Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Okura, Takehisa; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Taki, Mitsumasa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.295 - 307, 2021/10
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Okura, Takehisa; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Taki, Mitsumasa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(3), p.119 - 126, 2014/09
A method of deducing the I-131 concentration in a radioactive plume from the time history of peak count rates determined from pulse height spectra obtained from an NaI(Tl)scintillation detector employed as a detector of a monitoring post was presented. The concentrations of I-131 in the plumes were estimated from the count rates using the calculated response of the NaI(Tl) detector with egs5 for a model of a plume uniformly containing I-131. This method was applied to the data from the monitoring posts at Nuclear Science Research Institutes of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The estimated time history variation of I-131 concentrations in plumes was in fair agreement with those measured directly by an air sampling method. The difference was less than a factor of 4 for plumes that arrived on March 15 and March 21, indicating relatively high I-131 concentrations among the plumes studied in this work.
 and TbFe
and TbFe
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Abe, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Mitsuaki*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.109 - 112, 2013/03
We performed local structure analysis of SmFe and TbFe
and TbFe in the crystallization process from amorphous by using synchrotron X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method. The giant mangetostrictive materials of these compounds can be controlled its property by ion irradiation. In amorphous TbFe
in the crystallization process from amorphous by using synchrotron X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method. The giant mangetostrictive materials of these compounds can be controlled its property by ion irradiation. In amorphous TbFe and SmFe
and SmFe , the mosaic block size was small and the short-range order structure owing to Fe-Fe network maintained. In crystalline SmFe
, the mosaic block size was small and the short-range order structure owing to Fe-Fe network maintained. In crystalline SmFe , a rigid long-range order structure of Fe-Fe and Sm-Sm network coexisted and it had a large mosaic block size. On the other hand, in crystalline TbFe
, a rigid long-range order structure of Fe-Fe and Sm-Sm network coexisted and it had a large mosaic block size. On the other hand, in crystalline TbFe , Fe-Fe network degraded by Tb-Tb network owing to its lattice tolerance.
, Fe-Fe network degraded by Tb-Tb network owing to its lattice tolerance.
Onuki, Shun*; Abe, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen storage alloys are applied to the negative electrodes of the Ni-MH batteries. In such metal alloys high hydrogen absorption rate is required for the practical use. The electron/ion beam modifications are of effective methods to improve the hydrogen absorption rate in metal. In the present study, we have carried out the irradiation of electron beam and charged ion to La-Ni based hydrogen storage alloy. We measured the hydrogen absorption rates in irradiated/un-irradiated La-Ni based alloys. The samples used in this study were LaNi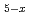 Al
Al alloys. An electron beam or several ion irradiations used the 2 MV Cockcroft-Walton electron accelerator or the TIARA(Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application) 400 kV ion implanter in JAEA. The hydrogen absorption rate measurements were also performed for the irradiated and un-irradiated La-Ni based alloy samples using the Severs equipment. The chemical compositions in the surface of the irradiated La-Ni bossed alloys were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy. The crystal structure and phase of the bulk into the irradiated La-Ni based alloys were determined by X-ray diffraction.
alloys. An electron beam or several ion irradiations used the 2 MV Cockcroft-Walton electron accelerator or the TIARA(Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application) 400 kV ion implanter in JAEA. The hydrogen absorption rate measurements were also performed for the irradiated and un-irradiated La-Ni based alloy samples using the Severs equipment. The chemical compositions in the surface of the irradiated La-Ni bossed alloys were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy. The crystal structure and phase of the bulk into the irradiated La-Ni based alloys were determined by X-ray diffraction.
