Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -AlOOH under mantle conditions using neutron diffraction
-AlOOH under mantle conditions using neutron diffractionSano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Molaison, J. J.*; Dos Santos, A. M.*; Tulk, C. A.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 8(1), p.15520_1 - 15520_9, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:92.48(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The pressure response of hydrogen bond in aluminous hydroxide  -AlOOH, which is an important candidate for water carrier to the deep Earth in a subducting slab, was investigated using neutron diffraction under high pressure. The symmetrization of hydrogen bond in which hydrogen locates at the center between two oxygen atoms was observed directly for the first time. The present result indicates that the changes of mineral properties such as increase in bulk modulus and sound velocities, which were previously found, were induced by the symmetrization and disorder state that was also found at just below the symmetrization pressure. Even the symmetrization is a small change in the hydrogen location but it is playing an important role in determining the physical properties of minerals.
-AlOOH, which is an important candidate for water carrier to the deep Earth in a subducting slab, was investigated using neutron diffraction under high pressure. The symmetrization of hydrogen bond in which hydrogen locates at the center between two oxygen atoms was observed directly for the first time. The present result indicates that the changes of mineral properties such as increase in bulk modulus and sound velocities, which were previously found, were induced by the symmetrization and disorder state that was also found at just below the symmetrization pressure. Even the symmetrization is a small change in the hydrogen location but it is playing an important role in determining the physical properties of minerals.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Seto, Yusuke*; Nagai, Takaya*; Utsumi, Wataru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 780, p.55 - 67, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)PLANET is a time-of-flight (ToF) neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature experiments. The large six-axis multi-anvil high-pressure press designed for ToF neutron diffraction experiments enables routine data collection at high pressures and high temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000 K, respectively. To obtain clean data, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators to eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell assembly. The high performance of the diffractometer for the resolution (
 /
/
 0.6%) and the accessible
0.6%) and the accessible  -spacing range (0.2-8.4
-spacing range (0.2-8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Iizuka, Riko*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Goto, Hirotada*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 218, p.95 - 102, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:33.77(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In situ neutron diffraction measurements combined with the pulsed neutron source at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) were conducted on high-pressure polymorphs of deuterated portlandite (Ca(OD) ) using a Paris-Edinburgh cell and a multi-anvil press. The atomic positions including hydrogen for the unquenchable high-pressure phase at room temperature (phase II') were first clarified. The bent hydrogen bonds under high pressure were consistent with results from Raman spectroscopy. The structure of the high-pressure and high-temperature phase (Phase II) was concordant with that observed previously by another group for a recovered sample. The observations elucidate the phase transition mechanism among the polymorphs, which involves the sliding of CaO polyhedral layers, position modulations of Ca atoms, and recombination of Ca-O bonds accompanied by the reorientation of hydrogen to form more stable hydrogen bonds.
) using a Paris-Edinburgh cell and a multi-anvil press. The atomic positions including hydrogen for the unquenchable high-pressure phase at room temperature (phase II') were first clarified. The bent hydrogen bonds under high pressure were consistent with results from Raman spectroscopy. The structure of the high-pressure and high-temperature phase (Phase II) was concordant with that observed previously by another group for a recovered sample. The observations elucidate the phase transition mechanism among the polymorphs, which involves the sliding of CaO polyhedral layers, position modulations of Ca atoms, and recombination of Ca-O bonds accompanied by the reorientation of hydrogen to form more stable hydrogen bonds.
Iizuka, Riko*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ushijima, Daichi*; Nakano, Satoshi*; Sano, Asami; Nagai, Takaya*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 38(10), p.777 - 785, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The pressure responses of portlandite and the isotope effect on the phase transition were investigated at room temperature from single-crystal Raman and IR spectra and from powder X-ray diffraction using diamond anvil cells under quasi-hydrostatic conditions in a helium pressure-transmitting medium. Phase transformation and subsequent peak broadening observed from the Raman and IR spectra of Ca(OH) occurred at lower pressures than those of Ca(OD)
occurred at lower pressures than those of Ca(OD) . In contrast, no isotope effect was found on the volume and axial compressions observed from powder X-ray diffraction patterns. X-ray diffraction lines attributable to the high-pressure phase remained up to 28.5 GPa, suggesting no total amorphization in a helium pressure medium within the examined pressure region. These results suggest that the H-D isotope effect is engendered in the local environment surrounding H(D) atoms.
. In contrast, no isotope effect was found on the volume and axial compressions observed from powder X-ray diffraction patterns. X-ray diffraction lines attributable to the high-pressure phase remained up to 28.5 GPa, suggesting no total amorphization in a helium pressure medium within the examined pressure region. These results suggest that the H-D isotope effect is engendered in the local environment surrounding H(D) atoms.
