Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
 Te
Te
Wang, Y.*; Kajihara, Shun*; Matsuoka, Hideki*; Saika, B. K.*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Ishizaka, Kyoko*; Iwasa, Yoshihiro*; Nakano, Masaki*
Nano Letters, 22(24), p.9964 - 9971, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:83.82(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.129 - 133, 2022/11
For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors composed of the NE213 liquid organic scintillators and photomultiplier tubes, which were connected to a multi-channel digitizer mounted with a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination applying the gate integration method to the FPGA. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics.
Matsuoka, Hideki*; Barnes, S. E.*; Ieda, Junichi; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Bahramy, M. S.*; Saika, B. K.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Wang, Y.*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(4), p.1807 - 1814, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:77.64(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) Se
Se epitaxial thin films
epitaxial thin filmsNakano, Masaki*; Wang, Y.*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Matsuoka, Hideki*; Majima, Yuki*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Hirata, Yasuyuki*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Kohama, Yoshimitsu*; et al.
Nano Letters, 19(12), p.8806 - 8810, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:92.05(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Yuji*; Tsukamoto, Masahiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yamashita, Yoshihiro*; Yamagata, Shuto*; Nishi, Takaya*; Higashino, Ritsuko*; Okubo, Tomomasa*; Nakano, Hitoshi*; Abe, Nobuyuki*
Applied Physics A, 124(4), p.288_1 - 288_6, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:63.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamics of titanium (Ti) melted by laser irradiation was investigated in a synchrotron radiation experiment. As an indicator of wettability, the contact angle between a selective laser melting (SLM) baseplate and the molten Ti was measured by synchrotron X-rays at 30 keV during laser irradiation. As the baseplate temperature increased, the contact angle decreased, down to 28 degrees at a baseplate temperature of 500 C. Based on this result, the influence of wettability of a Ti plate fabricated by SLM in a vacuum was investigated. It was revealed that the improvement of wettability by preheating suppressed sputtering generation, and a surface having a small surface roughness was fabricated by SLM in a vacuum.
C. Based on this result, the influence of wettability of a Ti plate fabricated by SLM in a vacuum was investigated. It was revealed that the improvement of wettability by preheating suppressed sputtering generation, and a surface having a small surface roughness was fabricated by SLM in a vacuum.
Hirose, Kentaro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Tanaka, Shoya*; L guillon, R.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro*; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Smallcombe, J.*; Vermeulen, M. J.; et al.
guillon, R.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro*; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Smallcombe, J.*; Vermeulen, M. J.; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 119(22), p.222501_1 - 222501_6, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:91.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fission-fragment mass distributions were measured for 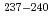 U,
U, 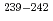 Np and
Np and 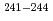 Pu populated in the excitation-energy range from 10 to 60 MeV by multi-nucleon transfer channels in the reaction
Pu populated in the excitation-energy range from 10 to 60 MeV by multi-nucleon transfer channels in the reaction  O +
O +  U at the JAEA tandem facility. Among them, the data for
U at the JAEA tandem facility. Among them, the data for  U and
U and 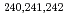 Np were observed for the first time. It was found that the mass distributions for all the studied nuclides maintain a double-humped shape up to the highest measured energy in contrast to expectations of predominantly symmetric fission due to the washing out of nuclear shell effects. From a comparison with the dynamical calculation based on the fluctuation-dissipation model, this behavior of the mass distributions was unambiguously attributed to the effect of multi-chance fission.
Np were observed for the first time. It was found that the mass distributions for all the studied nuclides maintain a double-humped shape up to the highest measured energy in contrast to expectations of predominantly symmetric fission due to the washing out of nuclear shell effects. From a comparison with the dynamical calculation based on the fluctuation-dissipation model, this behavior of the mass distributions was unambiguously attributed to the effect of multi-chance fission.
Enoto, Teruaki*; Wada, Yuki*; Furuta, Yoshihiro*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Okuda, Kazufumi*; Makishima, Kazuo*; Sato, Mitsuteru*; Sato, Yosuke*; Nakano, Toshio*; et al.
Nature, 551(7681), p.481 - 484, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:116 Percentile:97.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ohgama, Kazuya; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Oki, Shigeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(8), p.1155 - 1163, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)The power distribution and core characteristics in various configurations of fuel subassemblies with an innerduct structure in the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor were evaluated using a Monte Carlo code for neutron transport and burnup calculation. The correlation between the fraction of fuel subassemblies facing outward and the degree of power increase at the core center was observed regardless of the compositions. This indicated that the spatial fissile distribution caused by innerduct configurations was the major factor of the difference in the power distribution. A power increase was also found in an off-center region, and it tended to be greater than that at the core center because of the steep gradient of neutron flux intensity. The differences in the worth of control rods caused by innerduct configurations were confirmed.
