Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction during cryogenic cooling
neutron diffraction during cryogenic coolingYamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Morooka, Satoshi; Gong, W.; Fujii, Hidetoshi*; Tomota, Yo*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.192 - 201, 2024/01
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionSawaguchi, Takahiro*; Tomota, Yo*; Yoshinaka, Fumiyoshi*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118494_1 - 118494_14, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sublet, J.-Ch.*; Bondarenko, I. P.*; Bonny, G.*; Conlin, J. L.*; Gilbert, M. R.*; Greenwood, L. R.*; Griffin, P. J.*; Helgesson, P.*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Khryachkov, V. A.*; et al.
European Physical Journal Plus (Internet), 134(7), p.350_1 - 350_50, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:54.51(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear reaction with nuclear data is the origin of defects produced by cascade damage in irradiated materials. Therefore, it is important to consider nuclear reaction correctly for calculations of the damage energy of Primary Knock on Atom (PKA) and the number of Displacement Per Atom (DPA). Here, radiation damage metrics considering nuclear reaction enables us to simulate transport of each defect and clustering defects in the irradiated material. This paper reviews the theory of nuclear reaction and damage energy and describes the latest methodologies about uncertainty propagation and quantification in nuclear data and damage calculations based on molecular dynamics.
Fukuda, Kojiro*; Tomota, Yo*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.*; Woo, W.*; Seong, B. S.*; Kuwahara, Yoshitaka*; Ikuta, Fumiaki*
Materials Science and Technology, 33(2), p.172 - 180, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Vela, S.*; Mota, F.*; Deumal, M.*; Suizu, Rie*; Shuku, Yoshiaki*; Mizuno, Asato*; Awaga, Kunio*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Novoa, J.*; Ribas-Arino, J.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.4411_1 - 4411_9, 2014/07
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in the use of organic radicals as building blocks for bistable materials, i.e. materials that exist in two inter-exchangeable phases under identical thermodynamic conditions. The neutral radical TTTA is a prominent dithiazolyl-based compound because of its spin transition with a hysterisis nature near the room temperature. From ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, it has been evident that this phase transition is driven by the pair exchange dynamics of molecular stacking units accompanied by a significant gain of vibrational entropy.
Zhang, S. Y.*; Godfrey, E.*; Kockelmann, W.*; Paradowska, A.*; Bull, M. J.*; Korsunsky, A. M.*; Abbey, B.*; Xu, P. G.; Tomota, Yo*; Liljedahl, D.*; et al.
Materials Today, 12(7-8), p.78 - 84, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:51.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron diffraction methods offer a direct measure of the elastic component of strain deep within crystalline materials through precise characterisation of the interplanar crystal lattice spacing. The unique non-destructive nature of this measurement technique is particularly beneficial in the context of engineering design and archaeological materials science, since it allows the evaluation of a variety of structural and deformational parameters inside real components without material removal, or at worst with minimal interference. We review a wide range of recent experimental studies using the Engin-X materials engineering instrument at the ISIS neutron source and show how the technique provides the basis for developing improved insight into materials of great importance to applications and industry.
Zhang, S. Y.*; Godfrey, E.*; Abbey, B.*; Xu, P. G.; Tomota, Yo*; Liljedahl, D.*; Zanellato, O.*; Fitzpatrick, M.*; Kelleher, J.*; Siano, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of World Congress on Engineering 2009, Vol.2, p.1412 - 1419, 2009/00
Pulsed neutron beams available at the ISIS spallation source offer diverse possibilities for materials characterization using diffraction and imaging. In this paper, we review a range of applications of the time-of-flight neutron diffraction for the characterization of phase transformations and residual stress states in industrially-relevant situations. The setup of the ENGIN-X instrument at ISIS is described, followed by a series of case studies based on the recently obtained results.
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:89.22(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Cs(
Cs(
 = 1.63 m) by ABMR
= 1.63 m) by ABMRPinard, J.*; Duong, H. T.*; Marescaux, D.*; Stroke, H. H.*; Redi, O.*; Gustafsson, M.*; Nilsson, T.*; Matsuki, S.*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*; Kominato, K.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 753(1-2), p.3 - 12, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.02(Physics, Nuclear)The hfs separation 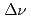 of
of  Cs(
Cs(
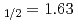 m) in the 6s
m) in the 6s  S
S ground state was obtained in a precision measurement near zero magnetic field by means of atomic beam magnetic resonance with laser optical pumping on-line with the CERN-PSB-ISOLDE mass separator. The result,
ground state was obtained in a precision measurement near zero magnetic field by means of atomic beam magnetic resonance with laser optical pumping on-line with the CERN-PSB-ISOLDE mass separator. The result, 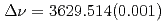 MHz, corrects significantly a previous published value from a high-field experiment. With our result, the precision of the nuclear magnetic moment,
MHz, corrects significantly a previous published value from a high-field experiment. With our result, the precision of the nuclear magnetic moment, 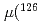 Cs)
Cs)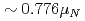 , is now limited by the influence of extended nuclear structure on the hfs (the Bohr-Weisskopf effect).
, is now limited by the influence of extended nuclear structure on the hfs (the Bohr-Weisskopf effect).
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Saito, Toru; Tomota, Yo*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Xu, P.*; Ryufuku, Susumu*
no journal, ,
New method for evaluation of microstructural factors such as intergranular strain, texture, dislocation density and block size by superimposing on the texture contour map was developed. Using this method enable us to find out the deformation mechanism from these microstructural factors. Moreover comprehensive and complementary evaluations for these microstructural factors lead to clarifying the deformation and destruction mechanisms. The microstructural factors of high nitrogen SUS310 and SUS316 with 25% cold rolling were evaluated by this method. It was considered that difference of dislocation substructure between them probably caused the fact that the intergranular strain of SUS316 was higher than that of SUS310.