Utsumi, Wataru; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Nagai, Takaya*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.50 - 52, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)The application of high pressure can induce dramatic changes in the physical properties of condensed matter. Diffraction experiments under high pressure provide precise structural information, which is fundamental to understand their origin. When in situ high pressure neutron diffraction becomes possible at J-PARC, further outstanding researches are expected such as crystal structure of hydrogen-bearing materials including hydrous minerals, order-disorder transitions of minerals, structure of light element liquid at high pressure, etc.. Conceptual designs of neutron optics and high pressure devices for J-PARC are introduced.
Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Furuno, Akiko; Kakefuda, Toyokazu; Harayama, Takaya*; Chino, Masamichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(3), p.257 - 267, 2008/09
The second version of WSPEEDI (WSPEEDI-II) which has functions to predict the radiological impact of nuclear accident abroad on Japan by quick calculations of air concentration, surface deposition and radiological doses is developed. WSPEEDI-II has the following functions for practical use. (1) High performance prediction of atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides from local to regional ranges with appropriate resolutions by introducing non-hydrostatic atmospheric dynamic model. (2) Source term estimation by coupling calculation results and monitoring data for the case that no source information is available from abroad. (3) On-line prediction data exchanges with major emergency response systems in the United States and Europe with the similar functions as WSPEEDI-II. (4) Web-based graphical user interface system for easy operation of WSPEEDI-II. (5) Preset East-Asian database for the quick start against a nuclear accident in Eastern Asia. This paper describes these new functions.
Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Terada, Hiroaki; Harayama, Takaya*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Kim, K.; Furuno, Akiko
JAEA-Research 2006-057, 67 Pages, 2006/09
A numerical simulation system SPEEDI-MP has been developed to apply for various environmental studies. SPEEDI-MP consists of dynamical models and material transport models for the atmospheric, terrestrial, and oceanic environments, database for model inputs, and system utilities for file management, visualization, etc. As a numerical simulation tool, a model coupling program (model coupler) has been developed. A coupled model system for water circulation has been constructed with atmosphere, ocean, wave, hydrology, and land-surface models using the model coupler. System utility GUIs are based on the Web technology, allowing users to manipulate all the functions on the system using their own PCs via the internet. In this system, the source estimation function in the atmospheric transport model can be executed on the grid computer system. Performance tests of the coupled model system for water circulation were also carried out for the flood and the storm surge events.
Yoshiasa, Akira*; Murai, Keiichiro*; Nagai, Takaya*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 40(4A), p.2395 - 2398, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.32(Physics, Applied)The pressure dependence of extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) Debye-Waller factors in AgBr has been investigated using the cumulant expansion method. The Br K-edge EXAFS spectra were measured in the transmission mode under high pressure ( 9.1GPa) at room temperature using a cubic anvil type apparatus (MAX90) and synchrotron radiation from the Photon Factory, Tsukuba. The effective pair potentials
9.1GPa) at room temperature using a cubic anvil type apparatus (MAX90) and synchrotron radiation from the Photon Factory, Tsukuba. The effective pair potentials 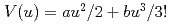 , were evaluated and the potential coefficient
, were evaluated and the potential coefficient  at 2.1, 4.2 and 6.1GPa are 1.59(4), 1.75(4) and 1.91(4) eV/
at 2.1, 4.2 and 6.1GPa are 1.59(4), 1.75(4) and 1.91(4) eV/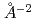 , respectively. The energies of the third-order anharmonic potential coefficient
, respectively. The energies of the third-order anharmonic potential coefficient  maintain nearly constant values with pressure though the third-order cumulant
maintain nearly constant values with pressure though the third-order cumulant 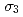 decreases with increasing in pressure.
decreases with increasing in pressure.
Fukui, Hiroyuki*; Otaka, Osamu*; Nagai, Takaya*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 27(6), p.367 - 370, 2000/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions
under high-temperature and high-pressure conditionsFukui, Hiroyuki*; Otaka, Osamu*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Nagai, Takaya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Science and Technology of High Pressure, p.554 - 557, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Wataru; Abe, Jun; Hattori, Takanori; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Igawa, Naoki; Kagi, Hiroyuki; Arima, Hiroshi*; Arakawa, Masashi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Wataru; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Abe, Jun; Nagai, Takaya*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
no journal, ,
J-PARC is a new high-intensity proton accelerator research facility in Japan. It has a spallation neutron source that will produce the world highest intensity pulsed neutron. It is expected that high pressure material science and the investigation of the Earth's interior will greatly improve at J-PARC. A Paris-Edinburgh cell and a cubic anvil high pressure apparatus have been brought to an Engineering Materials Diffractometer(BL19) to conduct the first high pressure experiment. As the next stage, we are planning to construct a dedicated high pressure beamline that will open in 2011.
