Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizuno, Takashi; Suzuki, Yohei*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Applied Geochemistry, 150, p.105571_1 - 105571_11, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:62.05(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM) affects both the redox conditions and carbon cycle in groundwater. However, examples of studies on crystalline rock deep in terrestrial subsurface as well as the potential host rock for geological disposal are few. Therefore, we conducted a paleohydrogeological study on fracture-filling calcite in the Toki Granite. The 
 O
O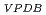 value (-32.7 to -0.59 permil) revealed that the groundwater that precipitated the calcite was groundwater derived from hydrothermal fluid, freshwater that came from the surface, and seawater that penetrated during marine transgression. On the other hand,
value (-32.7 to -0.59 permil) revealed that the groundwater that precipitated the calcite was groundwater derived from hydrothermal fluid, freshwater that came from the surface, and seawater that penetrated during marine transgression. On the other hand, 
 C
C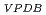 (-56.6 to 6.0 permil) was wider than the isotopic range of DIC that originated from hydrothermal, freshwater, and seawater sources (-25 to 2 permil). Calcite with
(-56.6 to 6.0 permil) was wider than the isotopic range of DIC that originated from hydrothermal, freshwater, and seawater sources (-25 to 2 permil). Calcite with 
 C
C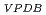 that was lighter than -25 permil was believed to have precipitated DIC, which was provided by AOM. In contrast to previous studies, the Mizunami AOM calcite was precipitated in a freshwater environment, indicating that various processes could have generated AOM in crystalline rocks deep in the terrestrial subsurface.
that was lighter than -25 permil was believed to have precipitated DIC, which was provided by AOM. In contrast to previous studies, the Mizunami AOM calcite was precipitated in a freshwater environment, indicating that various processes could have generated AOM in crystalline rocks deep in the terrestrial subsurface.
Mizuno, Takashi; Milodowski, A. E.*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Chemical Geology, 603, p.120880_1 - 120880_16, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:56.2(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This study has focused on the formation sequence and Rare earth elements with yttrium (REY) of fracture-filling calcite in the Toki Granite in the Mizunami area, central Japan. The morphological, chemical and isotopic characteristics of the calcite and chemistry of fluid inclusions reveal that the calcite in the Toki Granite can be differentiated into four discrete generations: Calcite I (oldest) to Calcite IV (most recent). The precipitation history of calcite reflects the changes in the hydrogeochemical regime of paleo-groundwaters, controlled by the evolution of groundwater by seawater infiltration associated with marine transgression and surface water infiltration associated with marine regression and uplift. The post-Archean average shale-normalized REY patterns in generations of calcite show no significant Ce anomaly, negative Eu anomaly, and light REY (LREY)-depleted pattern in dominates. These features are also common to the Toki Granite. The consistency of the features in each generation of calcite indicates that REY was supplied from the Toki Granite by water-rock interaction. The lack of a Ce anomaly in the calcite demonstrates that groundwaters have maintained reducing conditions during the calcite precipitation. However, the fractionation of LREY and heavy REY (HREY) in each generation of the calcite is more pronounced than in the granite. The fractionation process in the paleo-groundwaters from which each generation of calcite precipitated closely relates to the systematic variation of carbonate complex in REY series and/or pH in palaeo-groundwater. The findings of this study will be necessary for assessing the long-term safety of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste.
Kamei, Gento; Alexander, W. R.*; Clark, I. D.*; Degnan, P.*; Elie, M.*; Khoury, H.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Pitty, A. F.*; Salameh, E.*; Smellie, J. A. T.*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.141 - 147, 2010/10
Mizuno, Takashi; Milodowski, A. E.*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.193 - 201, 2010/10
West, J. M.*; Hama, Katsuhiro; Bateman, K.*; Coombs, P.*; Hards, V.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Wetton, P. D.*; Yoshida, Hidekazu
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.663, p.657 - 664, 2002/00
None
Hama, Katsuhiro; Hards, V. L.*; Milodo, A. E.*; West, J. M.*; Bateman, K.*; Coombs, P.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Wetton, P. D.*; Yoshida, Hidekazu; Aoki, Kazuhiro
Clay Minerals, 36(4), p.599 - 613, 2001/00
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:57.14(Chemistry, Physical)None
Yoshida, Hidekazu; Hama, Katsuhiro; West, J. M.*; Bateman, K.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Baker, S. J.*; Coombs, P.*; Hards, V. L.*; Spiro, B.*; Wetton, P. D.*
JNC TJ7400 99-013, 68 Pages, 1999/07
In April 1997 the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC)commissioned a Three-Task project from the Bretish Geological Survey (BGS). Task 1 was a continuation of work started in 1996 to examine microbial effects on redox and to quantify the effects of microbiological perturbations on the geological disposal of HLW(TRU). Task 2 was commissioned to provide information on theTsukiyoshi Fault for use in ongoing work at the Tono Geoscience Centre. Task 3 was to draft a Technical programme for use in ongoing work at the Tono Geoscience Centre.Task 3 was to draft a Technical programme for a geochemical study of the Tono site. This report details the results of Task 1, undertaken in 1998/99.
West, J. M.*; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Baker, S. J.*; Bateman, K.*; Coombs, P.*; Gillespie, M. R.*; Henney, P. J.*; Reeder, S.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Yoshida, Hidekazu
JNC TJ7400 99-002, 117 Pages, 1997/01
In February 1996 the Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corportation(PNC)of Japan commissioned a one year study from the British Geological Survey(BGS)to examine microbial effects on redox and to quantify the effects of microbiological perturbations on the geological disposal of HLW(TRU). The work was splitinto two tasks: Tas k 1:SKB REX Cooperation 'To perform laboratory experiments on bacterial processes to assess their influences on redox'.or Task 2:Microbiol ogical modelling the BGS developed code MGSE. This report details the results of Task 1.
Mizuno, Takashi; Milodowski, A. E.*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kamei, Gento; Alexander, W. R.*; Clark, I. D.*; Degnan, P.*; Elie, M.*; Khoury, H.*; Mader, U.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Pitty, A. F.*; Salameh, E.*; et al.
no journal, ,