystal can be retrieved by droplet-droplet contact both for repeated macroseeding and for mounting crystals in a capillary. Crystallization experiments with peroxiredoxin of
l) consisting of protein and precipitating agents. A crystal grows at the vapor-liquid interface; thereafter the grown crystal can be retrieved by droplet-droplet contact both for repeated macroseeding and for mounting crystals in a capillary. Crystallization experiments with peroxiredoxin of 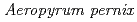 K1(thioredoxin peroxidase, ApTPx) and hen egg white lysozyme demonstrated that this large-scale hanging-drop method could produce a large-volume crystal very effectively. A neutron diffraction experiment confirmed that an ApTPx crystal (6.2 mm
K1(thioredoxin peroxidase, ApTPx) and hen egg white lysozyme demonstrated that this large-scale hanging-drop method could produce a large-volume crystal very effectively. A neutron diffraction experiment confirmed that an ApTPx crystal (6.2 mm ) obtained by this method diffracted to beyond 3.5
) obtained by this method diffracted to beyond 3.5  resolution.
resolution.
 resolution
resolutionShimizu, Noriko*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; Maruyama, Mihoko*; Takahashi, Yoshinori*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Hidaka, Koshi*; Hayashi, Yoshio*; Kimura, Toru*; Kiso, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Crystal Growth & Design, 10(7), p.2990 - 2994, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:72.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report crystal growth of human immunodeficiency virus 1 protease (HIV PR) in a complex with its inhibitor KNI-272 by six different methods. Comparative analysis indicates that top-seeded solution growth (TSSG) and TSSG combined with the floating and stirring technique (TSSG-FAST) are efficient strategies for rapidly obtaining large single crystals and effectively preventing polycrystallization of the seed crystal. Neutron diffraction analysis confirmed that the crystalobtained by TSSG is a high-quality single crystal. Furthermore, crystal shape was observed to be influenced by solution flow, suggesting that the degree of supersaturation significantly affects the crystal growth direction of HIV PR complex. This finding implies that the shape of the HIV PR complex crystal might be controlled by the solution flow rate.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Kimura, Kaname*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(12), p.4641 - 4646, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:111 Percentile:90.72(Multidisciplinary Sciences)To further understand the catalytic mechanism and inhibitor recognition of HIV-1 protease, we need to determine the locations of key hydrogen atoms in the catalytic aspartates Asp25 and Asp125. The structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with transition-state analog KNI-272 was determined by combined neutron crystallography at 1.9  resolution and X-ray crystallography at 1.4
resolution and X-ray crystallography at 1.4  resolution. The resulting structural data shows that the catalytic residue Asp25 is protonated and that Asp125 is deprotonated. The proton on Asp25 makes a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of the allophenylnorstatine group in KNI-272. The deprotonated Asp125 bonds to the hydroxyl proton of Apns. The results provide direct experimental evidence for proposed aspects of the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease; and can therefore contribute substantially to the development of specific inhibitors for therapeutic application.
resolution. The resulting structural data shows that the catalytic residue Asp25 is protonated and that Asp125 is deprotonated. The proton on Asp25 makes a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of the allophenylnorstatine group in KNI-272. The deprotonated Asp125 bonds to the hydroxyl proton of Apns. The results provide direct experimental evidence for proposed aspects of the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease; and can therefore contribute substantially to the development of specific inhibitors for therapeutic application.
Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; Okada, Shino*; Yamakami, Megumi*; Tamada, Taro; Hidaka, Koshi*; Hayashi, Yoshio*; Kimura, Toru*; Kiso, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 64(11), p.1003 - 1006, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.92(Biochemical Research Methods)This paper reports the crystallization and preliminary neutron diffraction measurements of HIV-1 protease, a potential target for anti-HIV therapy, complexed with an inhibitor (KNI-272). The aim of this neutron diffraction study is to obtain structural information about the H atoms and to determine the protonation states of the residues within the active site. The crystal was grown to a size of 1.4 mm by repeated macroseeding and a slow-cooling method using a two-liquid system. Neutron diffraction data were collected at room temperature using a BIX-4 diffractometer at the JRR-3 research reactor of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The data set was integrated and scaled to 2.3
by repeated macroseeding and a slow-cooling method using a two-liquid system. Neutron diffraction data were collected at room temperature using a BIX-4 diffractometer at the JRR-3 research reactor of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The data set was integrated and scaled to 2.3  resolution in space group P2(1)2(1)2, with unit-cell parameters a = 59.5, b = 87.4, c = 46.8
resolution in space group P2(1)2(1)2, with unit-cell parameters a = 59.5, b = 87.4, c = 46.8  .
.
Shibata, Yasushi*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Hori, Naohiko; Kishi, Toshiaki; Kumada, Hiroaki; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, Kei*; et al.
JAERI-Research 2005-009, 41 Pages, 2005/03
The measurement of neutron flux and boron concentration in the blood during medical irradiation is indispensable in order to evaluate the radiation in boron neutron capture therapy. It is, however, difficult to measure the blood boron concentration during neutron irradiation because access to the patient is limited. Therefore we prospectively investigated the predictability of blood boron concentrations using the data obtained at the first craniotomy after infusion of a low dosage of BSH. When the test could not be carried out, the blood boron concentration during irradiation was also predicted by using the 2-compartment model. If the final boron concentration after the end of the infusion is within 95% confidence interval of the prediction, direct prediction from biexponential fit will reduce the error of blood boron concentrations during irradiation to around 6%. If the final boron concentration at 6 or 9 hours after the end of infusion is out of 95% confidence interval of the prediction, proportional adjustment will reduce error and expected error after adjustment to around 12%.
