Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirota, Kazuo*; Ishitani, Yoshihide*; Nishida, Keigo*; Sago, Hiromi*; Xu, Y.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nakanishi, Shigeyuki; Kotake, Shoji
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-6) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2008/11
CFD simulation using the Reynolds stress model was performed to evaluate turbulence-induced forces on the piping. The turbulence energy with the CFD simulation was compared with pressure fluctuation distributions obtained by the test with a 1/3 scale elbow simulating the JSFR hot-leg piping. The profile of turbulence energy was good agreement with that of the pressure fluctuation. The magnitude of pressure fluctuation can also be estimated from calculated turbulence energy multiplied by a certain coefficient. In the vibration analysis, the power spectrum density (PSD) of the pressure fluctuation was derived from the measured normalized PSD multiplied by the coefficient. The vibration analysis method was proposed based on the PSDs derived by the above procedure and correlation lengths. The analysis results of vibration response showed good agreement with the flow-induced-vibration test results, thereby it can be said that the vibration analysis method developed in this study is valid.

Nishida, Hiromi*; Narumi, Issei
Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 71(4), p.1015 - 1020, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.84(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The radioresistant bacterium  is evolutionarily closely related to the themophilic bacterium
is evolutionarily closely related to the themophilic bacterium 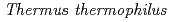 . These bacteria have a single gene encoding an aspartate kinase (AK).
. These bacteria have a single gene encoding an aspartate kinase (AK). 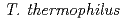 has an aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis, which does not use AK. Phylogenetic analysis showed that
has an aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis, which does not use AK. Phylogenetic analysis showed that  AK had different protein structure and different evolutionary history from
AK had different protein structure and different evolutionary history from 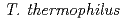 AK. Disruption analysis of
AK. Disruption analysis of  AK indicated that
AK indicated that  AK was not used for lysine biosynthesis but for threonine and methionine biosyntheses. Thus these two AKs have different evolutionary origins, but their functions are not different.
AK was not used for lysine biosynthesis but for threonine and methionine biosyntheses. Thus these two AKs have different evolutionary origins, but their functions are not different.
Ogata, Atsushi*; Okamoto, Hiromi*; Kusano, Kanya*; Endo, Ichita*; Nishida, Yasushi*; Sakae, Takeji*; Arai, Masatoshi*; Nakanishi, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Kiminori*
JAERI-Tech 2002-007, 28 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English