Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 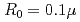 m.
m.
Nara, Fumiko*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Yamasaki, Shinichi*; Minami, Masayo*; Asahara, Yoshihiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Tsuchiya, Noriyoshi*; Yasuda, Yoshinori*
Geochemical Journal, 55(3), p.117 - 133, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:57.32(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The absolute date of the Millennium Eruption (ME) of Changbaishan Volcano is widely recognized as AD 946. The Baegdosan-Tomakomai (B-Tm) tephra dispersed during the ME is a robust-age key bed. In order to identify the tephra, refractive index and major-element compositions of volcanic glass shards are conventionally used. However, trace-element analysis has been rarely carried out, especially for rare-earth elements (REEs) and for tephra layer bulk sediments. Here we present the datasets of major- and trace-element compositions datasets for the glass shards and bulk sediments of the B-Tm and Towada caldera eruptions (To-a) tephra deposits from the Lake Ogawara sediment core, Tohoku region, northern Japan. The depth profiles of the major and trace elements show the significant peaks for the K O and some trace elements (Zn, Rb, Zr, Nb, Sn, Y, La, Ce, Nd, Th, and U) at the B-Tm tephra layer in the Lake Ogawara sediment core, but no peaks of these elements at the To-a tephra layer. High concentrations of the trace elements in the B-Tm tephra layer were observed in individual glass shards as well as in the bulk sediment. These concentrations are highlighted by the elemental abundance pattern normalized by the crustal abundance. The elemental pattern in individual glass shards from other Japanese tephras showed significant differences from those of the B-Tm tephra, especially in REEs compositions. The trace-element compositions of the glass shards and bulk sediment show strong advantages for distinguishing the B-Tm tephra from other Japanese tephras.
O and some trace elements (Zn, Rb, Zr, Nb, Sn, Y, La, Ce, Nd, Th, and U) at the B-Tm tephra layer in the Lake Ogawara sediment core, but no peaks of these elements at the To-a tephra layer. High concentrations of the trace elements in the B-Tm tephra layer were observed in individual glass shards as well as in the bulk sediment. These concentrations are highlighted by the elemental abundance pattern normalized by the crustal abundance. The elemental pattern in individual glass shards from other Japanese tephras showed significant differences from those of the B-Tm tephra, especially in REEs compositions. The trace-element compositions of the glass shards and bulk sediment show strong advantages for distinguishing the B-Tm tephra from other Japanese tephras.
Ohira, Hiroaki; Doda, Norihiro; Kamide, Hideki; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Minami, Masaki*
Proceedings of 2015 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2015) (CD-ROM), p.2585 - 2592, 2015/05
IAEA's Coordinated Research Project on Benchmark Analyses of Shutdown Heat Removal Test (SHRT) performed at the Experimental Breeder Reactor-II (EBR-II) has been carried out since 2012. The benchmark specifications were provided by the Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) and the model development for thermal-hydraulics codes and/or plant dynamics codes has been conducted by participating organizations. The experimental data were also provided by the ANL after the calculations have been performed as the blind simulation. JAEA participated in this benchmark analyses, and the plant dynamics analysis code; Super-COPD was applied to the SHRT-17 simulation. The calculated inlet temperature of the high pressure plenum agreed well with the test data in all simulation time. Although the Z-pipe inlet temperature and the IHX intermediate outlet temperature had some discrepancy in the first 400 sec. caused by larger mass flow rate of the primary pump and the perfect mixing model of upper plenum, these temperatures and the flow rate agreed well with the measured data after 400 sec. Hence it was concluded the present analytical model could predict the natural circulation in good accuracy.
Yoshikawa, Shinji; Minami, Masaki*; Takahashi, Tadao*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(4), p.709 - 714, 2011/04
In design problems of large-scale systems like fast breeder reactors, inter-relations among design specifications are very important where a selected specification option is transferred to other specification selections as a premise to be taken account in engineering judgments. These inter-relations are also important in design case studies with hypothetical adoption of rejected design options for evaluation of deviation propagations among design specifications. Some of these rejected options have potential worth for future reconsideration by some circumstance changes (e.g., advanced simulations to exclude needs for mock-up tests, etc), to contribute for flexibility in system designs. In this study, a computer software is built to visualize design problem structure by representing engineering knowledge nodes on individual specification selections along with inter-relations of design specifications, to validate the knowledge representation method and to derive open problems.