Onuki, Shun*; Abe, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Yoshihito*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onuki, Shun*; Abe, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen storage alloys are required high hydrogen absorption rate for the negative electrodes of the Ni-MH batteries applications. Surface modifications are crucial to improve the reactivity of hydrogen with metals because the dissociation of the H molecules in the gas phase or the dissociation of the H
molecules in the gas phase or the dissociation of the H O molecules in an electrochemical process is the first step of the overall reaction of hydrogen absorption by metals. In the present study, irradiation effects on electron beam and charged ions on hydriding characteristics of LaNi
O molecules in an electrochemical process is the first step of the overall reaction of hydrogen absorption by metals. In the present study, irradiation effects on electron beam and charged ions on hydriding characteristics of LaNi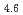 Al
Al alloy were studied. The hydrogen absorption rare measurements were also performed for the irradiated and un-irradiated samples using an electrochemical method. The crystal structure and phase of the bulk of the irradiated alloys were determined by X-ray diffraction. We will discus the effects of irradiation fo electron beam and ions on the improvement of the rate of hydrogen absorption by the LaNi
alloy were studied. The hydrogen absorption rare measurements were also performed for the irradiated and un-irradiated samples using an electrochemical method. The crystal structure and phase of the bulk of the irradiated alloys were determined by X-ray diffraction. We will discus the effects of irradiation fo electron beam and ions on the improvement of the rate of hydrogen absorption by the LaNi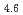 Al
Al alloys.
alloys.
Abe, Hiroshi; Onuki, Shun*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Onuki, Shun*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onuki, Shun*; Shinohara, Yoshiaki*; Sutrisna, F.*; Utsumi, Michiaki*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Abe, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
The ion irradiation treatment improved the hydrogen absorption rate. The irradiation of electron beam to the LaNi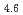 Al
Al hydrogen storage alloy surface was performed bye the dose of 1
hydrogen storage alloy surface was performed bye the dose of 1  10
10 e
e /cm
/cm , at 1 MeV and 2 MeV of acceleration energy, in vacuum at 2 Pa and atmospheric pressure in air. Electron beam irradiated sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the un-irradiated one. The maximum value of the hydrogen absorption rate was obtained in the sample irradiated by 2 MeV electron beam in the vacuum condition. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS) of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer by electron beam irradiation. The electron beam irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of the hydrogen absorption of La-Ni alloy.
, at 1 MeV and 2 MeV of acceleration energy, in vacuum at 2 Pa and atmospheric pressure in air. Electron beam irradiated sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the un-irradiated one. The maximum value of the hydrogen absorption rate was obtained in the sample irradiated by 2 MeV electron beam in the vacuum condition. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS) of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer by electron beam irradiation. The electron beam irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of the hydrogen absorption of La-Ni alloy.
Abe, Hiroshi; Onuki, Shun*; Shinohara, Yoshiaki*; Sutrisna, F.*; Utsumi, Michiaki*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Recently, Ni-MH batteries with hydrogen storage La-Ni based alloys as negative electrodes are installed many hybrid cars (HV: Hybrid Vehicle). In this study, we investigate the effects of ion irradiation on the electrochemical hydriding rate of the alkaline pretreatment LaNi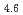 Al
Al alloy. We also analyzed the chemical compositions at the surface of the irradiated/un-irradiated samples, their crystal structures, and the phases of bulk. The samples were irradiated with K ion at an acceleration energy of 350 keV with a dose of 1
alloy. We also analyzed the chemical compositions at the surface of the irradiated/un-irradiated samples, their crystal structures, and the phases of bulk. The samples were irradiated with K ion at an acceleration energy of 350 keV with a dose of 1  10
10 cm
cm using the 400 kV ion implanter, at the TIARA, JAEA. X-ray Photoelectron spectra of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer was varied on irradiated conditions. These results suggest that improvement of initial hydrogen absorption rate for sample surface is caused by formation of conductive oxide layer by ion irradiation.
using the 400 kV ion implanter, at the TIARA, JAEA. X-ray Photoelectron spectra of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer was varied on irradiated conditions. These results suggest that improvement of initial hydrogen absorption rate for sample surface is caused by formation of conductive oxide layer by ion irradiation.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Nishihata, Yasuo; Abe, Hiroshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Takeuchi, Mitsuaki*; Tanakamaru, Tempei*; Shinohara, Yoshiaki*
no journal, ,
The material group that is called smart materials of ferroelectrics, magneto-strictive materials, shape-memory alloys, and hydrogen-storage materials can control physical properties by the elastic strain caused in the crystal. Because the irradiation by the ion beam and the electron beam can efficiently change the elastic strain in the crystal, it is efficient measures to the characteristic modification of a smart material. In this study group, pair-distribution function (PDF) was applied as an new visualization techniques of the crystallographic structure of the irradiation material. It examined whether the irradiation effect of smart materials was extractive by the PDF analysis.
Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Onuki, Shun*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Abe, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English