 OOH oxyhydroxide and implication for hydrogen bond symmetrization
OOH oxyhydroxide and implication for hydrogen bond symmetrizationSano, Asami; Yagi, Takehiko*; Okada, Taku*; Goto, Hirotada*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
no journal, ,
 OOH oxyhydroxide at high pressure
OOH oxyhydroxide at high pressureSano, Asami; Yagi, Takehiko*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Komatsu, Kazuki*
no journal, ,
Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru; Nagai, Takaya*; Inoue, Toru*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Yagi, Takehiko*
no journal, ,
The high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET is the new neutron beamline dedicated to the high-pressure studies. The main purpose is to reveal the effect of the hydrogen and water on the materials dynamics in the Earth. The most characteristic feature is to possess the huge high-pressure press with a maximum load of 1500 ton, which can simultaneously generate pressures and temperatures of 20 GPa and 2000K, respectively. The coupling this with the diffraction and imaging technique enables us to observed states of the materials and minerals at conditions relevant to Earth's upper mantle. In this paper, the details of the design are introduced.
Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi; Abe, Jun; Sano, Asami; Utsumi, Wataru; Nagai, Takaya*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Iitaka, Toshiaki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Inoue, Toru*; et al.
no journal, ,
The new beamline dedicated to high-pressure studies, PLANET is now being constructed at BL11 in MLF/J-PARC. The design concept and the current construction state are introduced. The most characteristic feature of this beamline is a huge press with the maximum load of 1500 ton. The coupling this with the state of the art neutron techniques reveals hydrogen positions and its effects on the physical properties of materials and minerals at tens of gigapascals and a few thousand Kelvins. This opens the door to explore deep interior of the hydrous Earth and Planets.
Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi; Abe, Jun; Sano, Asami; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru; Nagai, Takaya*; Inoue, Toru*; Iitaka, Toshiaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Material and Life Science experimental Facility (MLF) of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) will be one of the most powerful spallation neutron facilities in the world. We are constructing the powder diffractometer dedicated to high-pressure experiments (PLANET) on BL-11. PLANET aims to study structures of hydrogen-bearing materials including dense hydrous minerals of the Earth's deep interior, magmas and light element liquids. The instrument will realize diffraction and radiography experiments for powder and liquid/glass samples at high pressures up to 20 GPa and 2000 K using a large sized multi-anvil hydraulic press.
Sano, Asami; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Utsumi, Wataru; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*
no journal, ,
 -AlOOH, distorted rutile type oxyhydroxide, is an important hydrous mineral in the deep earth that has the ability to transport hydrogen into the lower mantle. Theoretical studies have pointed out that hydrogen would locate at the center between two oxygen atoms at high pressure, which is so called symmetrization of the hydrogen bond. To investigate the pressure response of strong hydrogen bond
-AlOOH, distorted rutile type oxyhydroxide, is an important hydrous mineral in the deep earth that has the ability to transport hydrogen into the lower mantle. Theoretical studies have pointed out that hydrogen would locate at the center between two oxygen atoms at high pressure, which is so called symmetrization of the hydrogen bond. To investigate the pressure response of strong hydrogen bond  -AlOOH, we conduct neutron diffraction experiment at SNAP in SNS. Neutron diffraction patterns of
-AlOOH, we conduct neutron diffraction experiment at SNAP in SNS. Neutron diffraction patterns of  -AlOOH was measured on SNAP to 7 GPa. The intensity of the peak that is only observed in the space group P2
-AlOOH was measured on SNAP to 7 GPa. The intensity of the peak that is only observed in the space group P2 nm become weak at high pressure suggesting the transition to H-disordered or symmetric hydrogen bond model with Pnnm.
nm become weak at high pressure suggesting the transition to H-disordered or symmetric hydrogen bond model with Pnnm.
Sano, Asami; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Hattori, Takanori
no journal, ,
 -AlOOH, distorted rutile type oxyhydroxide is an important hydrous mineral in the deep earth because it is stable at the lower mantle condition. X-ray diffraction study found the change in the compressibility at high pressure which would be attributed to the symmetrization of hydrogen bond, but there is a difference in the pressure where the compression behaviors change. To investigate the D/H isotope effect on the symmetrization, high pressure neutron diffraction experiments were conducted at SNAP, SNS. The intensity of 120 reflection continues to decrease at high pressure and become almost zero intensity at 6.7 GPa, suggesting the transition from P2
-AlOOH, distorted rutile type oxyhydroxide is an important hydrous mineral in the deep earth because it is stable at the lower mantle condition. X-ray diffraction study found the change in the compressibility at high pressure which would be attributed to the symmetrization of hydrogen bond, but there is a difference in the pressure where the compression behaviors change. To investigate the D/H isotope effect on the symmetrization, high pressure neutron diffraction experiments were conducted at SNAP, SNS. The intensity of 120 reflection continues to decrease at high pressure and become almost zero intensity at 6.7 GPa, suggesting the transition from P2 nm to Pnnm as a precursor of the symmetrization. Strong D/H isotope effect was found in the hydrogen bond geometry; O-H distances are longer than O-D whereas H...O distances are shorter than D...O.
nm to Pnnm as a precursor of the symmetrization. Strong D/H isotope effect was found in the hydrogen bond geometry; O-H distances are longer than O-D whereas H...O distances are shorter than D...O.