Shibata, Yasushi*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, Kei*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Hori, Naohiko; et al.
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.1055 - 1060, 2002/09
We prospectively investigated the predictability of blood boron concentrations using the data obtained at the first craniotomy after infusion of a low dose of sodium undecahydroclosododecaborate (BSH). Nine patients with malignant glial tumors underwent Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) between 1995 and 2001. In 7 patients, 1g of BSH was infused before the first tumor removal and boron concentrations were determined using prompt gamma ray analysis (PGA). Then, 12 hours before BNCT, patients were infused at a dose of 100mg/kg BSH, and the boron concentrations were determined again. The boron biodistribution data showed a biexponential pharmacokinetic profile. If the final boron concentration at 6 or 9 hours after the end of the infusion is within the 95% confidence interval of the prediction, direct prediction from biexponential fit will reduce the error of blood boron concentrations during irradiation to around 6%.
Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Nakai, Kei*; Zhang, T.*; Matsushita, Akira*; Takano, Shingo*; Endo, Kiyoshi*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.1073 - 1078, 2002/09
Since 1998 to 2002, a new clinical trial of an intraoperative boron neutron capture therapy (IOBNCT) at JRR-4 of Japan Atomic Energy Institute (JAERI) using BSH with mixed thermal/epithermal neutron beam has been accomplished. There have been 9 patients included in this study. The median survival time (MST) in GBM was 19.8 months and 16.8 months in AA. IOBNCT with mixed thermal/epithermal neutron beam provide better primary radiation effect than conventional therapy in selected cases. Our phase I/II clinical trial was effective in local tumor control. Further clinical trial with new design should be performed to prove the efficacy of IOBNCT.
Nakai, Kei*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Zhang, T.*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Matsuda, M.*; Matsushita, Akira*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Takano, Shingo*; et al.
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.1135 - 1138, 2002/09
7 patients have been undergoing Intraoperative boron neutron capture therapy (IOBNCT) for malignant glioma at Japan Atomic Energy Institute (JAERI). Post-BNCT MRI studies revealed one local recurrence and two distant recurrences. Distant recurrence is uncommon in the conventional radiation therapy. Symptomatic late radiation necrosis occurred in one case.
Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Nakai, Kei*; Zhang, T.*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Matsushita, Akira*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Takano, Shingo*; Nose, Tadao*; et al.
Posuto Shikuensu Jidai Ni Okeru Noshuyo No Kenkyu To Chiryo, p.427 - 435, 2002/07
no abstracts in English
Nose, Tadao*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Yoshida, Fumiyo*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Matsushita, Akira*; Nakai, Kei*; Yamada, Takashi*; et al.
UTRCN-G-29, p.114 - 123, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Matsushita, Akira*; Nakai, K.*; Yamada, Takashi*; Takano, Shingo*; Mizutani, Taro*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer, p.29 - 30, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Yasuda, Susumu*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Akira*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Matsushita, Akira*; Nakai, K.*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer, p.171 - 172, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yasushi*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, K.*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Hori, Naohiko; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer, p.145 - 146, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have determined a crystal structure of HIV-1 protease by neutron crystallography. The development of HIV-1 protease inhibitors is regarded as a major success of structure-based drug design and contributes to establish highly active anti-retroviral therapy for AIDS. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease and interaction between HIV-1 protease and its inhibitor, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a inhibitor, KNI-272 to 2.3  resolution by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
resolution by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Kimura, Kaname*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
HIV-1 protease is a dimeric aspartic protease that cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 to 1.9  resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4
resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4  resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
To understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic inhibitor, KNI-272 by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of allophenylnorstatine forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
In this study, we determined crystal structures of HIV-1 protease complexed with inhibitor by neutron and X-ray crystallography. Finally, we refined the structures to R-factor of 17.3% and free R-factor 20.3% by neutron crystallography and to R-factor of 10.4 % and free R-factor 12.4% by X-ray crystallography. The result shows that Asp 25 residue is protonated and Asp 125 is deprotonated. These information is important to resolve catalytic mechanism and design of new potent inhibitor.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
HIV-1 protease is a dimeric aspartic protease that cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 to 1.9  ; resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4
; resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4  ; resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
; resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Oka, Kiyoshi; Seki, Takeshi; Akatsu, Tomohiro; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Ihara, Satoshi*; Watanabe, Shinya*; Matsumura, Akira*; Kikuta, Kenichiro*
no journal, ,
For the neuroendoscopic surgery, we are developing a new laser-irradiating fiberscope system. In this system, we use a composite-type optical fiberscope (COF) with 1 mm in outer diameter, which can transmit both laser energy and images for observation simultaneously. The diameter of the cautery laser fiber is 0.1 mm, which is located in the center of the imaging fibers. In this animal experimental study, we conducted the laser-irradiation on the femoral artery and vein of a rat using a usual single core fiber of 0.1 mm in outer diameter and the COF in order to assess the availability of this system. As a result, the blood flow decreased to 1/2 or 1/3 after a cauterization with the single core fiber. Furthermore, in the laser irradiation with the COF, the contraction of the artery with minimal heat damage of adjacent tissue was confirmed. Under direct observation with optical fiberscope, the obliteration of arteries was safely and successfully performed.