Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ono, Takahiro; Kakutani, Satomi; Yoshida, Moeka; Suzuki, Soichiro
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(1), p.125 - 133, 2024/02
The Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was established for the purpose of developing and verifying remote control equipment for promoting the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and the external use of this center was started in 2016. The mission of this center is to contribute to the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and for the reconstruction of Fukushima Prefecture. In this review, we describe the equipment related to the full-scale mock-up test, the component test for a remote-control device and the virtual reality system in this center. In addition, the case examples for usage of these equipment are introduced.
Akiyama, Yoichi; Shibanuma, So; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamada, Taichi; Suzuki, Kenta; Yoshida, Moeka; Ono, Takahiro; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Watanabe, Kaho; Morimoto, Kyoichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-015, 60 Pages, 2023/09
Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development (NARREC) was established in Japan Atomic Energy Agency to promote a decommissioning work of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (Fukushima Daiichi NPS). NARREC consists of a Full-scale Mock-up Test Building and Research Management Building. Various test facilities are installed in these buildings for the decommissioning work of Fukushima Daiichi NPS. These test facilities are intended to be used for various users, such as companies engaged in the decommissioning work, research and development institutions, educational institutions and so on. The number of NARREC facility uses was 84 in FY2021. We participated booth exhibitions and presentations on the decommissioning related events. Moreover, we also contributed to the development of human resources by supporting the 6th Creative Robot Contest for Decommissioning. As a new project, "Narahakko Children's Classroom" was implemented for elementary school students in Naraha Town. This report summarizes the activities of NARREC in FY2021, such as the utilization of facilities and equipment of NARREC, the development of remote-control technologies for supporting the decommissioning work, arrangement of the remote-control machines for emergency response, and training for operators by using the machines.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
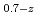 Pu
Pu Am
Am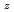 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sugimoto, Masatoshi*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Hino, Tetsushi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101156_1 - 101156_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)In current nuclear fuel cycle systems, to reduce the amount of high-level radioactive waste, minor actinides (MAs) bearing MOX fuel is one option for burning MAs using fast reactor. However, the effects of Am content in fuel on thermal conductivity are unclear because there are no experimental data on thermal conductivity of high Am bearing MOX fuel. In this study, The thermal conductivities of near stoichiometric (U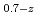 Pu
Pu Am
Am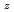 )O
)O solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT)
solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT) ) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U
) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U and Am
and Am . B values were independent of Am content.
. B values were independent of Am content.

Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato
2018 GIF Symposium Proceedings (Internet), p.315 - 320, 2020/05
Recently, a research group studying at Plutonium Fuel Development Facility (PFDF) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency has systematically measured vast amounts of physical properties in the non-stoichiometric (U, Pu)O . Lattice parameter, elastic modulus, thermal expansion, oxygen potential, oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient and thermal conductivity were successfully measured as function of Pu content, O/M ratio and temperature, and the effects of Pu content and O/M ratio on their physical properties were evaluated. In this work, those experimental data are reviewed, and latest experimental data set on the non-stoichiometric (U, Pu)O
. Lattice parameter, elastic modulus, thermal expansion, oxygen potential, oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient and thermal conductivity were successfully measured as function of Pu content, O/M ratio and temperature, and the effects of Pu content and O/M ratio on their physical properties were evaluated. In this work, those experimental data are reviewed, and latest experimental data set on the non-stoichiometric (U, Pu)O are presented. The data set would be available in development of a fuel performance code.
are presented. The data set would be available in development of a fuel performance code.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Saito, Kosuke; Uno, Masayoshi*
Nuclear Technology, 205(3), p.474 - 485, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study evaluated the effects of plutonium content and self-irradiation on the thermal conductivity of mixed-oxide (MOX) fuel. Samples of UO fuel and various MOX fuels were tested. The MOX fuels had a range of plutonium contents, and some samples were stored for 20 years. The thermal conductivity of these samples was determined from thermal diffusivity measurements taken via laser flash analysis. Although the thermal conductivity decreased with increasing plutonium content, this effect was slight. The effect of self-irradiation was investigated using the stored samples. The reduction in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation depended on the plutonium content, its isotopic composition, and storage time. The reduction in thermal conductivity over 20 years' storage can be predicted from the change of lattice parameter. In addition, the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation was recovered with heat treatment, and recovered almost completely at temperatures over 1200 K. From these evaluation results, we formulated an equation for thermal conductivity that is based on the classical phonon-transport model. This equation can predict the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel thermal conductivity by accounting for the influences of plutonium content and self-irradiation.