Hidaka, Akihide; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Yoko; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Sawada, Makoto; Kanaizuka, Seiichi*; Katogi, Aki; Shimada, Mayuka*; Ishikawa, Tomomi*; Ebine, Masako*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-011, 208 Pages, 2016/07
JAEA has been conducting the Instructor Training Program (ITP) since 1996 under the auspices of MEXT to contribute to human resource development in currently 11 Asian countries in the field of radiation utilization for seeking peaceful use of nuclear energy. ITP consists of Instructor Training Course (ITC), Follow-up Training Course (FTC) and Nuclear Technology Seminars. In the ITP, trainings or seminars relating to technology for nuclear utilization are held in Japan by inviting nuclear related people from Asian countries to Japan and after that, the past trainees are supported during FTC by dispatching Japanese specialists to Asian countries. News Letter is also prepared to provide the broad range of information obtained through the trainings for local people near NPPs in Japan. The present report describes the activities of FY2014 ITP and future challenges for improving ITP more effectively.
Nishihara, Kenji; Iwamura, Takamichi*; Akie, Hiroshi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Van Rooijen, W.*; Shimazu, Yoichiro*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.388 - 395, 2015/09
The present study focuses on transmutation of Pu and minor actinide in Japanese case without utilizing Pu as resource. Pu can be transmuted by two groups of technology: conventional ones without reprocessing of spent fuel from transmuter and advanced ones with reprocessing. Necessary number of transmuters, inventory reduction of actinide and impact on repository are revealed by nuclear material balance analysis. As a whole advanced technology performs better in transmutation efficiency, although required number of transmuters is larger.
Yamaji, Akifumi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu
Nuclear Technology, 179(3), p.309 - 322, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)HC-FLWR effectively utilizes the uranium (U) and the plutonium (Pu) resources by achieving a fissile Pu conversion ratio of 0.84 without a significant technical gap from the current BWR technology. In this study, a new core design concept for HC-FLWR has been developed to achieve the conversion ratio of 0.95. The concept of the FLWR/MIX fuel assembly, which had been originally proposed for tight fuel bundle, was used to raise the conversion ratio without deteriorating the core void reactivity characteristics. For a semi-tight fuel rod lattice with rod clearance of 0.20 to 0.25 cm, the design ranges of the conversion ratio and the average discharge burnup are 0.91 to 0.94 and 53 to 49 GWd/t, respectively. The conversion ratio can be raised to 0.97 by increasing the  U enrichment from 4.9 to 6.0 wt%. Two representative core designs and one alternative design option have been obtained. Hence, the flexibility of HC-FLWR concept to achieve the conversion ratio of 0.84 to 0.95 has been revealed.
U enrichment from 4.9 to 6.0 wt%. Two representative core designs and one alternative design option have been obtained. Hence, the flexibility of HC-FLWR concept to achieve the conversion ratio of 0.84 to 0.95 has been revealed.
Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Nakano, Yoshihiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR 2009) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/00
An advanced LWR with hard neutron spectrum named FLWR is a BWR-type reactor with a core consisting of hexagonal-shaped fuel assemblies with a triangular tight-lattice fuel rod configuration. It has been proposed in order to ensure sustainable energy supply in the future based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The reactor concept of the FLWR is designed to utilize the most of the existing Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) plant system. Therefore, only the core concept is new. The FLWR aims at effective and flexible utilization of uranium and plutonium resources by adopting a two-stage concept of core designs. The core in the first stage of FLWR is for intensive utilization and conservation of plutonium with no degradation of the isotopic quality of plutonium based on the experience of the current LWR-MOX utilizations. The one in the second stage realizes sustainable multiple plutonium recycling with a high conversion ratio over 1.0. When the technologies and infrastructures for multiple recycling with MOX spent fuel reprocessing are established, the core of the first stage proceeds to the second stage by only changing the fuel assembly design in the same reactor system. The present paper summarizes the recent core design studies of FLWR.
Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okubo, Tsutomu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 38(12), p.2689 - 2697, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)The isotopic composition and amount of Pu in spent fuel from high burnup BWR and PWR (HB-BWR, HB-PWR), each with 70 GWd/t discharge burnup and 6% U enrichment were estimated to evaluate FBR fuel composition in the transition period from LWRs to FBRs. The HB-BWR employs spectral shift rods. The fraction of fissile Pu (Puf) in HB-BWR spent fuel after 5 years cooling is 62%, which is larger than that of conventional BWRs with burnup of 45 GWd/t, because of the spectral shift operation. The amount of Pu produced in the HB-BWR is also larger than that produced in a conventional BWR. The HB-PWR uses a wider pitch 17 17 assembly to optimize neutron slowing down. The Puf fraction of HB-PWR spent fuel after 5 years cooling is 56%, which is smaller than that of conventional PWRs with burnup of 49 GWd/t, mainly because of the wider pitch. The amount of Pu produced in the HB-PWR is also smaller than that in conventional PWRs.
17 assembly to optimize neutron slowing down. The Puf fraction of HB-PWR spent fuel after 5 years cooling is 56%, which is smaller than that of conventional PWRs with burnup of 49 GWd/t, mainly because of the wider pitch. The amount of Pu produced in the HB-PWR is also smaller than that in conventional PWRs.
Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Nakano, Yoshihiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/12
An advanced LWR with hard neutron spectrum, named FLWR, aims at efficient and flexible utilization of nuclear resources by evolving its fuel assembly design under the same core configuration, mainly corresponding to available fuel cycle technologies and related infrastructures. The paper summarizes an evolution process of the FLWR fuel assembly design toward a sustainable fuel cycle by dividing the reactor operation into three stages, that is, the one based on the current LWR MOX fuel cycle infrastructure such as reprocessing of UO spent fuel and fabrication of MOX fuel, the one for transitioning from the LWR fuel cycle to the FR fuel cycle, and the one based on the FR fuel cycle infrastructures such as MOX spent fuel reprocessing.
spent fuel and fabrication of MOX fuel, the one for transitioning from the LWR fuel cycle to the FR fuel cycle, and the one based on the FR fuel cycle infrastructures such as MOX spent fuel reprocessing.
Akie, Hiroshi; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okubo, Tsutomu
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Uchikawa, Sadao; Okubo, Tsutomu; Nakano, Yoshihiro
Nuclear Technology, 172(2), p.132 - 142, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)The FLWR is a BWR-type reactor with hard neutron spectrum based on the well-experienced LWR technologies. The present paper has proposed a new concept of the fuel assembly design for the first stage of FLWR to conserve plutonium effectively with a fissile-plutonium conversion ratio of around 1.0, keeping negative void reactivity characteristics. The enriched UO fuel rods are arranged in the peripheral region of the assembly, surrounding the MOX fuel rods in the central region. Performance evaluation shows that the FLWR/MIX concept is effective for controlling the void reactivity characteristics in the tight-lattice fuel rod configuration and promising under the framework of the UO
fuel rods are arranged in the peripheral region of the assembly, surrounding the MOX fuel rods in the central region. Performance evaluation shows that the FLWR/MIX concept is effective for controlling the void reactivity characteristics in the tight-lattice fuel rod configuration and promising under the framework of the UO and MOX fuel technologies and related infrastructures which have been established for the current LWR-MOX utilization.
and MOX fuel technologies and related infrastructures which have been established for the current LWR-MOX utilization.
Okubo, Tsutomu; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Uchikawa, Sadao; Fukaya, Yuji
Revue G n
n rale Nucl
rale Nucl aire, (6), p.83 - 89, 2010/11
aire, (6), p.83 - 89, 2010/11
An advanced LWR concept of FLWR has been investigated in order to contribute to establish sustainable energy supply in the future by recycling Pu or TRU based on the well-developed LWR technology. The concept utilizes the tight-lattice core with the MOX fuel, and consists of two steps in the chronological sequence. The first is to realize early introduction of FLWR and is represented by a high conversion type one (HC-FLWR), which is basically intended to keep the smooth technical continuity from the LWR/MOX-LWR technologies. The second is represented by RMWR, which realizes a very high conversion ratio over 1.0 and is preferable for the long-term sustainable energy supply through Pu or TRU multiple recycling. The key point is that the two core concepts utilize the compatible and the same size fuel assemblies, and hence, the former concept can proceed to the latter in the same reactor system based flexibly on the future fuel cycle circumstances.
Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Nakano, Yoshiharu*; Fujii, Yuki*
Separation Science and Technology, 45(16), p.2431 - 2436, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:71.17(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)