Yamada, Fumiaki; Minami, Masaki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-023, 79 Pages, 2010/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency constructed a computational model for safety analysis of Monju reactor core to be built into a modularized plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD code, for the purpose of heat removal capability evaluation at the in total 21 defined transients in the annex to the construction permit application. The applicability of this model to core heat removal capability evaluation has been estimated by back to back result comparisons of the constituent models with conventionally applied codes and by application of the unified model.
Yoshikawa, Shinji; Minami, Masaki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-024, 28 Pages, 2009/01
A series of information required for numerical simulation of sodium thermal stratification observed at the plant trip test of "Monju" conducted in 1995 is provided, which consists of the test outline, geometry data of the reactor vessel upper plenum between the reactor core top and reactor outlet nozzles, and flow inlet boundary conditions at the reactor core top surface.
Isobe, Mitsutaka*; Toi, Kazuo*; Matsushita, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Kazuyuki*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Shimizu, Akihiro*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(10), p.S918 - S925, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:69.47(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Minami, Masaki*; Sakata, Hideaki; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamada, Fumiaki
JNC TN4410 2005-001, 123 Pages, 2005/03
A software system for straightforward and quick conceptual studies and technical evaluations of fast breeder reactor plants has been developed, mainly targeting the Japanese Demonstration Fast Breeder Reactor Monju. The studies and evaluations by this system used to be limited within steady and nominal conditions, excluding influences by changing specification values in accidental conditions. In this fiscal year, a new software component has been included in the system for simplified evaluation of transient characteristics, which is an essential for complete design of an FBR plant. This new evaluation function enabled to detect specifications to vary over acceptable range in transient conditions, and to notify necessity for re-adjustment of steady state design specification values. This system was also utilized to generate a sensitivity survey program in order to evaluate appropriateness of Monju design. The appropriateness of Monju design was evaluated in two ways. The first one is to follow specification selecting sequence as the as-built Monju has actually been designed. The second one is hypothetical deviations of major specifications of Monju and observation of the influences on other specifications. As a result, Monju design was confirmed to be adequate from the view point of need to meet design limitations at the design stage of Monju. This system is expected to be systematically re-arranged, because the system has now considerably complicated configuration after additions of various programs for many objects. This arrangement will facilitate future contribution of this system to technical studies in order for development of FBRs.
Yoshikawa, Shinji; Minami, Masaki*; Takahashi, Tadao*
no journal, ,
Aiming at profound understanding of fast breeder reactor plants, a trial software has been built to correlate various technical information items considered in the design stage of the Japanese prototype fast breeder reactor Monju, along with some decision making consequences as of plant characteristics evaluation.
Yoshikawa, Shinji; Minami, Masaki*
no journal, ,
This document provides a set of technical data for the thermal hydraulic analysis of liquid sodium in the upper plenum of Monju reactor vessel, consisting of the additional information which JAEA stated to be offered at first RCM held in September 2008 in Vienna, and the table of temperature versus time measured by the vertical array of thermocouples inserted in the reactor upper plenum during the turbine trip test of the system start-up tests conducted in December 1995.
Yamada, Fumiaki; Minami, Masaki*
no journal, ,
A computational model to simulate integrated behaviors of a reactor core and the connected heat transport system was built and verified by trial calculations on a set of representative anomaly transient event, in order for application of the plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD to evaluation of the cooling capability of Monju reactor core.
Doda, Norihiro; Igawa, Kenichi*; Minami, Masaki*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Ohira, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
Sodium-cooled fast reactors have been developed aiming at introducing natural circulation decay heat removal systems by utilizing the characteristic of having a large coolant temperature difference between at the inlet and at the outlet of reactor vessel. In this study, as part of validation for core hot spot evaluation method, which is required for adoption of natural circulation decay heat removal systems, EBR-II (Experimental Breeder Reactor II) shutdown heat removal test was simulated. The simulation results demonstrated that the evaluation method sufficiently predicts the whole plant thermal hydraulic behaviors and the maximum coolant temperature in a fuel subassembly in natural circulation decay heat removal.