fuel and various MOX fuels were tested. The MOX fuels had a range of plutonium contents, and some samples were stored for 20 years. The thermal conductivity of these samples was determined from thermal diffusivity measurements taken via laser flash analysis. Although the thermal conductivity decreased with increasing plutonium content, this effect was slight. The effect of self-irradiation was investigated using the stored samples. The reduction in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation depended on the plutonium content, its isotopic composition, and storage time. The reduction in thermal conductivity over 20 years' storage can be predicted from the change of lattice parameter. In addition, the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by self-irradiation was recovered with heat treatment, and recovered almost completely at temperatures over 1200 K. From these evaluation results, we formulated an equation for thermal conductivity that is based on the classical phonon-transport model. This equation can predict the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel thermal conductivity by accounting for the influences of plutonium content and self-irradiation.
Maeda, Seiichiro; Oki, Shigeo; Otsuka, Satoshi; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ozawa, Takayuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
The next generation fast reactor is being investigated in Japan, aiming at several targets such as "safety", "reduction of environmental burden" and "economic competitiveness". As for the safety aspect, FAIDUS concept is adopted to avoid re-criticality in core destructive accidents. The uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuel, in which minor actinide elements are included, will be applied to reduce the amount and potential radio-toxicity of radioactive wastes. The high burn-up fuel is pursued to reduce fuel cycle cost. The candidate concept of the core and fuel design, which could satisfy various design criteria by design devisals, has been established. In addition, JAEA is investigating material properties and irradiation behavior of MA-MOX fuel. JAEA is developing the fuel design code especially for the fuel pin with annular pellets of MA-bearing MOX. Furthermore, JAEA is developing oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel cladding for the high burnup fuel.
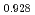 Am
Am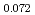 )O
)O at high temperatures
at high temperaturesMatsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1296 - 1302, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The oxygen potentials of (Pu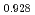 Am
Am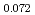 )O
)O were measured at 1873K, 1773K and 1473K by gas equilibrium method. It was shown that following the reduction of Am at the O/M ratio above 1.96, Pu was reduced at the O/M ratio below 1.96.
were measured at 1873K, 1773K and 1473K by gas equilibrium method. It was shown that following the reduction of Am at the O/M ratio above 1.96, Pu was reduced at the O/M ratio below 1.96.
 -PuO
-PuO -ZrO
-ZrO pseudo-ternary system
pseudo-ternary systemMorimoto, Kyoichi; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Masashi; Sugata, Hiromasa*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1247 - 1252, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)As a part of decommissioning plan of the damaged reactors at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, some strategies for removing of debris from the reactors are discussed. In these considerations, it is necessary to predict a melt progression during the severe accident based on theoretical evidences. Melting temperature is one of the most important thermal characteristics to analyse a melt progression during the severe accident. In this study, the melting temperatures of specimens of U, Pu and Zr mixed oxide prepared as simulated debris were measured by the thermal arrest technique. From the results of this measurement, the influences of Pu and Zr
and Zr contents on the melting temperature of the simulated debris were evaluated.
contents on the melting temperature of the simulated debris were evaluated.
Kato, Masato; Hirooka, Shun; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Akashi, Masatoshi; Maeda, Koji; Watanabe, Masashi; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Proceedings of 19th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2014/08
Uranium and plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel has been developed for Japan sodium-cooled fast reactors. Science based fuel technologies have been developed to analyse behaviours of MOX pellets in the sintering process and irradiation conditions. The technologies can provide appropriate sintering conditions, irradiation behaviour analysis results and so on using mechanistic models which are derived based on theoretical equations to represent various properties.
Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Washiya, Tadahiro
Proceedings of 19th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2014/08
Since the severe accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, technologies to remove fuel debris from the damaged core have been developed. However, many subjects such as how to access to the core, cut the fuel debris, control criticality safety, estimate fissile materials, store removed debris and so on are still in existence. Purpose of this work is to evaluate the fuel debris properties by using analysis of simulated fuel debris and to estimate the inner state such as temperature profile and density profile which depend on elapsed time after the accident. The reported properties such as melting temperature, thermal conductivity and thermal expansion were obtained by the simulated fuel debris manufactured from UO and zircaloy.
and zircaloy.
 at high temperatures up to 2190 K
at high temperatures up to 2190 KMorimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 443(1-3), p.286 - 290, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, measurement was conducted for the sliced MOX pellets containing 30% of Pu prepared by a conventional powder metallurgy technology. Oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratios of the samples were adjusted in the range from 1.92 to 2.00. The thermal diffusivities of these samples were measured at temperature up to 2150 K with the laser flash method. Thermal diffusivities of the near-stoichiometric samples obtained in the cooling process were greatly lower than those in the heating process unlike measurement below 1770 K. On the other hand, they were almost identical for the sample of 1.946 in O/M. It was also shown that thermal diffusivity decreased with the temperature but increased with the O/M.
 -MOX system
-MOX systemUchida, Teppei; Hirooka, Shun; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Sato, Daisuke*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference; Nuclear Energy at a Crossroads (GLOBAL 2013) (CD-ROM), p.1549 - 1553, 2013/09
 and zircaloy-2
and zircaloy-2Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Uchida, Teppei; Akashi, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 437(1-3), p.130 - 134, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and zircalloy-2
and zircalloy-2Kato, Masato; Uchida, Teppei; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.91 - 96, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and zircalloy-2
and zircalloy-2Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Uchida, Teppei; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.97 - 101, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
Proceedings of Plutonium Futures; The Science 2010 (CD-ROM), p.339 - 340, 2010/09
Nuclear fuel pellets are stored before loading into a reactor. In some cases, the fuel pellets are left for several years. When uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel pellets are stored for a long time, lattice defects induced by self-irradiation ( decay) accumulate and these defects affect physical properties of the pellets, i.e. lattice parameter, electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of fuel pellets is one of the most important properties for fuel design and performance analyses; it is known to decrease due to the defects induced by self-irradiation, but it can be recovered by heating the pellets. In this study, the recovery behavior of thermal conductivity of a MOX fuel pellet stored for long time was investigated as a function of time and temperature, in order to make it easy to analyze the thermal performance of fuel pellets.
decay) accumulate and these defects affect physical properties of the pellets, i.e. lattice parameter, electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of fuel pellets is one of the most important properties for fuel design and performance analyses; it is known to decrease due to the defects induced by self-irradiation, but it can be recovered by heating the pellets. In this study, the recovery behavior of thermal conductivity of a MOX fuel pellet stored for long time was investigated as a function of time and temperature, in order to make it easy to analyze the thermal performance of fuel pellets.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ozawa, Takayuki; Kato, Masato
Proceedings of Plutonium Futures; The Science 2010 (CD-ROM), p.341 - 342, 2010/09
Thermal conductivity of oxide fuel is important for fuel design and performance analyses. Uranium dioxide and uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) are used as fuels in light water reactors (LWRs), and the thermal conductivities of these oxide fuels have been measured in various laboratories. In a review of oxide fuel properties, it was reported that the thermal conductivity of oxide fuel would decrease with burn-up increase. In this study, burn-up effect on MOX fuel thermal conductivity was discussed.
 Pu
Pu )O
)O (1.92
(1.92 x
x 2.00) based fuels containing actinides and/or lanthanides
2.00) based fuels containing actinides and/or lanthanidesKomeno, Akira; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 9, p.012016_1 - 012016_7, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:93.82(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)It is expected that the important data for design of fast reactor fuel can be provided by evaluating the relationship between fuel composition and phase separation with reported and new measurement data. According to evaluation with reported data and new measured data, a relationship between fuel composition and phase separation temperature of MOX fuel was indicated. Higher minor actinides-containing MOX had a lower phase separation temperature at O/M ratio region from 1.92 to 1.96.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki
Proceedings of 10th OECD/NEA Information Exchange Meeting on Actinide and Fission Product Partitioning and Transmutation (CD-ROM), p.201 - 209, 2010/00
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed homogeneous MOX fuel containing minor actinide (MA) elements such as Np and Am. To measure physical properties of the fuel is essential for its development, because their data are needed to evaluate irradiation behavior. In this report, the physical properties, melting temperature, thermal conductivity, lattice parameter, oxygen potential and phase separation behavior, were reviewed, and effect of MA content was discussed.